SQL Insert Into Statement

Introduction to SQL INSERT INTO STATEMENT
SQL (Structured Query Language) reigns supreme. SQL allows us to perform a multitude of operations on databases, and one of the fundamental statements every database enthusiast should master is the INSERT INTO statement.
In this page, we’ll discuss about the intricacies of SQL INSERT INTO statements, equipping you with the knowledge needed to excel in this crucial aspect of database management.
Understanding SQL INSERT INTO Statements
The SQL INSERT INTO statement is a powerful tool used to add new records (rows) into a database table. It plays a pivotal role in maintaining and updating data within a database.
SQL, or Structured Query Language, is a powerful tool for managing and manipulating data in relational databases. The “INSERT INTO” statement is a fundamental part of SQL, allowing you to add new records to a database table. Whether you’re populating a database with initial data or continuously updating it, understanding how to use “INSERT INTO” is crucial.
SQL INSERT INTO STATEMENT SYNTAX :
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);
table_name: Specifies the name of the table where you want to insert data.(column1, column2, column3, ...): Lists the columns in the table where data will be inserted.VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...): Contains the actual data that you want to insert into the specified columns.
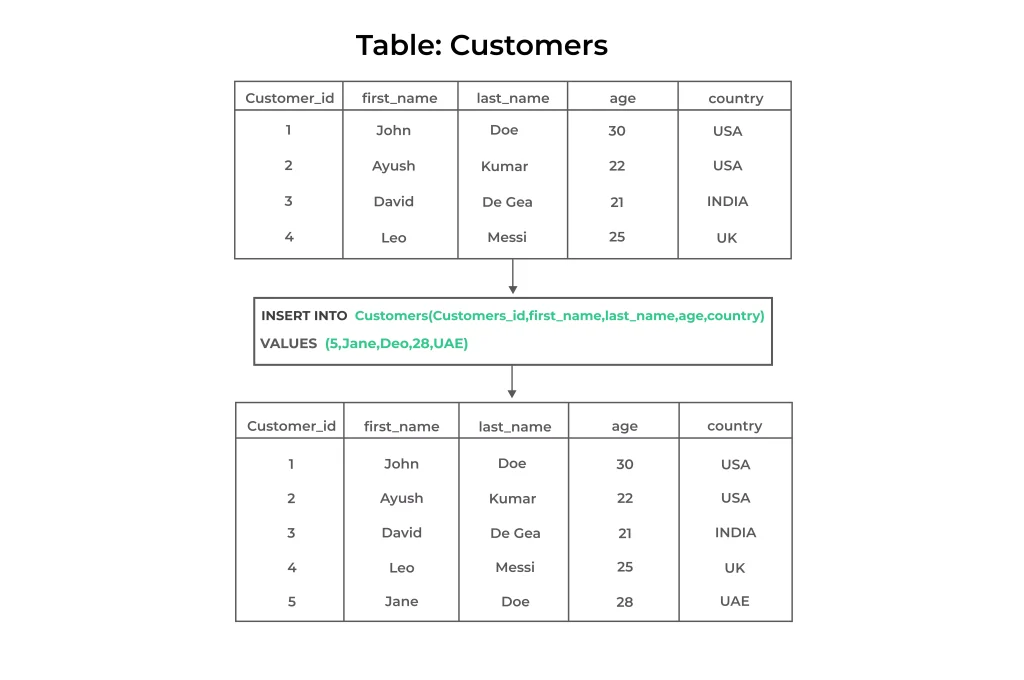
Inserting Data into a Single Table
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, job_title)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'Software Engineer');
INSERT INTO employees (first_name, last_name, job_title)
VALUES ('Jane', 'Smith', 'Data Analyst'),
('Mike', 'Johnson', 'Database Administrator'),
('Emily', 'Davis', 'UX Designer');
Click below to access free SQL quizzes related to Introduction to SQL which will be helpful in your placement exams
SQL INSERT INTO for SQL Server and MySQL
- SQL INSERT INTO for SQL Server
- SQL INSERT INTO for MySQL
-- Inserting a single record
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, ...)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);
-- Inserting multiple records
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, ...)
VALUES
(value1a, value2a, value3a, ...),
(value1b, value2b, value3b, ...),
(value1c, value2c, value3c, ...);
Explanation : In SQL Server, you can use INSERT INTO to insert one or more records into a table, following the same principles discussed earlier.
-- Inserting a single record
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, ...)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);
-- Inserting multiple records
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, ...)
VALUES
(value1a, value2a, value3a, ...),
(value1b, value2b, value3b, ...),
(value1c, value2c, value3c, ...);
Explanation : The syntax for MySQL is virtually identical to SQL Server and follows the same principles for inserting single or multiple records.
Example of SQL INSERT :
We have a table named employees with columns employee_id, first_name, and last_name. We want to insert a new employee into this table:
INSERT INTO employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name) VALUES (101, 'John', 'Doe');
Explanation :
This SQL statement inserts a new record with an employee_id of 101, first_name as ‘John,’ and last_name as ‘Doe’ into the employees table.
SQL INSERT INTO Best Practices.
Conclusion
In conclusion of Introduction of SQL INSERT INTO statement is crucial for effective database management. With the knowledge and best practices shared in this guide, you are well-equipped to manipulate and maintain your database records with precision. Remember to validate your data, use transactions, optimize indexing, and implement error handling to ensure smooth and reliable data insertion processes.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




