ArrayList in Java
What is an ArrayList?
Arraylists is a part of collection framework in java and is a kind of a resizable array which can be found in the java.util Package.
It implements the List interface of the collections framework.
Here, in the page we will discuss more about the ArrayList that are used in java.
ArrayLists in Java:
In Java, You can store the elements in a dynamic array using the Java ArrayList class of collection Framework. It is Similar to an array, but arraylist has no size restrictions. we can add or remove elements of an arraylist anytime. As a result, it is significantly more adaptable than a conventional array but it may be slower than standard arrays.
Syntax:
ArrayList<> Prep = new ArrayList<>(); // Initialiazation of an ArrayList.
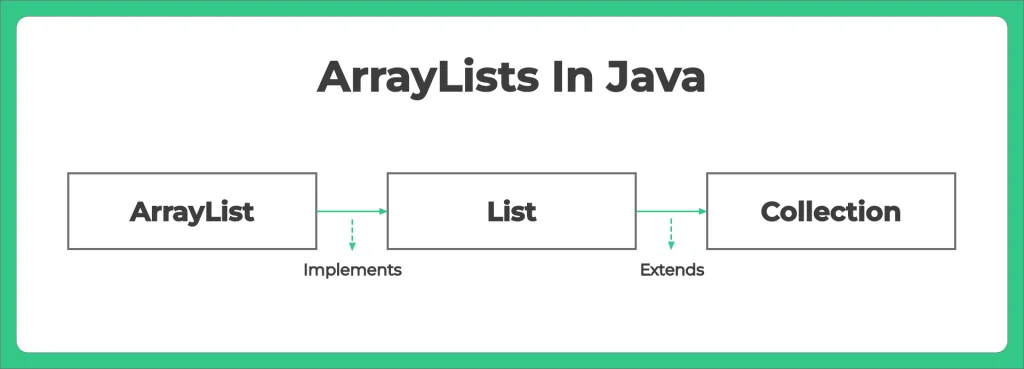
Basic Inbuilt Operations Of ArrayList:
There are several Operations of ArrayList that are available in java collection framework. Some of the important Operations are listed below:
Add Function:
The add() function is used to add an element to the arraylist in java.
Example:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to the Arraylist
arr.add(1);
arr.add(2);
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
Output: [1, 2]
Delete Function:
The Delete() function in java is used to delete an element of an arraylist in java. We can delete an element with the help of its index.
Example:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to the arraylist
arr.add(1);
arr.add(2);
arr.add(3);
System.out.println("Before Deleting :" + arr);
// removing an element using the remove function
arr.remove(1);
System.out.println("After Deleting :" + arr);
}
}
Output: Before Deleting :[1, 2, 3] After Deleting :[1, 3]
Set Function:
The set() function in java is used to change an element of an arraylist in java. We can change an element by the index of that arraylist.
Example:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to the arraylist
arr.add(1);
arr.add(2);
arr.add(3);
System.out.println("Before Changing :" + arr);
// changing a specific element of arraylist
arr.set(1, 5);
System.out.println("After Changing :" + arr);
}
}
Output: Before Changing :[1, 2, 3] After Changing :[1, 5, 3]
Size Function:
The size() function in java is used to check the size or the length of the arraylist.
Example:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to the arraylist
arr.add(1);
arr.add(2);
arr.add(3);
// Printing the size of the arraylist using size function
System.out.println("Size of the ArrayList is : " + arr.size()); // size() function
of arraylist
}
}
Output: Size of the ArrayList is : 3
Sort Function:
The sort() function in java is used to sort the elements of the arraylist.
Example:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList<>();
// Adding elements to the arraylist
arr.add(2);
arr.add(4);
arr.add(1);
System.out.println("Before Sorting : " + arr);
// sorting the array of arraylist
Collections.sort(arr);
System.out.println("After Sorting : " + arr);
}
}
Output: Before Sorting : [2, 4, 1] After Sorting : [1, 2, 4]
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment