Key Constraints in DBMS
Key Constraints in DBMS
On this article, we will learn about Key Constraints in DBMS .Constraints or nothing but the rules that are to be followed while entering data into columns of the database table .Constraints or nothing but the rules that are to be followed while entering data into columns of the database table which we will discuss on this page.

CHECK IN DBMS
- Constraints or nothing but the rules that are to be followed while entering data into columns of the database table
- Constraints ensure that data entered by the user into columns must be within the criteria specified by the condition
- For example, if you want to maintain only unique IDs in the employee table or if you want to enter only age under 18 in the student table etc
- We have 5 types of key constraints in DBMS
NOT NULL:ensures that the specified column doesn’t contain a NULL value.UNIQUE :provides a unique/distinct values to specified columns.DEFAULT:provides a default value to a column if none is specified.CHECK :checks for the predefined conditions before inserting the data inside the table.PRIMARY KEY:it uniquely identifies a row in a table.FOREIGN KEY:ensures referential integrity of the relationship
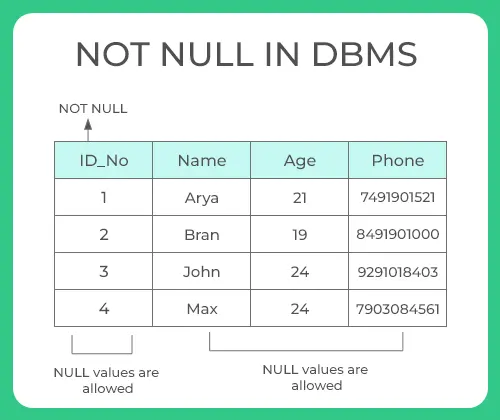
Not Null
- Null represents a record where data may be missing data or data for that record may be optional
- Once not null is applied to a particular column, you cannot enter null values to that column and restricted to maintain only some proper value other than null
- A not-null constraint cannot be applied at table level
Example
CREATE TABLE Orders (
OrderID int NOT NULL,
OrderNumber int NOT NULL,
PersonID int,
PRIMARY KEY (OrderID),
FOREIGN KEY (PersonID) REFERENCES Persons(PersonID)
);- In the above example, we have applied not null on three columns ID, name and age which means whenever a record is entered using insert statement all three columns should contain a value other than null
- We have two other columns address and salary, where not null is not applied which means that you can leave the row as empty or use null value while inserting the record into the table
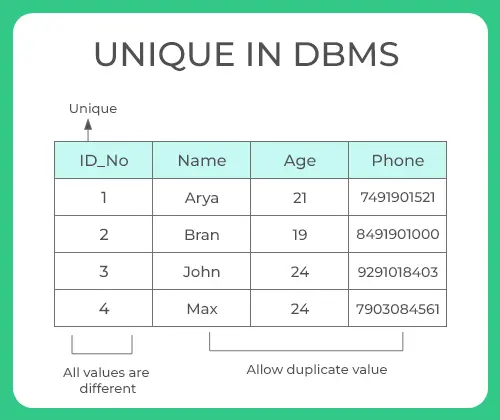
Unique
- Sometimes we need to maintain only unique data in the column of a database table, this is possible by using a
uniqueconstraint - Unique constraint ensures that all values in a column are unique
Example
CREATE TABLE Persons ( ID int UNIQUE, LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL, FirstName varchar(255), Age int, );
In the above example, as we have used unique constraint on ID column we are not supposed to enter the data that is already present, simply no two ID values are same
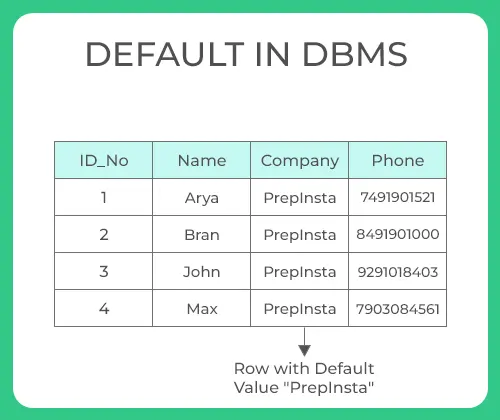
DEFAULT
Defaultclause in SQL is used to add default data to the columns- When a column is specified as default with some value then all the rows will use the same value i.e each and every time while entering the data we need not enter that value
- But default column value can be customized i.e it can be overridden when inserting a data for that row based on the requirement.
Example for DEFAULT clause
The following SQL sets a DEFAULT value for the “city” column when the “emp” table is created:
My SQL / SQL Server / Oracle / MS Access:
CREATE TABLE emp ( ID int NOT NULL, LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL, FirstName varchar(255), Age int, City varchar(255) DEFAULT 'hyderabad' );
- As a result, whenever you insert a new row each time you need not enter a value for this default column that is entering a column value for a default column is optional and if you don’t enter the same value is considered that is used in the default clause
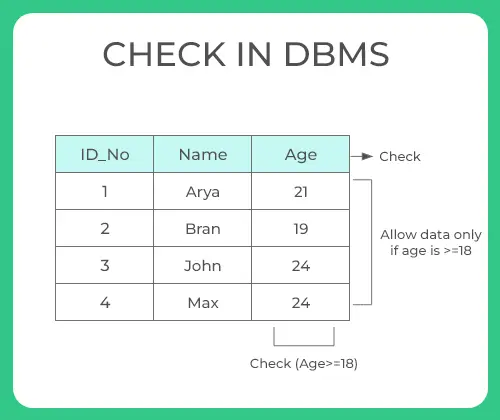
Check
- Suppose in real-time if you want to give access to an application only if the age entered by the user is greater than 18 this is done at the back-end by using a
checkconstraint - Check constraint ensures that the data entered by the user for that column is within the range of values or possible values specified.
Example for check constraint
CREATE TABLE STUDENT ( ID int , Name varchar(255) , Age int, CHECK (Age>=18) );
- As we have used a check constraint as (Age>=18) which means values entered by the user for this age column while inserting the data must be less than or equal to 18 otherwise an error is shown
- Simply, the only possible values that the age column will accept is [0 -17]
Primary Key
A primary key is a constraint in a table that uniquely identifies each row record in a database table by enabling one or more the columns in the table as the primary key.
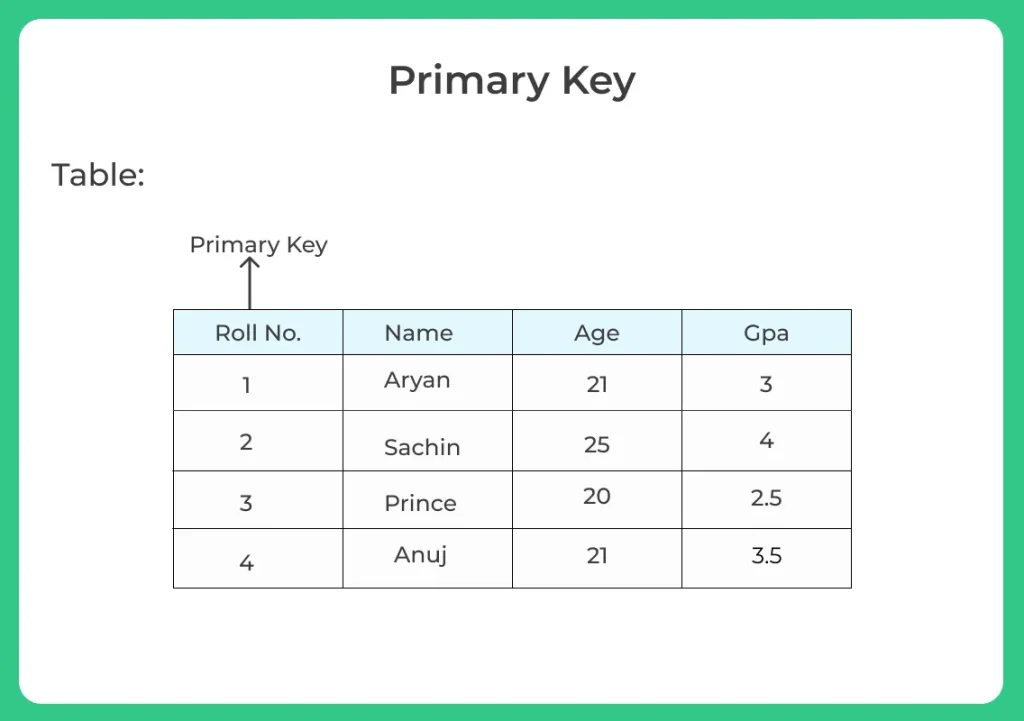
Creating a primary key
A particular column is made as a primary key column by using the primary key keyword followed with the column name
CREATE TABLE EMP ( ID INT NAME VARCHAR (20) AGE INT COURSE VARCHAR(10) PRIMARY KEY (ID) );
- Here we have used the primary key on ID column then ID column must contain unique values i.e one ID cannot be used for another student.
- If you try to enter duplicate value while inserting in the row you are displayed with an error
- Hence primary key will restrict you to maintain unique values and not null values in that particular column
Foreign Key
- The
foreign keya constraint is a column or list of columns that points to the primary key column of another table - The main purpose of the foreign key is only those values are allowed in the present table that will match the primary key column of another table.
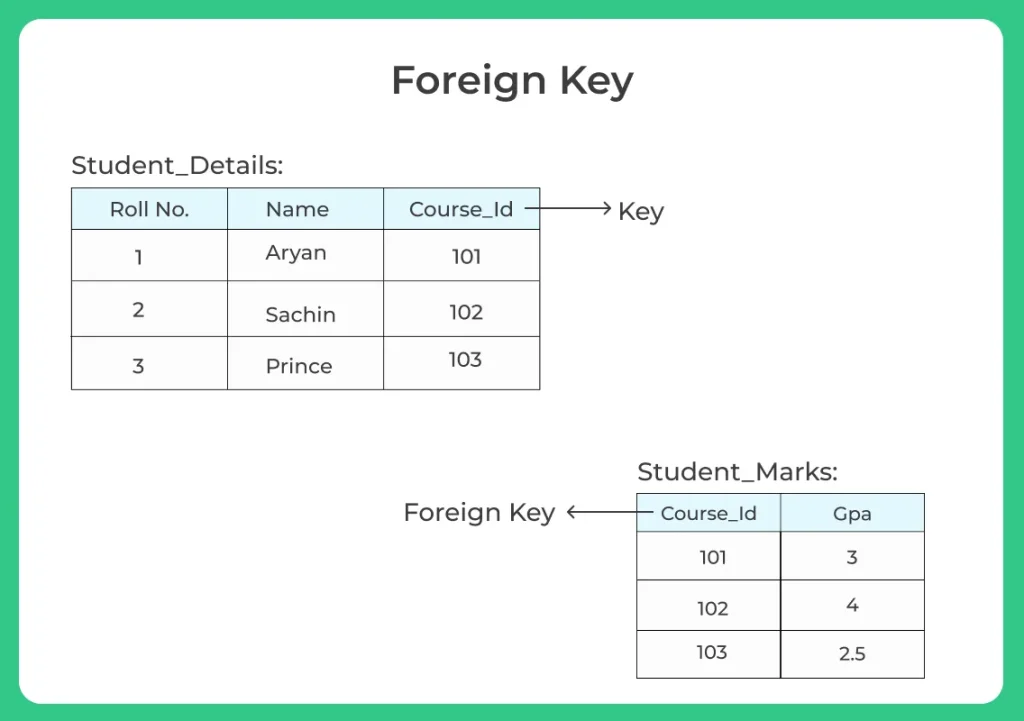
Example to create a foreign key
Reference Table
CREATE TABLE CUSTOMERS1( ID INT , NAME VARCHAR (20) , COURSE VARCHAR(10) , PRIMARY KEY (ID) );
Child Table
CREATE TABLE CUSTOMERS2( ID INT , MARKS INT, REFERENCES CUSTOMERS1(ID) );
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription





super concept