Linear Search in C
Linear Search in C Programming Language
In this article, you will learn: What is Linear Search in C, How Linear Search works and Time and Space Complexity of the methods for Linear Search with Example Input/Output.
When working with data in C programming, one of the most basic tasks is finding an element in a list or array. This process is called searching. One of the simplest and most intuitive searching techniques is called Linear Search.

What is Linear Search in C?
Linear Search is a straightforward searching technique. It is used to search for an element (called the “key”) inside an array or list.
In Linear Search:
- You start from the first element of the array.
- You compare each element with the key, one by one.
- If a match is found, you return the index (position) of the element.
- If the key is not present in the array, you return -1 or indicate that it was not found.
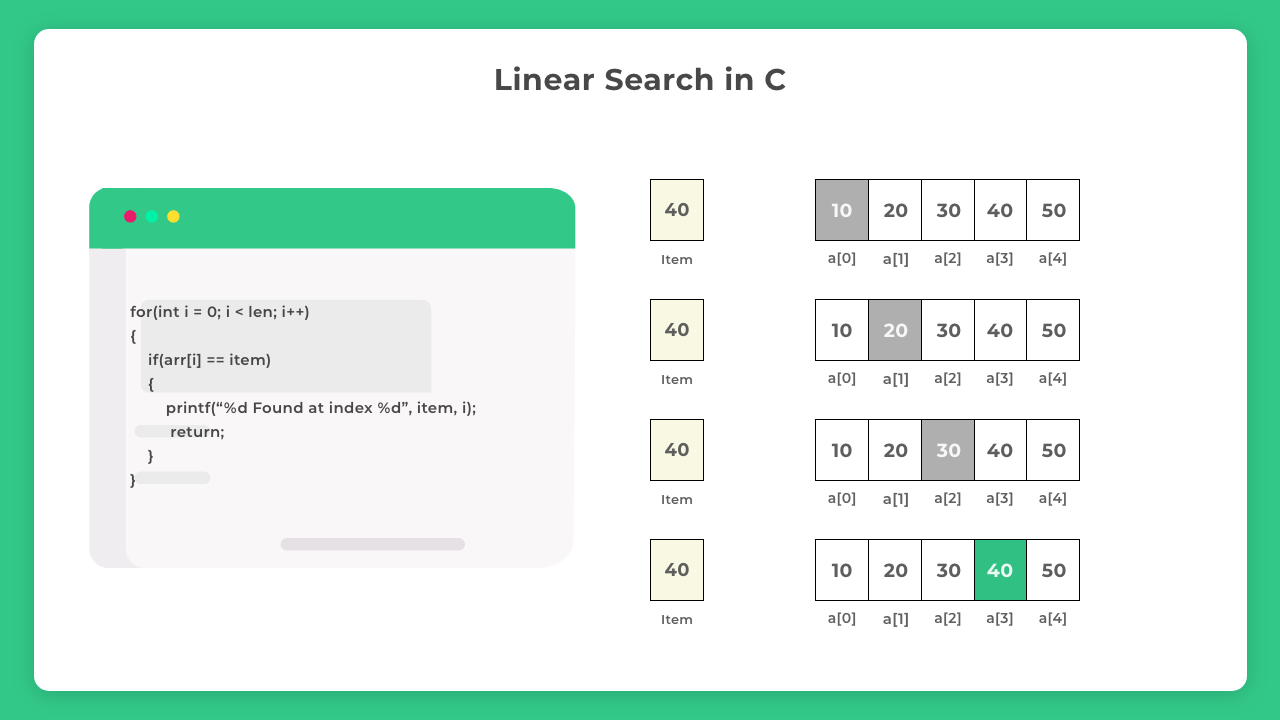
Algorithm of Linear Search:
Here is a step by step explanation of how Linear Search works:
- Start from the first element of the array (index = 0).
- Compare the current element with the key:
If the element matches the key, return its index.
If it does not match, move to the next element.
Repeat step 2 until either:
Key is found.
You reach the end of the array.
If the key is not found after checking all elements, return -1.
2. Does not require the array to be sorted.
3. Works for both small and unsorted arrays.
2. Time complexity is linear — inefficient for big datasets.
Methods to Perform Linear Search
There are 2 common ways to implement Linear Search in C:
- Iterative Method — using loops (for loop or while loop).
- Recursive Method — using recursion (function calls itself).
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banner
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Methods to implement Linear Search
Code 1: Iterative Method
#include<stdio.h>
int linearSearch(int arr[], int size, int key) {
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if(arr[i] == key) {
return i; // Element found, return index
}
}
return -1; // Element not found
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {10, 25, 35, 45, 50, 60};
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int key;
printf("Enter the element to search: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
int result = linearSearch(arr, size, key);
if(result != -1) {
printf("Element %d found at index %d\n", key, result);
} else {
printf("Element %d not found in the array\n", key);
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter the element to search: 35 Element 35 found at index 2
Code 2: Recursive Method
#include<stdio.h>
int linearSearchRecursive(int arr[], int size, int key, int index) {
if(index >= size) {
return -1; // Element not found
}
if(arr[index] == key) {
return index; // Element found
}
return linearSearchRecursive(arr, size, key, index + 1);
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {5, 15, 25, 35, 45, 55};
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int key;
printf("Enter the element to search: ");
scanf("%d", &key);
int result = linearSearchRecursive(arr, size, key, 0);
if(result != -1) {
printf("Element %d found at index %d\n", key, result);
} else {
printf("Element %d not found in the array\n", key);
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter the element to search: 15 Element 15 found at index 1
1. Best Case: The key is found at the first position. Time Complexity = O(1)
2. Average Case: The key is somewhere in the middle. Time Complexity = O(n)
3. Worst Case: The key is not present or at the last position. Time Complexity = O(n)
Overall: Time Complexity = O(n)
2. Only a few extra variables are used (index, key).
Space Complexity = O(1)
Conclusion:
Linear Search is one of the easiest and most basic search algorithms in C.
It is best used for:
- Small arrays.
- Unsorted data.
Although it is not the most efficient search algorithm, learning linear search is essential for beginners because it builds understanding of loops, conditions, and how data is processed.

FAQ's related to Linear Search
Answer:
Linear search in C programming language is a simple search algorithm used to find a specific element in an array or list. In linear search, each element of the array is checked one by one until the desired element (key) is found or the end of the array is reached.
Answer:
To implement linear search in C, you can use either an iterative method using loops (for or while loop) or a recursive function. The basic logic involves comparing each element of the array with the target value. If a match is found, its index is returned. For example, a simple C program for linear search will loop through the array and print the index if the element matches the key.
Answer:
The time complexity of linear search in C is O(n), where ‘n’ is the number of elements in the array. In the worst case, linear search has to check each element one by one, resulting in linear time. The best case is O(1) if the element is found at the first position.
Answer:
Advantages of linear search in C include its simplicity and the fact that it works on unsorted arrays. It is easy to implement and understand. The disadvantages of linear search are that it is not efficient for large datasets and has linear time complexity (O(n)), making it slower compared to binary search for large or sorted arrays.
Answer:
The main difference between linear search and binary search in C is that linear search checks every element one by one, while binary search divides the array and eliminates half the search space in each step. Linear search works on both sorted and unsorted arrays, whereas binary search requires the array to be sorted. Binary search is more efficient with a time complexity of O(log n), compared to O(n) for linear search.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




thank you so much ,it’s really very helpful
awesome
nice
Really helpful
Thanks a ton, for the appreciation jaspreet, you must visit our Linked List section in the Data Structure Page, you will find some good content there too – https://prepinsta.com/data-structures/#linked
nice
thanks for these study material in summary with pictorial representation.