Circular Queue using Linked List in C Programming
Implementation of Circular Queue using Linked List
Using Circular Queue is better than normal queue because there is no memory wastage. Linked list provide the facility of dynamic memory allocation so it is easy to create. When we implement circular Queue using linked list it is similar to circular linked list except there is two pointer front and rear in circular Queue where as circular linked list has only one pointer head. Lets see how to implement Circular Queue using Linked list in C Programming.

Implementing Circular Queue using Linked List in C
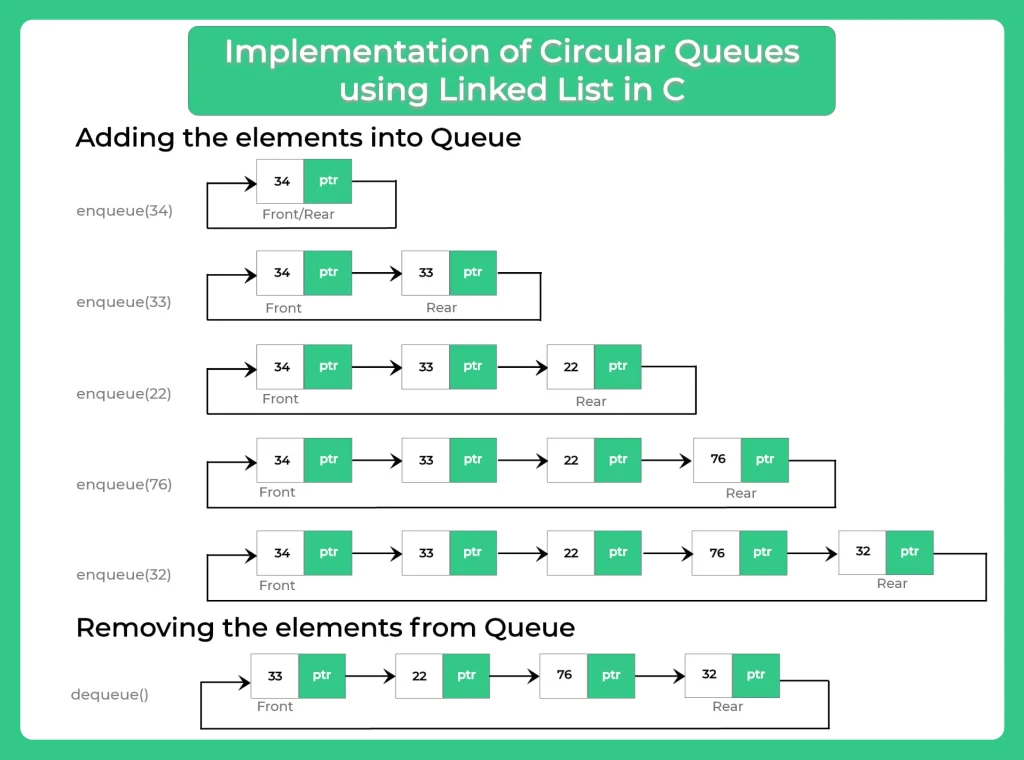
enqueue(data)
- Create a struct node type node.
- Insert the given data in the new node data section and NULL in address section.
- If Queue is empty then initialize front and rear from new node.
- Queue is not empty then initialize rear next and rear from new node.
- New node next initialize from front
dequeue()
- Check if queue is empty or not.
- If queue is empty then dequeue is not possible.
- Else Initialize temp from front.
- If front is equal to the rear then initialize front and rear from null.
- Print data of temp and free temp memory.
- If there is more than one node in Queue then make front next to front then initialize rear next from front.
- Print temp and free temp.
print()
- Check if there is some data in the queue or not.
- If the queue is empty print “No data in the queue.”
- Else define a node pointer and initialize it with front.
- Print data of node pointer until the next of node pointer becomes NULL.
C Program to Implement Circular Queue using Linked list
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *f = NULL;
struct node *r = NULL;
void enqueue (int d) //Insert elements in Queue
{
struct node *n;
n = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
n->data = d;
n->next = NULL;
if ((r == NULL) && (f == NULL))
{
f = r = n;
r->next = f;
}
else
{
r->next = n;
r = n;
n->next = f;
}
}
void dequeue () // Delete an element from Queue
{
struct node *t;
t = f;
if ((f == NULL) && (r == NULL))
printf ("\nQueue is Empty");
else if (f == r)
{
f = r = NULL;
free (t);
}
else
{
f = f->next;
r->next = f;
free (t);
}
}
void display ()
{ // Print the elements of Queue
struct node *t;
t = f;
if ((f == NULL) && (r == NULL))
printf ("\nQueue is Empty");
else
{
do
{
printf (" %d", t->data);
t = t->next;
}
while (t != f);
}
}
int main ()
{
enqueue (34);
enqueue (22);
enqueue (75);
enqueue (99);
enqueue (27);
printf ("Circular Queue: ");
display ();
printf ("\n");
dequeue ();
printf ("Circular Queue After dequeue: ");
display ();
return 0;
}
Circular Queue: 34 22 75 99 27 Circular Queue After dequeue: 22 75 99 27



Login/Signup to comment