SQL Foreign Key
Introduction to SQL Foreign Key
A foreign key is a column or a set of columns in a relational database table that refers to the primary key or a unique key of another table. It establishes a link between the data in two tables, creating a relationship between them.
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of the SQL Foreign Operator, its syntax, usage of wildcard characters, performance considerations, best practices, and real-world use cases.
What is Foreign Key In SQL?
In SQL (Structured Query Language), a foreign key is a field or a set of fields in a table that refers to the primary key of another table. It establishes a link or relationship between two tables by referencing the primary key column(s) of one table to the foreign key column(s) in another. This relationship is crucial for maintaining referential integrity in a relational database.
Syntax of the SQL Foreign Key:
- The syntax for creating a foreign key in SQL typically follows the CREATE TABLE statement.
CREATE TABLE child_table (
column1 datatype1,
column2 datatype2,
-- other columns
FOREIGN KEY (foreign_key_column) REFERENCES parent_table(parent_key_column)
); Let’s break down the syntax:
CREATE TABLE child_table: This part of the statement is used to create a new table called child_table.
(column1 datatype1, column2 datatype2, …): These are the columns of the child_table along with their data types.
FOREIGN KEY (foreign_key_column): This is where you define the foreign key. foreign_key_column is the column in the child_table that will act as the foreign key.
REFERENCES parent_table(parent_key_column): This specifies the referenced table and column. parent_table is the table containing the primary key (parent_key_column) that foreign_key_column in the child_table refers to.
Properties of FOREIGN KEY in SQL
In SQL, a FOREIGN KEY constraint has several properties and characteristics that help define and maintain the relationship between tables.
Uniqueness:
- Referencing Column Uniqueness: The values in the column(s) of the referencing (foreign key) table must be unique or NULL.
- Referenced Column Uniqueness: The values in the referenced (primary key) column(s) of the referenced table must be unique.
Referential Integrity:
- The FOREIGN KEY constraint ensures referential integrity by enforcing that values in the referencing column(s) of one table correspond to values in the referenced column(s) of another table.
Relationship Type:
- The relationship between tables is typically one-to-many, where one row in the referencing table can correspond to multiple rows in the referenced table.
CASCADE Actions:
- CASCADE DELETE: When a referenced row is deleted, the corresponding rows in the referencing table can be automatically deleted.
- CASCADE UPDATE: When a referenced key is updated, the corresponding values in the referencing table can be automatically updated.
NULL Values:
- The values in the referencing column(s) can be NULL unless the FOREIGN KEY constraint is defined with the
NOT NULLoption.
- The values in the referencing column(s) can be NULL unless the FOREIGN KEY constraint is defined with the
Enforcement:
- FOREIGN KEY constraints are enforced by the database management system (DBMS) to ensure data consistency.
Relationship Between Foreign key and Primary key
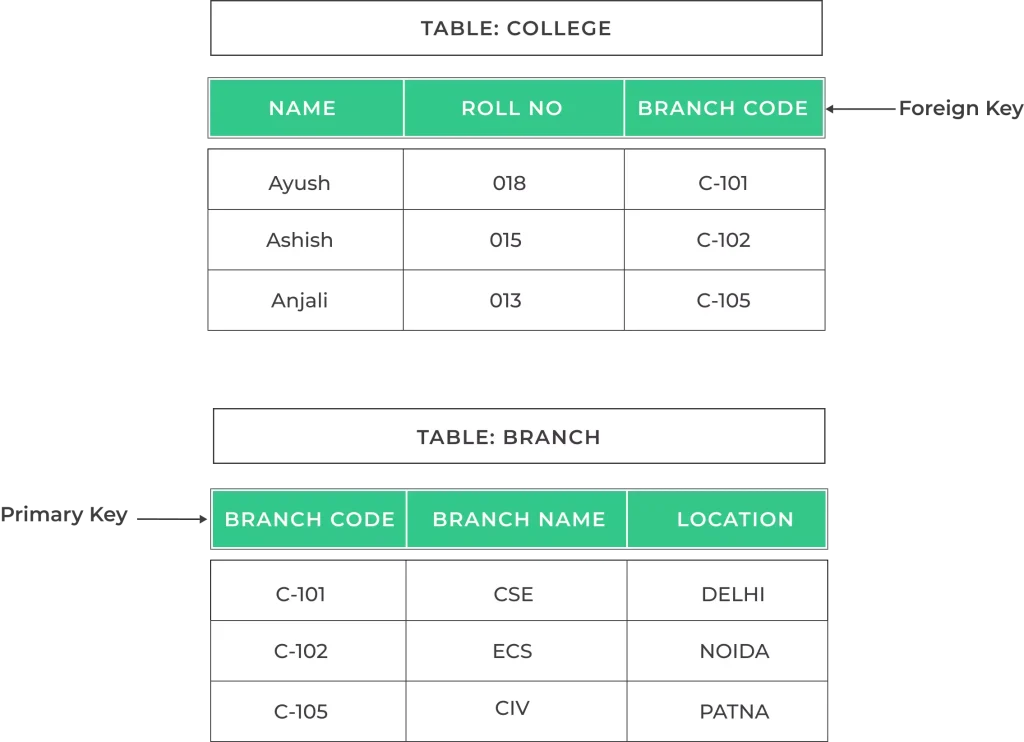
Relationship between primary key and foreign key
The relationship between a primary key and a foreign key is a fundamental concept in relational databases.
Definition:
- A Primary Key is a column or set of columns in a table that uniquely identifies each record in that table. It ensures the uniqueness of each row.
- A Foreign Key is a column or set of columns in a table that refers to the primary key of another table. It establishes a link between the two tables.
Purpose:
- The Primary Key is used to uniquely identify records within its own table. It provides a way to ensure data integrity and avoid duplicate records.
- The Foreign Key is used to establish relationships between tables. It represents a connection to the primary key of another table, creating a parent-child relationship.
Uniqueness:
- The values in a Primary Key column must be unique and cannot contain NULL values.
- The values in a Foreign Key column typically reference the values in the corresponding Primary Key column of another table.
Relationship Type:
- The relationship between a Primary Key and a Foreign Key is often a one-to-many relationship. This means that one record in the table with the primary key can be related to multiple records in the table with the foreign key.
Referential Integrity:
- The use of a Foreign Key enforces referential integrity. It ensures that values in the foreign key column(s) of one table match the values in the primary key column(s) of another table.
Foreign Key on CREATE TABLE:
- when creating a table with a FOREIGN KEY in SQL using the CREATE TABLE statement:
- child_table: The table being created.
- column1 datatype1, column2 datatype2: Columns in the new table.
- FOREIGN KEY (foreign_key_column): Declaration of the foreign key in the child table.
- REFERENCES parent_table(parent_key_column): Specification of the referenced primary key in the parent table. This establishes a relationship between the two tables.
CREATE TABLE child_table (
column1 datatype1,
column2 datatype2,
FOREIGN KEY (foreign_key_column) REFERENCES parent_table(parent_key_column)
); Foreign Key on ALTER TABLE:
- when creating a table with a FOREIGN KEY in SQL using the CREATE TABLE statement:
- child_table: The name of the table to which you want to add the FOREIGN KEY constraint.
- fk_constraint_name: A user-defined name for the FOREIGN KEY constraint. This name must be unique within the database.
- foreign_key_column: The column in the child table that will be the FOREIGN KEY.
- parent_table: The name of the referenced (parent) table.
- parent_key_column: The column in the parent table that is the target of the FOREIGN KEY
ALTER TABLE child_table ADD CONSTRAINT fk_constraint_name FOREIGN KEY (foreign_key_column) REFERENCES parent_table(parent_key_column);
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




