Find non-repeating elements in an array Python
Non-repeating elements in an array in python
Here, in this page we will discuss the program to print the non-repeating elements in python programming language. We are given with an integer array and need to print those elements which occurs only one time.
Example
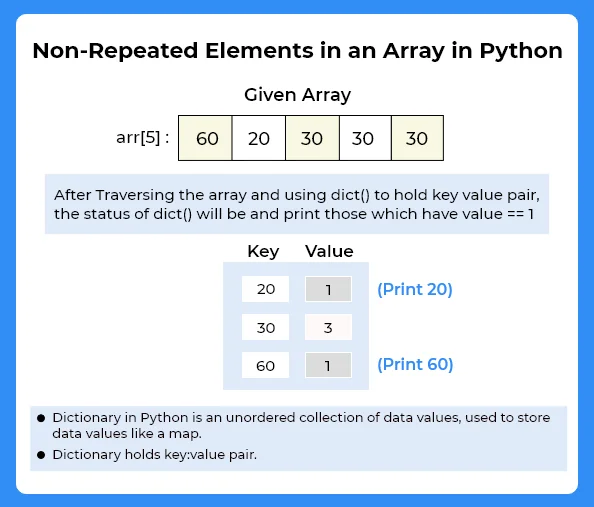
Input : arr[8] = [10, 20, 70, 90, 80, 20, 10, 20]Output : 70 90 80
Explanation : 70, 90 and 80 are occur 1 time in the given array, 10 occurs 2 times and 20 occurs 3 times.
Methods Discussed :
- Method 1 : Using Two for loops
- Method 2 : Using dictionary
Method 1 :
In this method we will count the frequency of each elements using two for loops and print those elements which have frequency equals to one.
- To check the status of visited elements create a array of size n.
- Run a loop from index 0 to n and check if (visited[i]==1) then skip that element.
- Otherwise create a variable count = 1 to keep the count of frequency.
- Run a loop from index i+1 to n
- Check if(arr[i]==arr[j]), then increment the count by 1 and set visited[j]=1.
- After complete iteration of inner for loop and check if count == 1 then print those element.
Time and Space Complexity :
- Time Complexity : O(n2)
- Space Complexity : O(n)
Method 1 : Code in Python
Run
# Python 3 program to count unique elements
def count(arr, n):
# Mark all array elements as not visited
visited = [False for i in range(n)]
# Traverse through array elements
# and count frequencies
for i in range(n):
# Skip this element if already
# processed
if (visited[i] == True):
continue
# Count frequency
count = 1
for j in range(i + 1, n, 1):
if (arr[i] == arr[j]):
visited[j] = True
count += 1
if count == 1 :
print(arr[i]);
# Driver Code
arr = [10, 30, 40, 20, 10, 20, 50, 10]
n = len(arr)
count(arr, n)Output
30 40 50
Method 2 :
In this method we will count use dictionary to count the frequency of each elements and then check if that frequency is equal to 1 or not.
- Declare a dictionary dict() say, mp = dict().
- Start iterating over the entire array
- If element is present in map, then increase the value of frequency by 1.
- Otherwise, insert that element in map.
- After complete iteration over array, start traversing map and check if value is equal to 1,then print the key value.
Time and Space Complexity:
- Time Complexity : O(n)
- Space Complexity : O(n)
Method 2 : Code in Python
Run
def count(arr, n):
mp = dict()
# Traverse through array elements
# and count frequencies
for i in range(n):
if arr[i] in mp.keys():
mp[arr[i]] += 1
else:
mp[arr[i]] = 1
# Traverse through map and print
# frequencies
for x in mp:
if mp[x]==1 :
print(x);
# Driver Code
arr = [10, 30, 40, 20, 10, 20, 50, 10]
n = len(arr)
count(arr, n)Output
30 40 50
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription




from collections import Counter
a=[10, 20, 40, 30, 50, 20, 10, 20]
result = [j for j,k in Counter(a).most_common() if k==1]
for j in result:
print(j)
lis1=[1,2,3,4,1,2,1,6,7,8,7,5]
lis2=[]
for i in range(len(lis1)):
for j in range(i+1,len(lis1)):
if lis1[i] == lis1[j]:
if lis1[i] not in lis2:
lis2.append(lis1[i])
print(lis2)
lis3=[]
for i in lis1:
if i not in lis2:
lis3.append(i)
print(lis3)
arr=[1,2,3,4,1,1,2,3,3,4,2,2,5]
dict={}
for num in arr:
if num in dict:
dict[num]+=1
else:
dict[num]=1
for key,value in dict.items():
if value<=1:
print(key)
# arr = [10, 20, 40,40, 30,11,15, 50, 20, 10, 20]
# arr_1 = []
# for i in arr:
# if i not in arr_1:
# arr_1.append(i)
# for i in arr_1:
# count_1 = arr.count(i)
# if count_1==1:
# print(i,end = ” “)
a=[10, 20, 70, 90, 80, 20, 10, 20]
d={}
for i in a:
if i in d:
d[i]+=1
else:
d[i]=1
for key,value in d.items():
if value==1:
print(key,end=” “)
lst = [10, 20, 40, 30, 50, 20, 10, 20]
for i in lst:
if lst.count(i)==1:
print(i)
arr=list(map(int,input().split()))
for i in set(arr):
if arr.count(i)==1:
print(i)
arr=[10,20,20,10,30,40,50,40]
arr1=[]
arr2=[]
for i in range(len(arr)):
if arr[i] not in arr1:
arr1.append(arr[i])
elif arr[i] in arr1:
arr2.append(arr[i])
for i in range(len(arr1)):
if arr1[i] not in arr2:
print(arr1[i], end=” “)
a=list(map(int,input().split()))
arr2=[]
b=Counter(a)
print(b)
for i in b:
if a.count(i)==1:
arr2.append(i)
print(*arr2)
//Lets do it in C:
#include
int main()
{
int arr[100],n,i,j;
printf(“Enter the length of array : “);
scanf(“%d”,&n);
printf(“Enter element in array: \n”);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int flag=0;
if(arr[i]!=NULL)
{
for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)
{
if(arr[i]==arr[j])
{
arr[j]=NULL;
flag=1;
}
}
if(flag==0)
{
printf("Non Repeating elements: %d\n",arr[i]);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
from collections import*
l=[1,11,11,2,1,21,2,1,4,4,4,5,5,98,75,65,65]
p=[]
s=Counter(l)
for i in s:
if s[i]>1:
pass
else:
print(i)