SQL Full Outer Join

Introduction to SQL Full Outer Join
SQL (Structured Query Language) plays a pivotal role in managing and manipulating data. One of the essential operations in SQL is joining tables to retrieve and combine data from multiple sources.
The SQL FULL OUTER JOIN is a powerful tool that can be immensely useful in complex data scenarios.
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of the SQL FULL OUTER JOIN, exploring its syntax, use cases, advantages and skills needed to harness the full potential of your database queries.
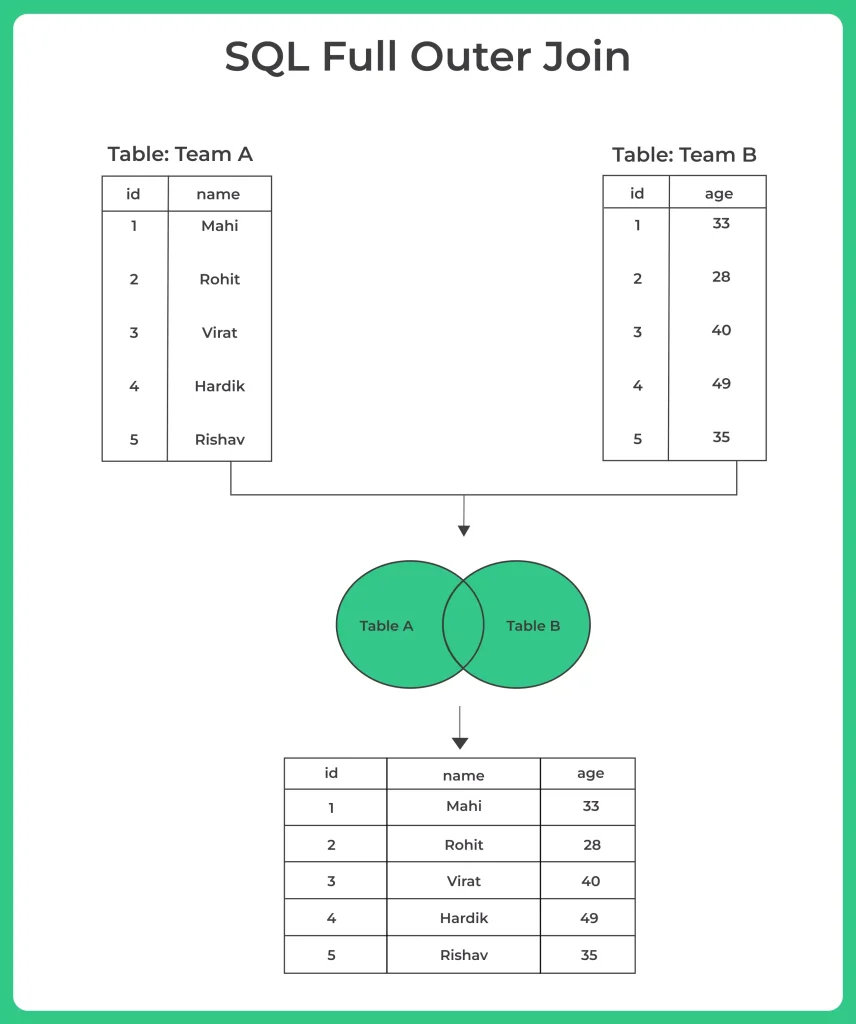
What is a SQL FULL OUTER JOIN?
SQL Full Outer Join, often referred to simply as a “Full Join,” is a crucial operation for combining data from two or more tables in a relational database. It allows us to merge records from multiple tables, including unmatched rows from both sides, creating a complete dataset that retains all available information.
Key Characteristics of SQL Full Outer Join
Understanding SQL FULL OUTER JOIN Syntax
- ‘table1’ and ‘table2’ are the tables you want to join.
- ‘column’ represents the common column on which the join is based.
- ‘* signifies’ that you want to select all columns from both tables.
SELECT * FROM table1 FULL OUTER JOIN table2 ON table1.column = table2.column;
Practical Applications SQL Full Outer Join
Data Integration :
- One of the primary applications of Full Outer Joins is data integration. Let’s consider a scenario where you have two tables: one containing customer information and another containing order details. By performing a Full Outer Join on the customer ID, you can create a comprehensive dataset that includes all customers and their respective order information. This is invaluable for businesses seeking a 360-degree view of their customer base.
Finding Discrepancies :
Full Outer Joins are also instrumental in identifying discrepancies or anomalies between two datasets. For instance, in a comparison between an inventory list and a sales record, a Full Outer Join can reveal items that are in the inventory but haven’t been sold (and vice versa).
Data Cleanup :
In cases where data quality is a concern, Full Outer Joins can help identify incomplete or erroneous records. By examining the NULL values in the result set, you can pinpoint areas that require data cleanup or further investigation.
SQL Full Join Examples
SELECT Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderID FROM Customers FULL OUTER JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID;
- In this example, the Full Outer Join ensures that you get a comprehensive list of all customers, including those who haven’t placed any orders and all orders, including those without associated customers.
Click below to access free SQL quizzes which will be helpful in your placement exams
SQL Full Outer Join vs. Union
| Aspect | Full Outer Join | Union | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Combines rows from two tables with common columns based on a specified condition (joining) and includes all rows from both tables. | Combines rows from two or more tables into a single result set without considering duplicates. | |
| Resulting Rows | Includes all rows from both tables, matching rows based on a specified condition and filling in NULL values for non-matching rows. | Combines rows from tables, retaining all distinct rows from each table. | |
| Syntax | Uses ‘FULL OUTER JOIN’ followed by the ‘ON’ clause to specify the join condition. | Uses ‘UNION’ to combine rows and ‘UNION ALL’ to combine all rows, regardless of duplicates. | |
| Use Cases | Useful for retrieving related data from multiple tables and including both matching and non-matching rows. | Useful for combining rows from multiple tables when you want to create a single, distinct result set. | |
| Example | sql SELECT * FROM Table1 FULL OUTER JOIN Table2 ON Table1.Column = Table2.Column; |
|
Advantages of Using FULL OUTER JOIN :
Conclusion
SQL Full Outer Join is a powerful tool that unlocks the potential of relational databases, allowing businesses to extract valuable insights from their data. By mastering Full Outer Join and adhering to best practices, organizations can make informed decisions, drive efficiency, and stay competitive in today’s data-driven world.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription

Question 1.
What’s the difference between a Full Outer Join and other types of joins?
The key difference lies in inclusivity. A Full Outer Join retrieves all rows from both tables, whereas other joins may exclude certain records.

Question 2.
When should I use a Full Outer Join?
Use a Full Outer Join when you need a comprehensive view of your data, want to handle unmatched records, or are merging datasets from various sources.

Question 3.
Are Full Outer Joins supported in all SQL database systems?
Most modern SQL database systems support Full Outer Joins, but it’s essential to check the specific documentation for your database to ensure compatibility.

Question 4.
Where can I learn more about SQL joins and query optimization?
To further enhance your SQL skills, explore online resources, SQL tutorials, and documentation provided by your database management system.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




