SQL Joins
Introduction to SQL Joins
SQL joins are essential for retrieving data from multiple tables in a database, and mastering them is crucial for anyone working with databases, from data analysts to software developers.
In this page, we’ll discuss about the intricacies of SQL joins, providing you with a concepts and understanding that will empower you to leverage this powerful database technique effectively.
Understanding SQL Joins
SQL, or Structured Query Language, is the backbone of database management systems. It allows you to interact with and extract meaningful information from your data. SQL joins, in particular, are used when you have data spread across multiple tables and need to combine it to extract insights or generate reports.
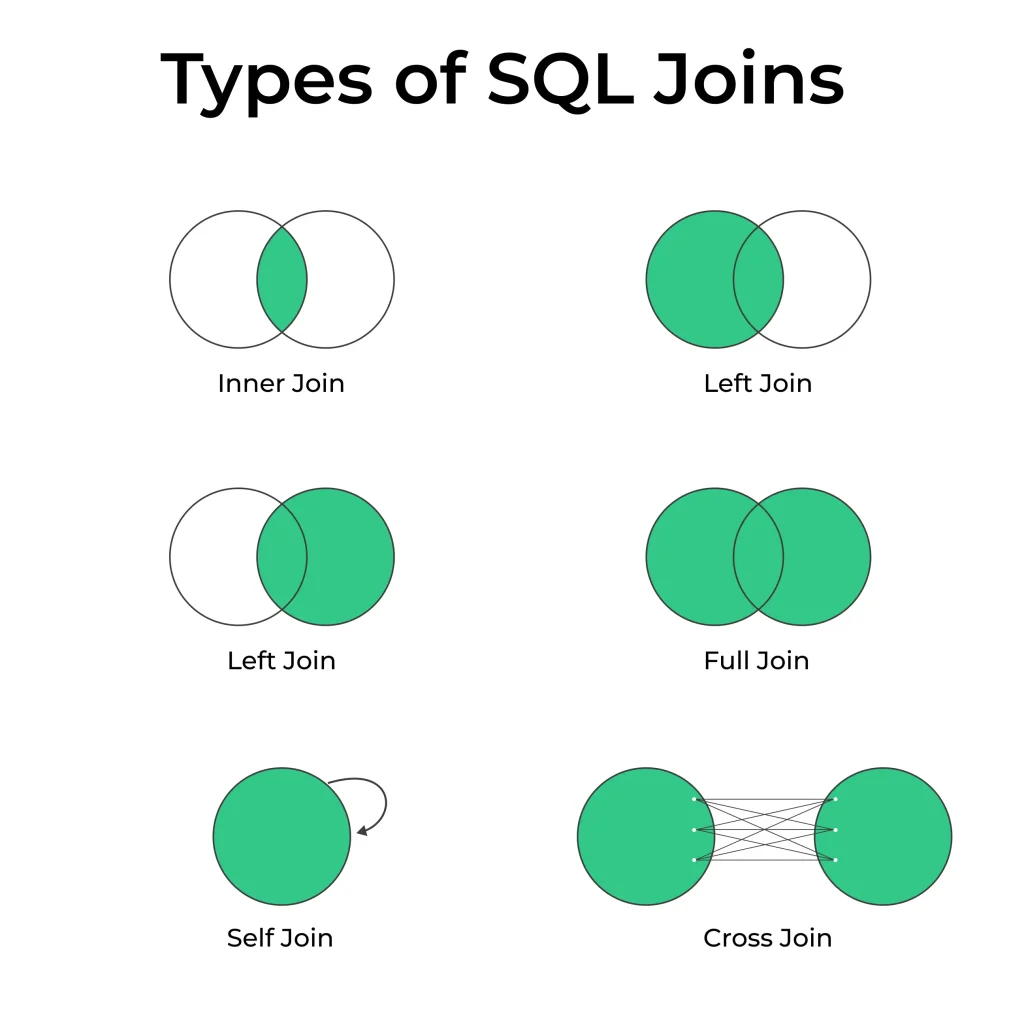
SQL Joins Types
There are several types of SQL joins, each serving a unique purpose. Let’s explore the most common ones:
- Inner Join
- Left Join
- Right Join
- Full Outer Join
SELECT employees.name, departments.department_name FROM employees INNER JOIN departments ON employees.department_id = departments.department_id;
- In this SQL query, we’re selecting the names of employees and their corresponding department names from two tables, ’employees’ and ‘departments,’ by joining them on the ‘department_id’ column.
SELECT customers.customer_name, orders.order_date FROM customers LEFT JOIN orders ON customers.customer_id = orders.customer_id;
This query retrieves customer names along with their order dates. If a customer has not placed any orders, the order date will be NULL.
SELECT orders.order_date, order_details.product_name FROM orders RIGHT JOIN order_details ON orders.order_id = order_details.order_id;
In this example, we’re extracting order dates and product names. If there are orders without corresponding details, those rows will still be included in the result, with NULL values for product names.
SELECT employees.name, departments.department_name FROM employees FULL OUTER JOIN departments ON employees.department_id = departments.department_id;
This query retrieves employee names and department names, including cases where there are employees without assigned departments and departments without employees.
Click below to access free SQL quizzes related to Introduction to SQL which will be helpful in your placement exams
SQL Joins Example
Suppose you’re managing an e-commerce website and need to generate a report that lists customer names along with the products they’ve purchased.
SELECT customers.customer_name, products.product_name FROM customers LEFT JOIN orders ON customers.customer_id = orders.customer_id LEFT JOIN order_details ON orders.order_id = order_details.order_id LEFT JOIN products ON order_details.product_id = products.product_id;
Explanation : In this query, we’re using left joins to combine data from four tables: ‘customers,’ ‘orders,’ ‘order_details,’ and ‘products.’ The result will be a comprehensive list of customer names and the products they’ve purchased.
The Anatomy of a SQL Join
To perform a SQL join, you need to specify the following components:
- Tables to Join: Identify the tables you want to combine.
- Join Condition: Define the columns that link the tables together.
- Result Set: Specify which columns you want to include in the output.
Example :
SELECT employees.name, departments.department_name FROM employees INNER JOIN departments ON employees.department_id = departments.id;
Advanced SQL Joins
Self-Join
A self-join occurs when a table is joined with itself. This is particularly useful for hierarchical data, such as organizational structures.
Cross Join
A cross join, also known as a Cartesian join, combines all rows from one table with all rows from another table. While it can result in a large dataset, it has its applications, such as generating combinations.
Advantages of Using SQL Joins
SQL joins offer several advantages when working with relational databases:
Data Integration
- SQL joins allow you to combine data from different sources, making it easier to analyze and gain insights from your data.
Reduced Redundancy
- Instead of duplicating data across tables, SQL joins help minimize redundancy, which leads to more efficient storage and maintenance.
Improved Data Accuracy
- By linking related data using SQL joins, you can maintain data accuracy and consistency throughout your database.
Flexibility
- SQL joins provide the flexibility to retrieve precisely the data you need, regardless of how it’s distributed across tables.
Conclusion
In conclusion of Introduction of SQL joins, SQL joins are a fundamental aspect of database management, and mastering them opens up a world of possibilities for data analysis and reporting. In this page, we’ve explored the various types of SQL joins, their advantages, and provided a practical example to demonstrate their use.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




