C Program for Printing reverse of a Linked List without actually reversing
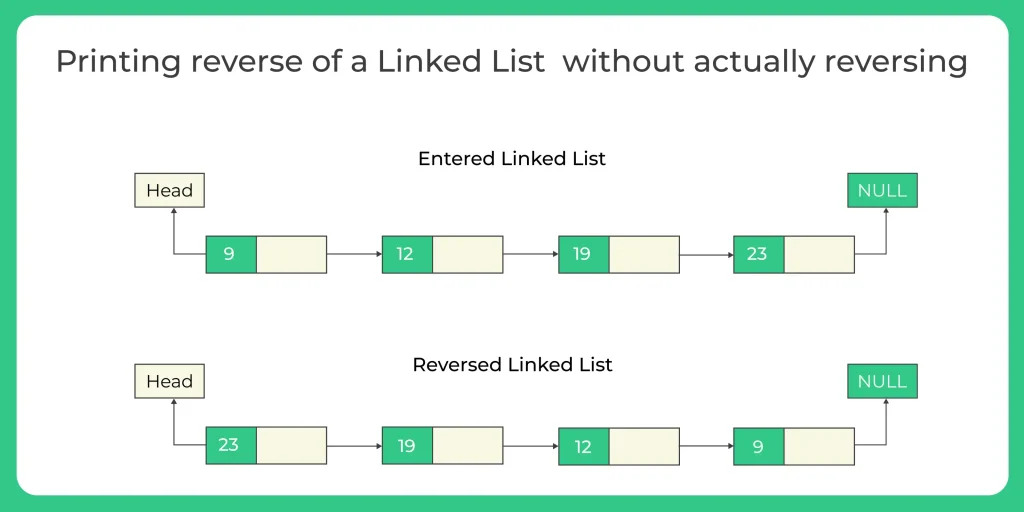
Reverse printing a Linked List without actually reversing the Linked List
Here we will learn how to code a C program for Reverse Printing a Linked List, without actually reversing it. This is a pretty simple problem in which we will make a linked list, and instead of printing it in the usual manner we will traverse to the tail of the Linked List, and will print it in the reverse order. Let’s see how to code a program for this problem.
How do you reverse a Linked List ?
In this program we are not actually reversing a Linked List, but just printing the Linked List backwards, for doing so we will be following the below steps -:
- Step 1 – Take a pointer ptr.
- Step 2 – Check whether the Linked List has nodes or not.
- Step 3 – If the linked list is empty, return 0.
- Step 4 – If the linked list has nodes, move the pointer ahead till it reaches NULL.
- Step 5 – Backtrack and print the data of the nodes
Algorithm for Reverse Printing a Linked List
- CREATE A FUNCTION DISPLAY
- if, HEAD = NULL
- RETURN 0
- ELSE
- RECURSIVELY CALL DISPLAY(HEAD->NEXT)
- PRINT(HEAD->DATA)
C Program for Reverse printing a Linked List
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node //code for making a node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
void display (struct node *head) //method for reverse display nodes
{
if (head == NULL)
return;
// print the list after head node
display (head->next);
// After everything else is printed, print head
printf ("%d ", head->data);
}
int main ()
{
struct node *prev, *head, *p;
int n, i;
printf ("Enter size of Linked List: ");
scanf ("%d", &n);
head = NULL;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
p = malloc (sizeof (struct node));
printf ("Enter the data: ");
scanf ("%d", &p->data);
p->next = NULL;
if (head == NULL)
head = p;
else
prev->next = p;
prev = p;
}
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Enter size of Linked List: 5
Enter the data: 1
Enter the data: 2
Enter the data: 3
Enter the data: 4
Enter the data: 5
5 4 3 2 1



Login/Signup to comment