0
Notifications Mark All Read
- Login
- Get Prime
Weak Entity and Strong Entity in DBMS
Weak Entity And Strong Entity in DBMS
On this page, we will learn about Weak Entity and Strong Entity in DBMS.
The entity defines the type of data stored, simply it is nothing but a database table .

Strong entity
- Strong Entity is independent of any other entity in the schema
Example – A student entity can exist without needing any other entity in the schema or a course entity can exist without needing any other entity in the schema
- A Strong entity is nothing but an entity set having a primary key attribute or a table that consists of a primary key column
Representation
- The strong entity is represented by a single rectangle.
- The relationship between two strong entities is represented by a single diamond.
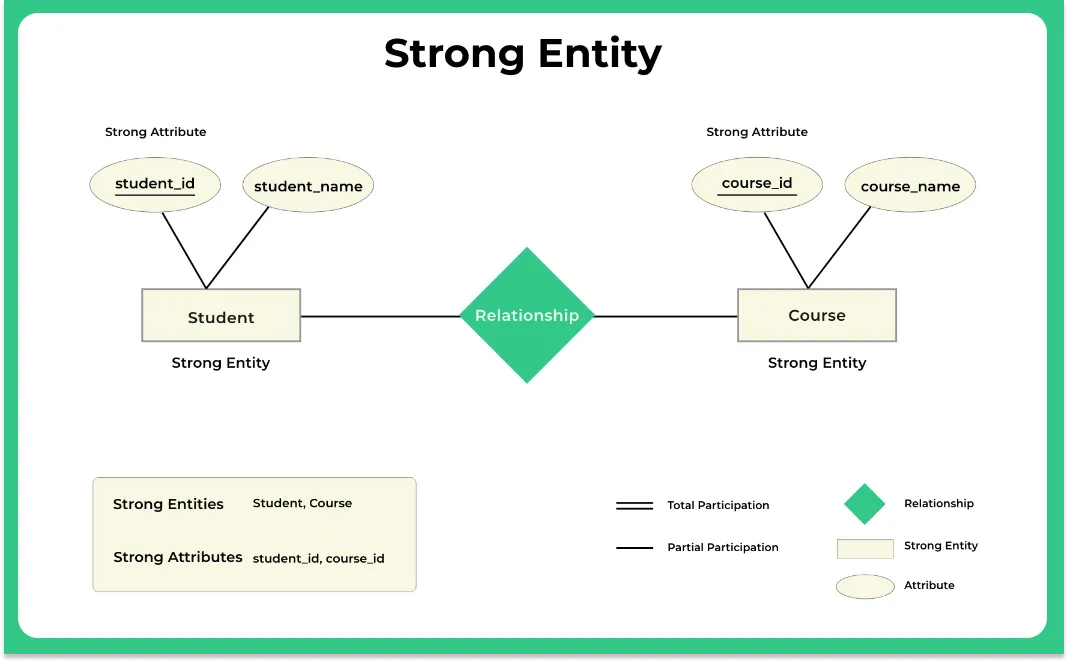
Examples for the strong entity
- Consider the ER diagram which consists of two entities student and course
- Student entity is a strong entity because it consists of a primary key called student id which is enough for accessing each record uniquely
- In the same way, the course entity contains of course ID attribute which is capable of uniquely accessing each row.
Weak entity
- A weak entity is an entity set that does not have sufficient attributes for Unique Identification of its records.
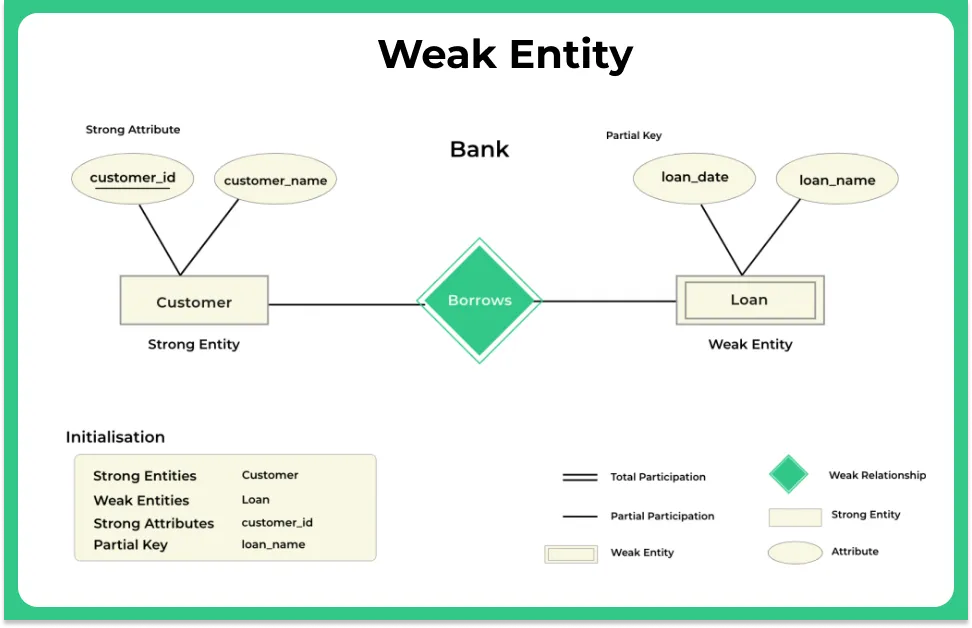
Example 1 – A loan entity can not be created for a customer if the customer doesn’t exist
Example 2 – A dependents list entity can not be created if the employee doesn’t exist
- Simply a weak entity is nothing but an entity that does not have a primary key attribute
- It contains a partial key called a discriminator which helps in identifying a group of entities from the entity set
- A discriminator is represented by underlining with a dashed line
Representation
- A double rectangle is used for representing a weak entity set
- The double diamond symbol is used for representing the relationship between a strong entity and a weak entity which is known as identifying relationship
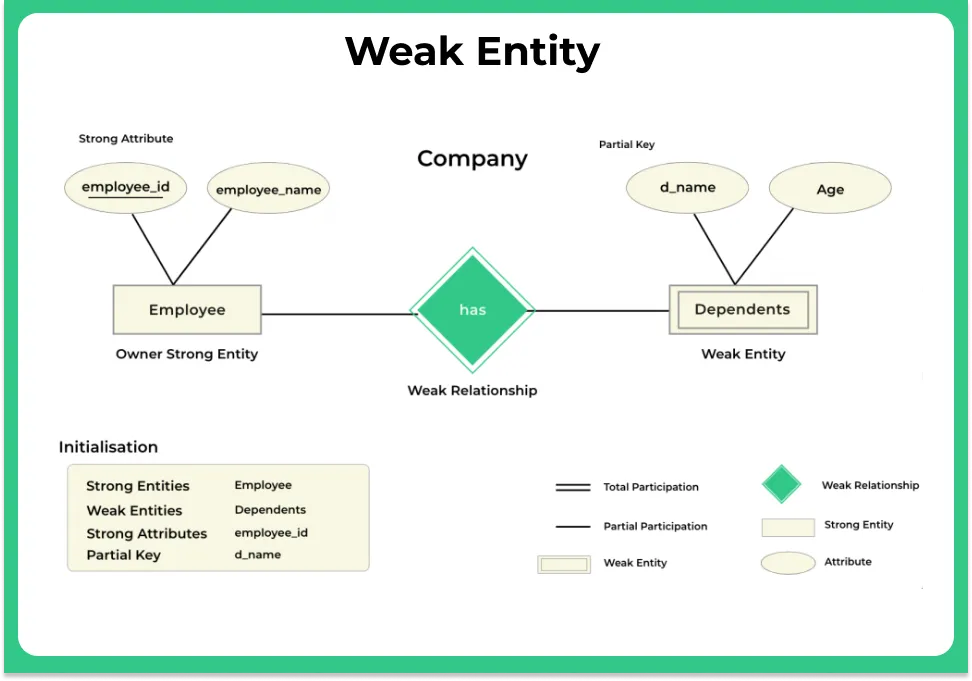
Example for weak entity
- In the ER diagram, we have two entities Employee and Dependents.
- Employee is a strong entity because it has a primary key attribute called Employee number (Employee_No) which is capable of uniquely identifying all the employee.
- Unlike Employee, Dependents is weak entity because it does not have any primary key .
- D_Name along with the Employee_No can uniquly identfy the records of Depends. So here the D_Name (Depends Name) is partial key.
This would be wrong way to think as -
If student s1 doesn't exist then courses c1, c2 ... others can exist as they may have taken courses or college chooses to have one course that is taken by none of student this semester.
But, if customer c1 doesn't exist then loan L1 for him can not exist at all as loan L1 is uniquely dependent on existence of customer C1
Strong entity vs Weak entity
| Strong entity | Weak entity |
|---|---|
| Strong entity always has a primary key. | It will not have a primary key but it has partial discriminator key. |
| It is not dependent on any other entity. | Weak entity is dependent on the strong entity. |
| Represented by a single rectangle. | Represented by double rectangle. |
| Relationship between two strong entities is represented by a single diamond. | Relationship between a strong entity and the weak entity is represented by double Diamond. |
| A strong entity may or may not have total participation. | It has always total participation. |
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others

 0
0



Login/Signup to comment