C Program for Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list
Insertion at nth node in the linked list
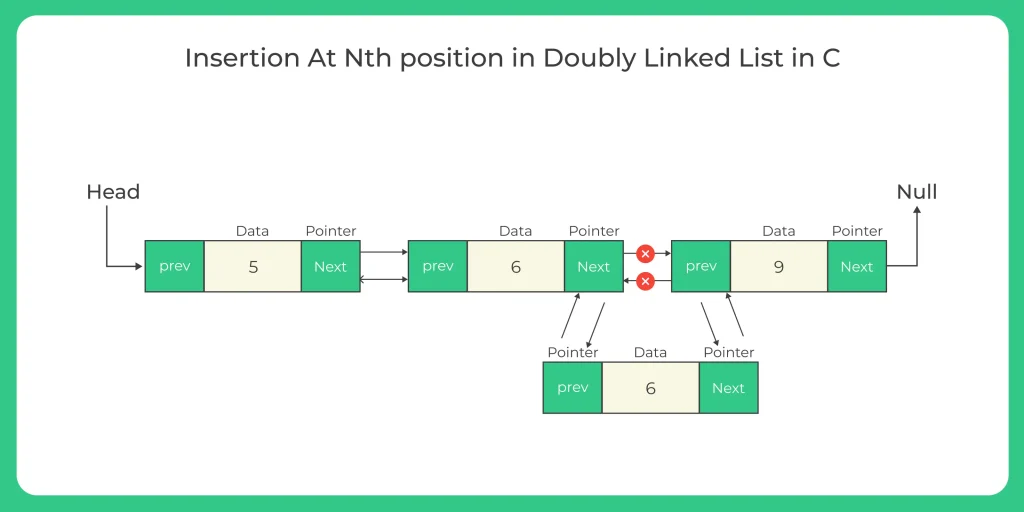
In this section we will learn how to make C Program for Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list in which we have to input new node in the linked list according to the user demand like the position and node data.Doubly linked list is the updated version of singly linked list having two pointer previous and next so that we can move in two direction of the list.
For Example :-
Input : 14 66 84 25 74
Enter the data you want to insert : 98
Enter the position : 2
Output : 14 98 66 84 25 74

Working for Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list
- Take a new_node then new_node with data has to be inserted at the nth of the linked list.
- Lets begin traversing the linked list from head and move until the (pos – 1)th node.
- If you reachout the (pos- 1) node, the next pointer of the new_node is set to the address having by the next pointer of the (pos – 1) th node.
- Then take the next pointer of the (pos – 1) th node to point to the new_node and the previous pointer of the new_node is pointed to the (pos – 1) th node.
- Atlast the new_node next to previous pointer must be made to point to the new_node of the linked list.
- Return the new_node.
Construction of Node Structure in the doubly linked list
struct node
{
struct node *prev;
int data;
struct node *next;
} 
Algorithm for Insertion at After nth Node
- Calculate the size of the node
- If the position you want to enter is less than 1
- Invalid position But, if 0 then use insertAtStart method
- If the position you want to enter is greater than size then
- Invalid position, but if the position is equal to size then use insertLast method
- else create a temp node and assign it the address of the head
- Create a new node and assign it the data value
- Iterate to the position you want to enter after in the linked list
- Assign this new node’s next and previous nodes
- Assign previous node’s next to this new node
- Assign next node’s previous to this new node
C Program for Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list :-
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
void insertLast (struct Node **head, int data);
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data);
// helper function for insertion after position
int calcSize (struct Node *node)
{
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
void insertPosition (int pos, int data, struct Node **head)
{
int size = calcSize (*head);
/*If pos is 0 then should use insertStart method
If pos is less than or equal to 0 then can't enter at all
If size is lesser than pos then bufferbound issue*/
if (pos < 0 || size < pos)
{
printf ("Can't insert, %d is not a valid position\n", pos);
return;
}
// Insert after 0th position would mean insert at start
if (pos == 0)
insertStart (head, data);
// insert after size'th position would mean insert at the last
else if (pos == size)
insertLast (head, data);
else
{
struct Node *temp = *head;
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
while (--pos)
temp = temp->next; //temp2 = 10 as 12->next is 10
struct Node *temp2 = temp->next; //(25)->next = 10 as 12->next is 10
newNode->next = temp->next; //(25)->prev = 12
newNode->prev = temp; // (12)->next = 25
temp->next = newNode; // (10)->prev = 25
temp2->prev = newNode; //new node added in b/w 12 and 10
}
}
void insertLast (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
//need this if there is no node present in linked list at all
if (*head == NULL)
{
*head = newNode;
newNode->prev = NULL;
return;
}
struct Node *temp = *head;
while (temp->next != NULL)
temp = temp->next;
temp->next = newNode;
newNode->prev = temp;
}
void insertStart (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
newNode->prev = NULL; //If the linked list already had atleast 1 node
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = newNode;
// *head->prev = newNode; would not work it has (*head) must be used
//changing the new head to this freshly entered node
*head = newNode;
}
// function to print the doubly linked list
void display (struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *end;
printf ("List in Forward direction: ");
while (node != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", node->data);
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\nList in backward direction: ");
while (end != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", end->data);
end = end->prev;
}
}
int main ()
{
/*Need & i.e. address as we need to change head address */
struct Node *head = NULL;
insertStart (&head, 12);
insertStart (&head, 16);
insertStart (&head, 20);
insertLast (&head, 10);
insertLast (&head, 14);
insertLast (&head, 18);
insertLast (&head, 11);
//Inserts after 3rd position
printf ("linked before insertion at specific position\n");
display (head);
printf ("\n\nlinked after insertion at specific position\n");
insertPosition (3, 25, &head);
/*No need for & i.e. address as we do not need to change head address */
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
linked before insertion at specific position List in Forward direction: 20 16 12 10 14 18 11 List in backward direction: 11 18 14 10 12 16 20 linked after insertion at specific position List in Forward direction: 20 16 12 25 10 14 18 11 List in backward direction: 11 18 14 10 25 12 16 20



Login/Signup to comment