Relationship Cardinality in DBMS
Cardinality Relationship in DBMS
On this page, we will learn about the Relationship Cardinality in DBMS.
Cardinality Relationship has two different meanings in DBMS –
1. Cardinality for Data models
2. Cardinality for Query Optimization
Cardinality Relationship for Data Models
There are the following four types of Cardinality Relationship in DBMS –
- One to One
- One to Many
- Many to One
- Many to Many
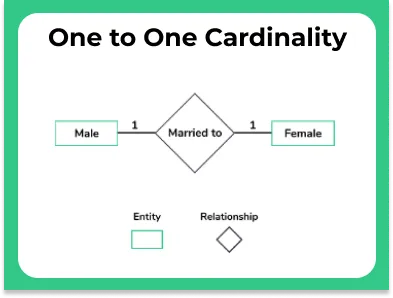
One to One
A relationship between a husband and wife can be considered as one to one, where The Entities are Husband and Wife and the Relationship is Marriage This means, if you put this information in a DBMS table, a particular row of one table only associates itself with single and unique row of another table.
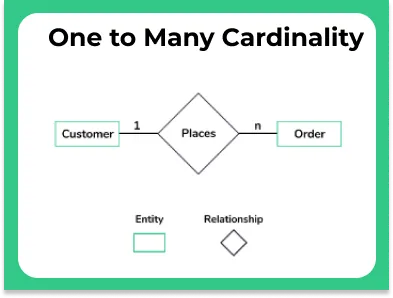
One to Many
A relationship between a Company (1) and Employees (n) can be considered as one to many, where The Entities are company and employees and the Relationship is pays. This means, if you put this information in a DBMS table, a particular row of one table associates itself with multiple rows of another table.
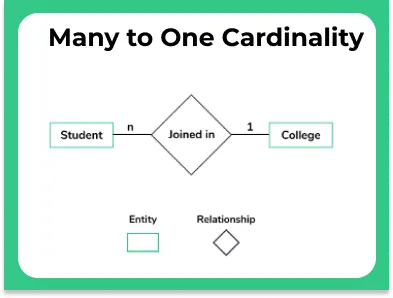
Many to One
A relationship between a Students and University can be considered as one to one, where The Entities are Students and University and the Relationship is study. This means, if you put this information in a DBMS table, multiple rows of student table associates itselves with single row of University table.
Many to Many
A relationship between a students and courses can be considered as many to many, where The Entities are students and courses and the Relationship is enroll. This means, if you put this information in a DBMS table, a multiple rows of one table associates itself with multiple rows of another table.
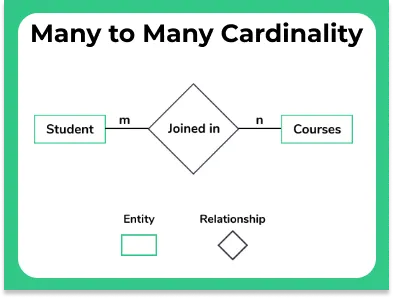
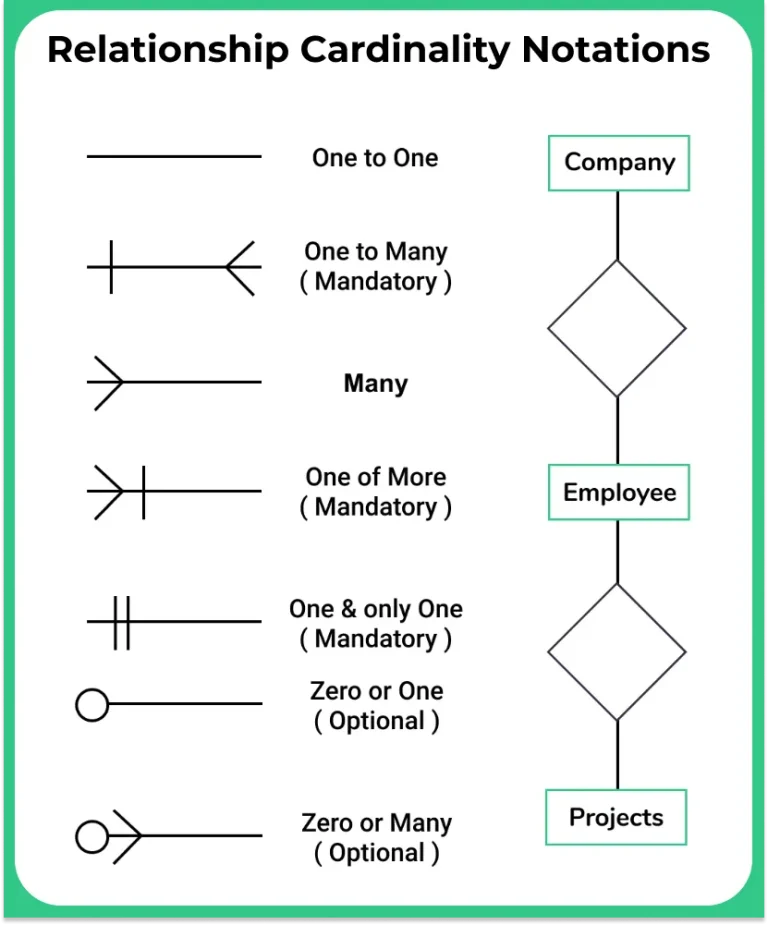
Cardinality Notations
- New Notations (Kaushik Style) – These follow 1, n, m structure only and are in fashion of being used.
- Old Notations (Bachman Style) – These follow pictorial representation of relationship without using 1, n, m. You can find examples below, however, these are unpopular these days.
Cardinality Relationship for Query Optimization
In terms of this, the system with less redundancy that is less duplicacy has high cardinality. For example one table with all unique entities in a column will have higher cardinality than the one with duplicate values.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment