Java HashSet Class

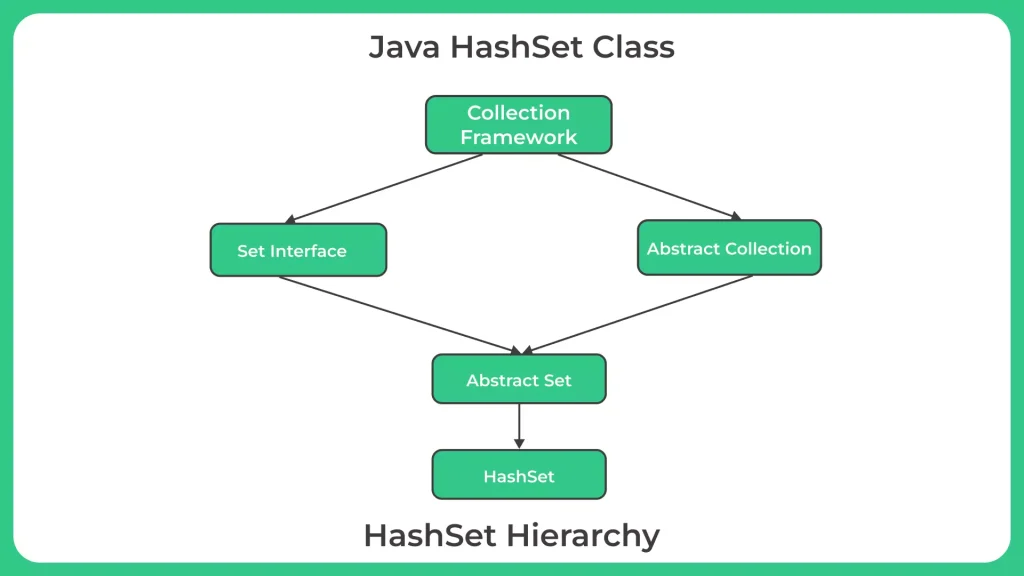
What is Java HashSet?
The HashSet class in Java is a collection class that implements the Set interface. It stores a set of unique elements in no particular order.
The HashSet class provides constant-time performance for the basic operations such as add, remove, and contains, assuming that the hash function is well-distributed.
To understand more about Java HashSet Class, Read the Complete Article.
Steps to Create HashSet in java.
- Here are the Steps to Create HashSet in java .
- Create a new Java class file and name it HashSet.java.
- Declare the class name and add the necessary imports:
- Declare a private HashSet variable to store the values:
- Create a constructor for the class:
- Define the methods you want to include in the HashSet class, such as add, remove, and size:
- Save the file and compile it. If there are no errors, you can now use your HashSet class in other Java programs.
Let’s look at the Java Program on Methods of HashSet to perform certain operations.
Example 1: Java Program to Access HashSet Elements
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a HashSet
HashSet set = new HashSet();
// add some elements to the set
set.add("apple");
set.add("banana");
set.add("orange");
set.add("kiwi");
// print the set using an iterator
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
String element = iterator.next();
System.out.println(element);
}
// check if the set contains an element
boolean containsKiwi = set.contains("kiwi");
System.out.println("Set contains kiwi: " + containsKiwi);
// remove an element from the set
set.remove("orange");
// print the set using a for-each loop
for(String element : set) {
System.out.println(element);
}
// clear the set
set.clear();
System.out.println("Set is empty: " + set.isEmpty());
}
}
Output
banana orange apple kiwi Set contains kiwi: true banana apple kiwi Set is empty: true
Example 2: Java program to Remove Elements in hashset
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a HashSet
HashSet set = new HashSet();
// add some elements to the set
set.add("apple");
set.add("banana");
set.add("orange");
set.add("kiwi");
System.out.println("Set before removal: " + set);
// remove an element from the set
set.remove("orange");
System.out.println("Set after removal: " + set);
// remove all elements in another set from this set
HashSet removeSet = new HashSet();
removeSet.add("apple");
removeSet.add("kiwi");
set.removeAll(removeSet);
System.out.println("Set after removeAll: " + set);
// remove all elements from the set
set.clear();
System.out.println("Set after clear: " + set);
}
}
Output
Set before removal: [banana, orange, apple, kiwi] Set after removal: [banana, apple, kiwi] Set after removeAll: [banana] Set after clear: []
Set Operations in Java HashSet
In Java, a HashSet is a collection that stores a set of unique elements.Java HashSet provides various set operations such as union, intersection, and difference of two sets.
- Here are some common set operations that can be performed using Java HashSet:
- Union: The union of two sets A and B is a set that contains all the elements of A and all the elements of B, but no duplicates.
- Intersection: The intersection of two sets A and B is a set that contains only the elements that are in both A and B.
- Difference: The difference of two sets A and B is a set that contains only the elements that are in A but not in B.
- Subset: A set A is a subset of a set B if all the elements of A are also elements of B.
- Superset: A set B is a superset of a set A if all the elements of A are also elements of B.
Example 3: Union of Sets
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create two sets
Set set1 = new HashSet();
Set set2 = new HashSet();
// add some elements to set1
set1.add(1);
set1.add(2);
set1.add(3);
set1.add(4);
// add some elements to set2
set2.add(3);
set2.add(4);
set2.add(5);
set2.add(6);
// perform the union of the two sets
Set union = new HashSet(set1);
union.addAll(set2);
// print the union of the two sets
System.out.println("Union of sets: " + union);
}
}
Output
Union of sets: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Example 4: Intersection of Sets
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create two sets
Set set1 = new HashSet();
Set set2 = new HashSet();
// add some elements to set1
set1.add(1);
set1.add(2);
set1.add(3);
set1.add(4);
// add some elements to set2
set2.add(3);
set2.add(4);
set2.add(5);
set2.add(6);
// perform the intersection of the two sets
Set intersection = new HashSet(set1);
intersection.retainAll(set2);
// print the intersection of the two sets
System.out.println("Intersection of sets: " + intersection);
}
}
Output
Intersection of sets: [3, 4]
Example 5: Difference of Sets
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create two sets
Set set1 = new HashSet();
Set set2 = new HashSet();
// add some elements to set1
set1.add(1);
set1.add(2);
set1.add(3);
set1.add(4);
// add some elements to set2
set2.add(3);
set2.add(4);
set2.add(5);
set2.add(6);
// perform the difference of the two sets
Set difference = new HashSet(set1);
difference.removeAll(set2);
// print the difference of the two sets
System.out.println("Difference of sets: " + difference);
}
}
Output
Difference of sets: [1, 2]
Example 6: SubSets in Set Operation
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
// Find all subsets of the set
Set subsets = getSubsets(set);
// Print out the subsets
for (Set subset : subsets) {
System.out.println(subset);
}
}
private static Set getSubsets(Set set) {
Set subsets = new HashSet<>();
int numSubsets = 1 << set.size(); // 2^n where n is the number of elements in the set
for (int i = 0; i < numSubsets; i++) {
Set subset = new HashSet<>();
int bitmask = i;
// Use a bitmask to determine which elements to include in the subset
while (bitmask > 0) {
int index = (int) (Math.log(bitmask & -bitmask) / Math.log(2)); // Get the index of the rightmost set bit
int element = (int) set.toArray()[index]; // Get the element at that index
subset.add(element);
bitmask &= ~(1 << index); // Clear the rightmost set bit
}
subsets.add(subset);
}
return subsets;
}
}
Output
[] [1] [2] [1, 2] [3] [1, 3] [2, 3] [1, 2, 3]
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others





