C Program for Deletion from nth position in doubly linked list
Deletion from particular position in doubly linked list
In this article we will learn C Program for Deletion from nth position in doubly linked list, the task is to delete the specific node by the user input.Here we have given algorithm ,working and code to understand better .
For Example :-
Input : 61 4 77 10 32
Enter the position from where you want to delete node : 3
Output : 61 4 10 32

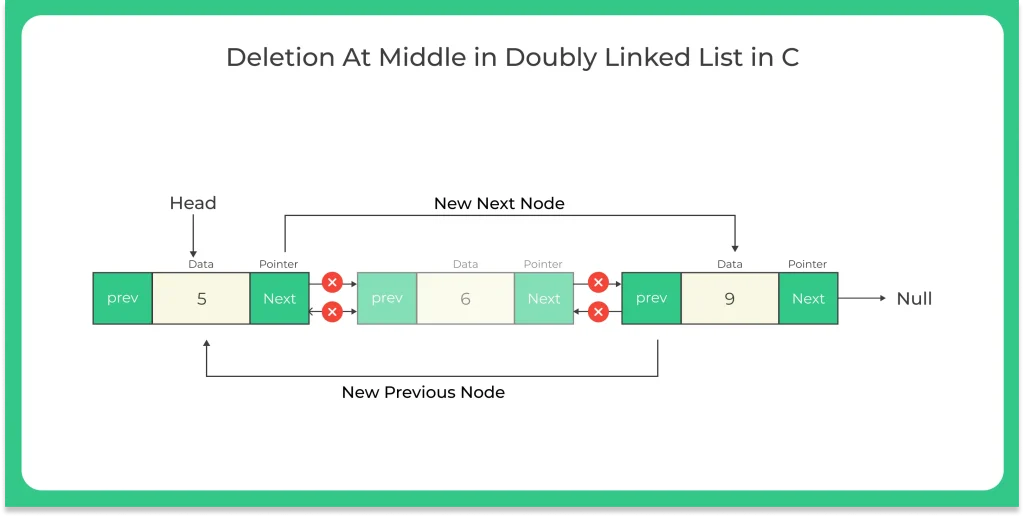
Working needed for deleting node from the nth node in the doubly linked list :-
- Make a new doubly linked list.
- Then copy the address of head pointer into a temporary pointer .
- Traverse the linked list until we find the desired position.
- After that we have to make the next pointer of this node point to null so that it can be the new last node of the list.
How to made node Structure in the doubly linked list
struct node
{
struct node *prev;
int data;
struct node *next;
} 
Algorithm require for deleting node from the specific position in the linked list
- IF HEAD = NULL (GOTO STEP 9 AND END OF IF LOOP)
- NOW ASSIGN EXTRA = HEAD
- REPEAT STEP 4 WHILE TEMP → DATA != VALUE
- ASSIGN EXTRA = EXTRA → NEXT
- ASSIGN POINTER = EXTRA → NEXT
- ASSIGN EXTRA → NEXT = POINTER → NEXT
- ASSIGN POINTER → NEXT → PREVIOUS = EXTRA
- REMOVE POINTER
- EXIT
Code for Deletion from nth position in a Doubly Linked List
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
int getLength (struct Node *node);
void insert (struct Node **head, int data)
{
struct Node *freshNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
freshNode->data = data;
freshNode->next = *head;
freshNode->prev = NULL;
// If the linked list already had atleast 1 node
if (*head != NULL)
(*head)->prev = freshNode;
// freshNode will become head
*head = freshNode;
}
void deleteFront (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *tempNode = *head;
// if DLL is empty
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete\n");
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (tempNode->next == NULL)
{
printf ("%d deleted\n", tempNode->data);
*head = NULL;
return;
}
// move head to next node
*head = (*head)->next;
// assign head node's previous to NULL
(*head)->prev = NULL;
printf ("%d deleted\n", tempNode->data);
free (tempNode);
}
void deleteEnd (struct Node **head)
{
struct Node *tempNode = *head;
// if DLL is empty
if (*head == NULL)
{
printf ("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete\n");
return;
}
// if Linked List has only 1 node
if (tempNode->next == NULL)
{
printf ("%d deleted\n", tempNode->data);
*head = NULL;
return;
}
// else traverse to the last node
while (tempNode->next != NULL)
tempNode = tempNode->next;
struct Node *secondLast = tempNode->prev;
// Curr assign 2nd last node's next to Null
secondLast->next = NULL;
printf ("%d deleted\n", tempNode->data);
free (tempNode);
}
void deleteNthNode (struct Node **head, int n)
{
//if the head node itself needs to be deleted
int len = getLength (*head);
// not valid
if (n < 1 || n > len)
{
printf ("Enter valid position\n");
return;
}
// delete the first node
if (n == 1)
{
deleteFront (head);
return;
}
if (n == len)
{
deleteEnd (head);
return;
}
struct Node *tempNode = *head;
// traverse to the nth node
while (--n)
{
tempNode = tempNode->next;
}
struct Node *previousNode = tempNode->prev; // (n-1)th node
struct Node *nextNode = tempNode->next; // (n+1)th node
// assigning (n-1)th node's next pointer to (n+1)th node
previousNode->next = tempNode->next;
// assigning (n+1)th node's previous pointer to (n-1)th node
nextNode->prev = tempNode->prev;
// deleting nth node
printf ("%d deleted \n\n", tempNode->data);
free (tempNode);
}
// required for deleteNthNode
int
getLength (struct Node *node)
{
int len = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
//function to print the doubly linked list
void display (struct Node *node)
{
struct Node *end = NULL;
while (node != NULL)
{
printf (" %d ", node->data);
end = node;
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n\n");
}
int
main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
insert (&head, 7);
insert (&head, 8);
insert (&head, 9);
insert (&head, 10);
insert (&head, 11);
insert (&head, 12);
printf ("Linked List Before Deletion");
display (head);
// delete 3rd node
deleteNthNode (&head, 3);
printf ("Linked List After Deletion");
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List Before Deletion 12 11 10 9 8 7 10 deleted Linked List After Deletion 12 11 9 8 7



Login/Signup to comment