Java Type Casting
What is Java Type Casting?
- Java Type Casting is a mechanism provided by the Java programming language to convert a value of one data type to another.
- It’s important to note that casting from a larger data type to a smaller data type can result in data loss if the value of the larger data type exceeds the range of the smaller data type.
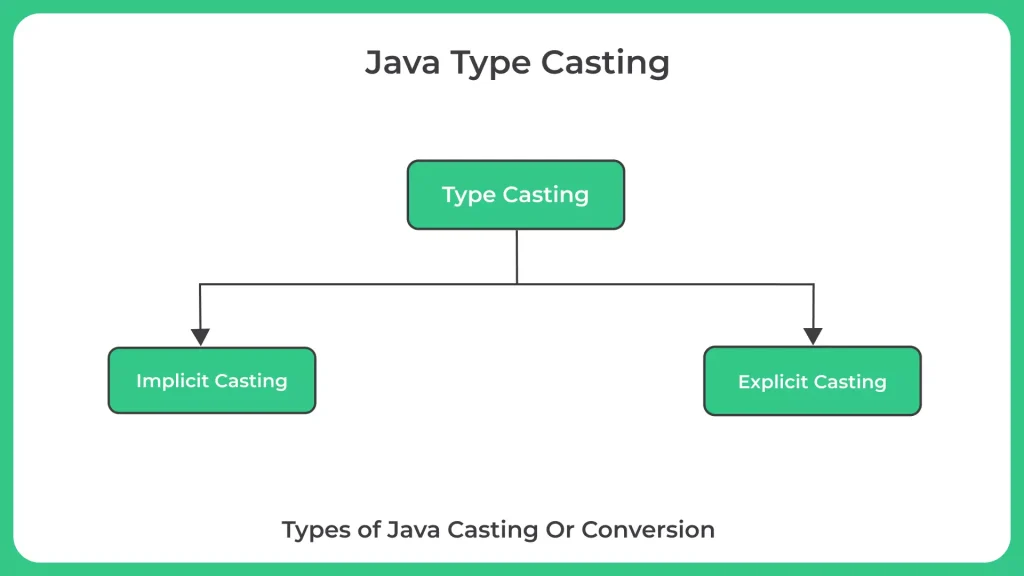
- There are two types of casting in Java: Implicit Casting and Explicit Casting.
- Implicit Casting
- Explicit Casting
- To understand the Java Type Casting, Read the Complete Article.
Type Casting:
Type casting is a process of converting a variable from one data type to another. This process is also known as data type conversion or simply casting.
- The two types of typecasting are:
- Implicit Type Casting: Automatic type conversion is another name for this casting style. When the compiler automatically transforms one data type into another without the need for explicit code, it happens. Only when the size of the data type being converted is equal to or less than that of the target data type is this possible. Changing an integer value to a long value, for instance.
- Explicit Type Casting: Manual type conversion is another name for this casting style. When a programmer manually transforms one data type to another using special syntax, like a cast operator, it is known as data type conversion. When the data type being converted has a bigger size than the data type it is being converted to, this kind of casting is required. Changing a double value to an integer, for instance.
It’s important to note that type casting can result in data loss if the value being cast is outside of the acceptable range of the target data type. Therefore, it’s essential to make sure that the value being cast is within the acceptable range of the target data type to avoid data loss.
Let’s look at the Java Wrapper Class to perform certain operations.
Example 1: Java Program For Implicit Casting
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int numInt = 10;
double numDouble = numInt; // Implicit type casting from int to double
System.out.println("The value of numInt is: " + numInt);
System.out.println("The value of numDouble is: " + numDouble);
}
}
Output
The value of numInt is: 10 The value of numDouble is: 10.0
Explanation:
In this program, we have an integer variable called numInt with a value of 10. We then declare a double variable called numDouble and assign numInt to it. Since numDouble is of type double, and numInt is of type int, an implicit type casting occurs from int to double. The value of numDouble will be equal to 10.0. We then print out the values of numInt and numDouble to verify the result of the type casting.
Example 2: Java Program to Explicit Casting
Run
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double numDouble = 10.5;
int numInt = (int) numDouble; // Explicit type casting from double to int
System.out.println("The value of numDouble is: " + numDouble);
System.out.println("The value of numInt is: " + numInt);
}
}
Output
The value of numDouble is: 10.5 The value of numInt is: 10
Explanation:
In this program, we have a double variable called numDouble with a value of 10.5. We then declare an integer variable called numInt and assign numDouble to it after performing an explicit type casting. Since numInt is of type int, and numDouble is of type double, an explicit type casting occurs from double to int by using the (int) cast operator. The value of numInt will be equal to 10, as the decimal part of numDouble is lost during the type casting. We then print out the values of numDouble and numInt to verify the result of the type casting.
Example 3 :Type conversion from int to String
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 123;
// Converting int to String using Integer.toString()
String str1 = Integer.toString(num);
System.out.println("The string value using Integer.toString() is: " + str1);
// Converting int to String using String.valueOf()
String str2 = String.valueOf(num);
System.out.println("The string value using String.valueOf() is: " + str2);
}
}
Output
The string value using Integer.toString() is: 123 The string value using String.valueOf() is: 123
Explanation:
In this program, we first declare an int variable called num with a value of 123. We then convert num to a String using the Integer.toString() method and assign it to a String variable called str1. We also convert num to a String using the String.valueOf() method and assign it to a String variable called str2. Finally, we print out the two string values that were generated.
Example 4 :Type conversion from String to int
Run
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "123";
// Converting String to int using Integer.parseInt()
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("The integer value is: " + num);
}
}
Output
The string value using Integer.toString() is: 123 The string value using String.valueOf() is: 123
Explanation:
In this program, we first declare a String variable called str with a value of "123". We then convert str to an int using the Integer.parseInt() method and assign it to an int variable called num. Finally, we print out the resulting integer value.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment