Binary Search Tree – BST

What are Binary Search Tree?
In the Article, we will Discuss about the Binary Search Tree of java.
The binary search tree is useful in applications that require fast searching, insertion, and deletion of data. For example, it can be used to implement a symbol table or a dictionary, where each key-value pair is stored in a node of the tree.
Java Binary Tree:
A binary tree is a type of tree data structure in which each node has at most two children, referred to as the left child and the right child.
Here are some important properties of binary trees:
- Each node in a binary tree has at most two children.
- The topmost node of the tree is called the root node.
- Nodes with no children are called leaf nodes or terminal nodes.
- The height of a binary tree is the length of the longest path from the root node to a leaf node.
- The depth of a node in a binary tree is the length of the path from the root node to that node.
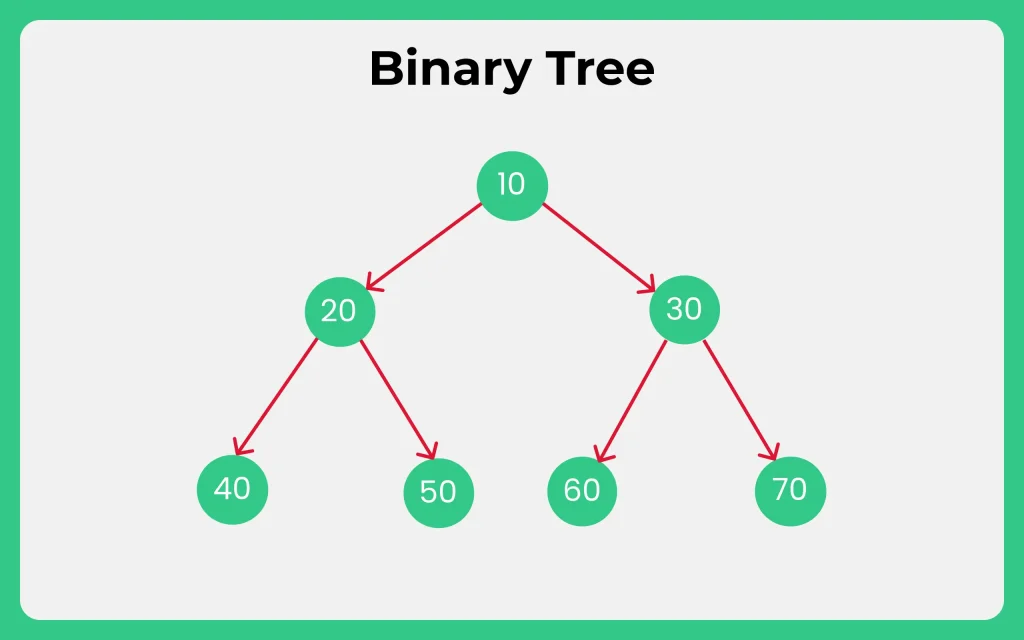
A binary tree can be defined recursively as follows: a binary tree is either empty (null) or consists of a node, called the root, and two subtrees, called the left subtree and the right subtree. Each of the subtrees is also a binary tree.
In Java, binary trees are usually implemented using a Node class. Each node contains a data element and references to its left and right child nodes, which can be null if there are no children.
Binary Search Tree – BST
A binary search tree is a data structure which is used to store and retrieve data efficiently. It is a tree-like structure where each node has at most two child nodes, and the left child node has a value less than or equal to the parent node’s value, while the right child node has a value greater than or equal to the parent node’s value.
In Java, a binary search tree can be implemented using a class that represents the tree and another class for each node in the tree. The node class typically contains fields for the node’s value, left child node, and right child node.
Properties of a Binary Search Tree are:
Java Program to Implement Binary Search Tree:
class Node {
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class BinarySearchTree {
Node root;
public BinarySearchTree() {
this.root = null;
}
public void insert(int value) {
this.root = insertRecursive(this.root, value);
}
private Node insertRecursive(Node current, int value) {
if (current == null) {
return new Node(value);
}
if (value < current.value) {
current.left = insertRecursive(current.left, value);
} else if (value > current.value) {
current.right = insertRecursive(current.right, value);
} else {
// value already exists
}
return current;
}
public boolean contains(int value) {
return containsRecursive(this.root, value);
}
private boolean containsRecursive(Node current, int value) {
if (current == null) {
return false;
}
if (value == current.value) {
return true;
} else if (value < current.value) {
return containsRecursive(current.left, value);
} else {
return containsRecursive(current.right, value);
}
}
}
Explanation:
In the above program, This implementation allows for inserting values into the tree and checking if a value exists in the tree using the insert() and contains() methods, respectively. It uses recursion to traverse the tree and find the appropriate location for inserting or searching for a value.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment