Java Variables and Literals
What is Java Variables and Literals?
Java Variables and Literals are where variables are used to store data values, while literals are used to represent fixed values in code.
Java literal is a fixed value that appears directly in the code, and its value cannot be changed during program execution.
To understand the more about Java Variables and Literals, Read the Complete Article.
Rules for Naming Variables in Java
- Here are some rules for naming variables in Java:
Variable names must begin with a letter, an underscore (_), or a dollar sign ($).
After the first character, variable names may contain letters, digits, underscores, or dollar signs.
Variable names are case sensitive, meaning that myVariable and myvariable are two different variables.
Java reserves a set of keywords that cannot be used as variable names, such as if, else, while, and class.
Variable names should be descriptive and meaningful. A good variable name should indicate the purpose of the variable in the program.
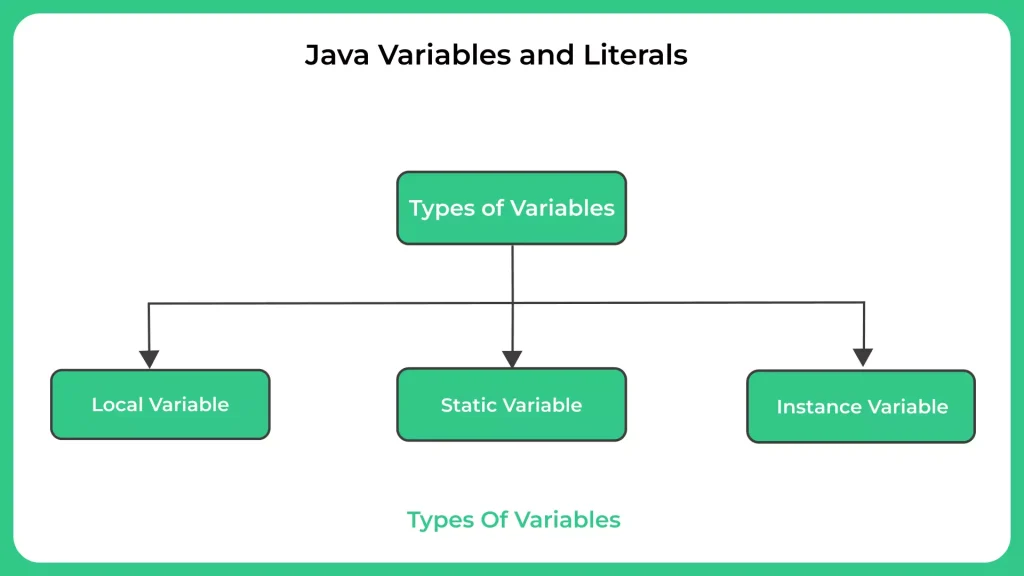
Types of variables in Java programming
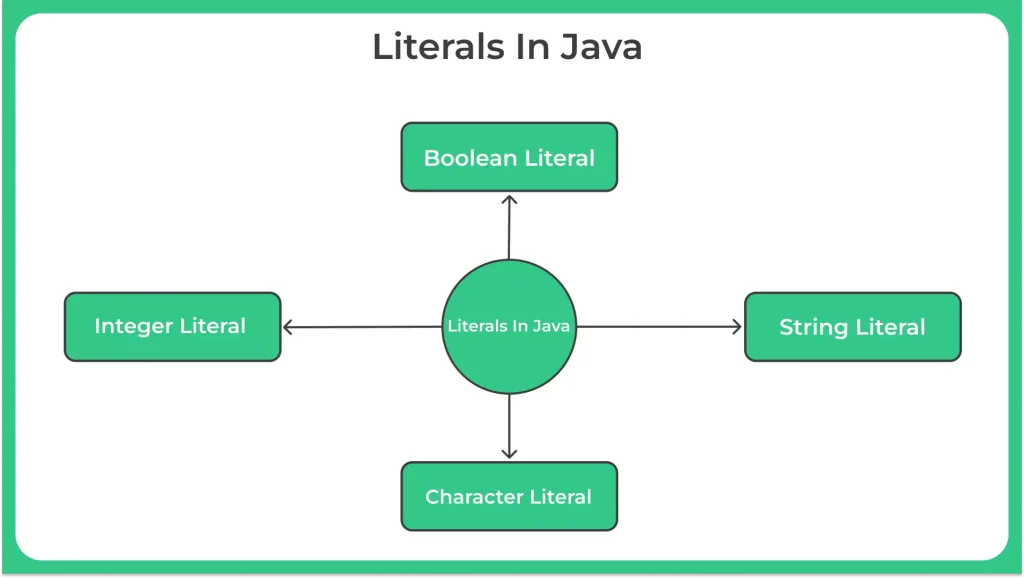
Java Literals
A Java literal is a fixed value that is directly used in the source code of a program. Literals can be of different types, such as integers, floating-point numbers, characters, strings, booleans, or null. They are constant values that cannot be changed during program execution.
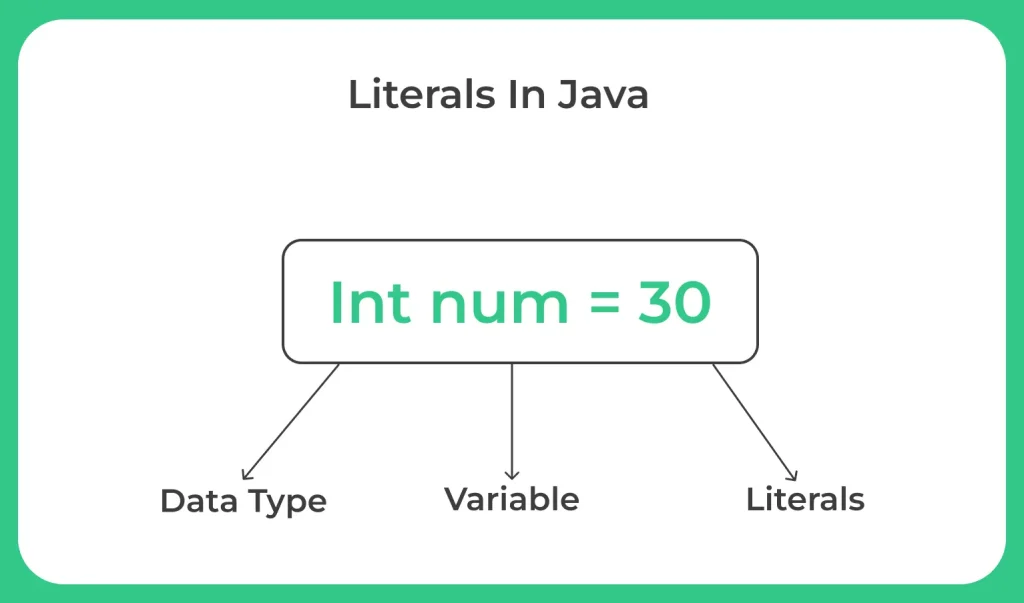
Examples Of Literals In Java
int num = 10; // integer literal double price = 5.99; // floating-point literal char letter = 'A'; // character literal String name = "John"; // string literal boolean isTrue = true; // boolean literal Object obj = null; // null literal
Example 2: Various types of Java literals including integer, floating-point, character, string, and boolean literals.
//JavaLiteralsExample
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Integer literals
int decimalLiteral = 100;
int binaryLiteral = 0b1100100;
int octalLiteral = 0144;
int hexadecimalLiteral = 0x64;
System.out.println("Decimal literal: " + decimalLiteral);
System.out.println("Binary literal: " + binaryLiteral);
System.out.println("Octal literal: " + octalLiteral);
System.out.println("Hexadecimal literal: " + hexadecimalLiteral);
// Floating-point literals
float floatLiteral = 3.14159f;
double doubleLiteral = 3.141592653589793;
System.out.println("Float literal: " + floatLiteral);
System.out.println("Double literal: " + doubleLiteral);
// Character and string literals
char charLiteral = 'a';
String stringLiteral = "Hello, World!";
System.out.println("Character literal: " + charLiteral);
System.out.println("String literal: " + stringLiteral);
// Boolean literals
boolean trueLiteral = true;
boolean falseLiteral = false;
System.out.println("True literal: " + trueLiteral);
System.out.println("False literal: " + falseLiteral);
}
}
Output
Decimal literal: 100 Binary literal: 100 Octal literal: 100 Hexadecimal literal: 100 Float literal: 3.14159 Double literal: 3.141592653589793 Character literal: a String literal: Hello, World! True literal: true False literal: false
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment