Real Time Operating System
Real Time Operating System
Real Time Operating System (RTOS) plays a crucial role in managing computer resources and ensuring timely and predictable responses in critical applications. Operating systems (OS), in general, provide the necessary interface for users to interact with their devices while efficiently handling hardware and software resources.
In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of RTOS, its key features, real-world applications, and the challenges associated with its implementation.

Understanding the Basics of Operating Systems
An operating system acts as an intermediary between the hardware and software of a computer system, managing tasks, memory, storage, and input/output operations.
It provides a layer of abstraction that enables applications to run efficiently on various hardware platforms.Unlike general-purpose operating systems, such as Windows or Linux, which prioritize fairness and resource sharing, RTOS prioritizes responsiveness and deterministic behavior.
Types of Real Time Systems
- Hard Real-Time Systems: In hard real time systems, missing a deadline can have catastrophic consequences. These systems are used in critical applications such as aerospace, medical devices, and industrial control systems, where timing accuracy is of utmost importance.
- Soft Real-Time Systems: Soft real-time systems have more relaxed timing requirements. While missing a deadline in a soft real-time system may not result in catastrophic failure, it can lead to degraded performance or reduced system efficiency. Multimedia streaming, video games, and interactive applications often fall into this category.
Firm Real-Time Operating System: The firm real-time operating system operates within time constraints, for example, Visual inspection in industrial automation, video conferencing, etc. The time limits in these systems are not stringent, but if these deadlines are missed, it is highly likely that some undesired results may occur.
Importance of a Real Time Operating System
- Deterministic Timing: Ensures tasks are executed within precise time constraints, essential for real time applications.
- Multitasking Support: Efficiently manages multiple tasks running simultaneously without interference.
- High Reliability: Provides stability and fault tolerance, crucial for critical systems like medical devices or automotive controls.
- Efficient Resource Management: Optimizes CPU, memory, and I/O usage for predictable system behavior.
- Priority Based Scheduling: Allows high priority tasks to preempt lower priority ones, ensuring critical operations are handled promptly.
Applications of RTOS in Embedded Systems
RTOS facilitates real-time control and coordination in various embedded system applications, including:
- Robotics and automation systems
- Medical monitoring and diagnostic devices
- Aerospace and avionics systems
- Automotive systems and driver assistance
- Industrial control systems
- Home automation and smart devices
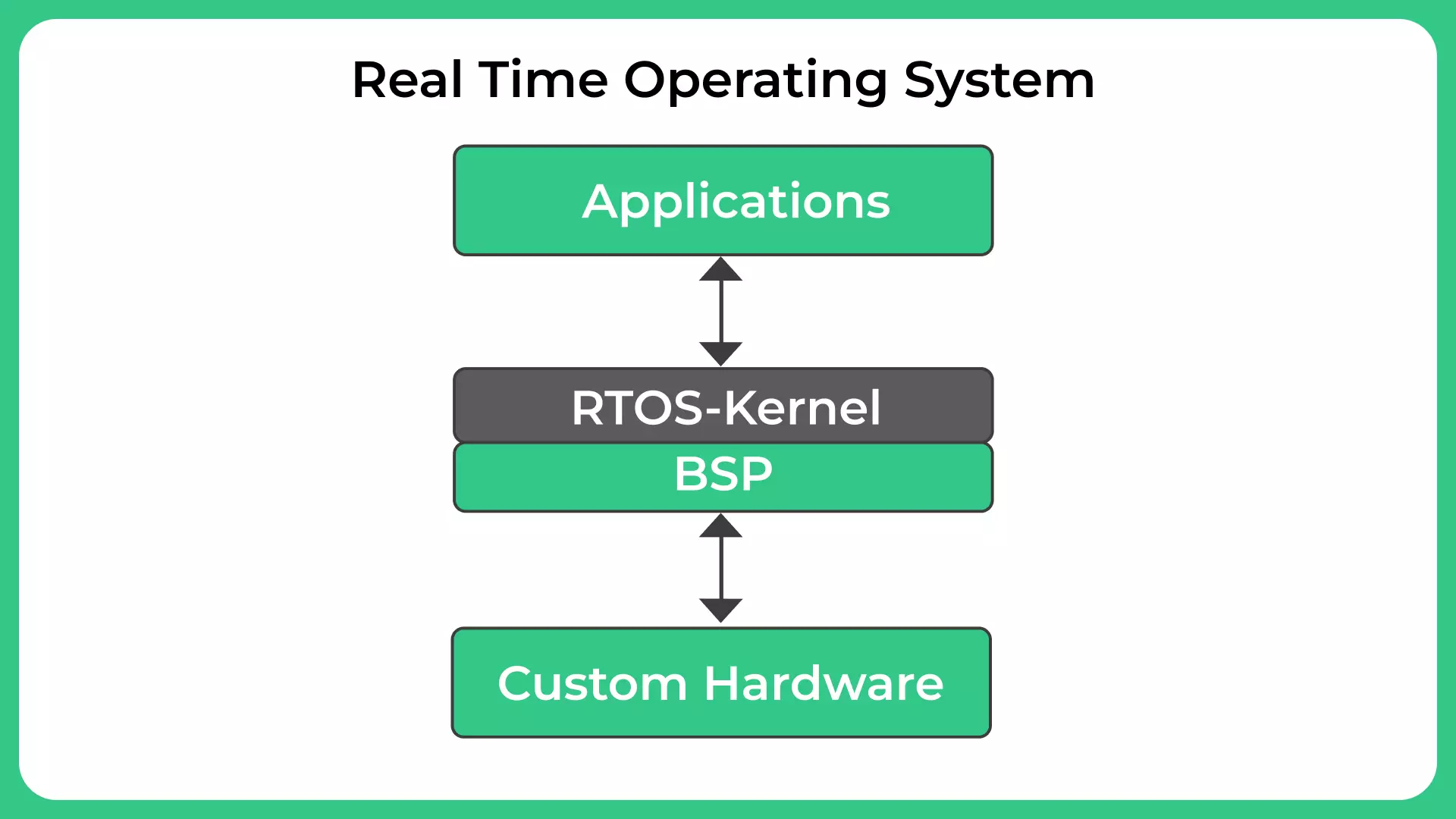
Using an RTOS in embedded systems offers several advantages, including:
- Deterministic and predictable behavior
- Efficient resource utilization
- Real-time response to external events
- Task isolation and protection
- Simplified development and debugging
- Scalability for varying system complexities
What is the difference between RTOS and OS?
| Feature | RTOS (Real-Time Operating System) | OS (General-Purpose Operating System) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Designed for real-time applications that require precise timing and reliability | Designed for general computing tasks like browsing, media, office work |
| Response Time | Predictable and deterministic response time | Variable response time; not suitable for time-critical tasks |
| Task Scheduling | Priority-based, often preemptive to meet deadlines | Uses complex scheduling algorithms focusing on fairness and throughput |
| Examples | FreeRTOS, VxWorks, RTEMS | Windows, Linux, macOS |
| Resource Usage | Lightweight, optimized for minimal resource usage | Typically resource-intensive |
| Use Cases | Embedded systems, robotics, automotive control systems | Desktops, laptops, mobile phones |
RTOS in IoT Applications
RTOS enables real-time monitoring, control, and coordination of IoT devices. It ensures timely data processing, event handling, and communication, making it essential for various IoT applications such as:
- Smart home automation
- Industrial IoT (IIoT)
- Wearable devices
- Environmental monitoring
- Healthcare and telemedicine devices
Conclusion
Real Time Operating Systems (RTOS) provide a specialized platform for time-critical applications, ensuring determinism, fast response times, and efficient resource management.They find extensive usage in embedded systems, IoT devices, and various industries such as aerospace, healthcare, and automotive.
While working with RTOS comes with challenges, their benefits make them invaluable in scenarios where timing accuracy and reliability are paramount.
FAQs
While technically possible, RTOS is not optimized for standard desktops or mobiles due to their complex hardware and user oriented design.
RTOS can be used in beginner projects, especially with platforms like FreeRTOS, but requires basic understanding of multitasking and timing.
RTOS optimizes task execution and enables low power modes, helping reduce energy consumption in embedded and battery operated devices.
C and C++ are the most commonly used languages for RTOS development due to their performance and low-level hardware access.



Login/Signup to comment