SQL AND, OR, and NOT Operators

Introduction
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a programming language that enables users to manage data stored in relational databases. SQL uses various operators to perform various operations, including data retrieval and manipulation.
The AND, OR, and NOT operators are some of the most commonly used operators in SQL. In this article, we will explore what these operators are, how they work, and how to use them to get the most out of SQL.
What are SQL Operators?
In SQL, operators are used to perform various operations on data. Operators are used to perform mathematical, logical, and comparison operations. The AND, OR, and NOT operators are used for logical operations.
What is the AND Operator?
The AND operator is a logical operator used to combine two or more conditions in a WHERE clause to retrieve records that meet all of the conditions. The AND operator returns records where all conditions are true.
Examples of AND Operator
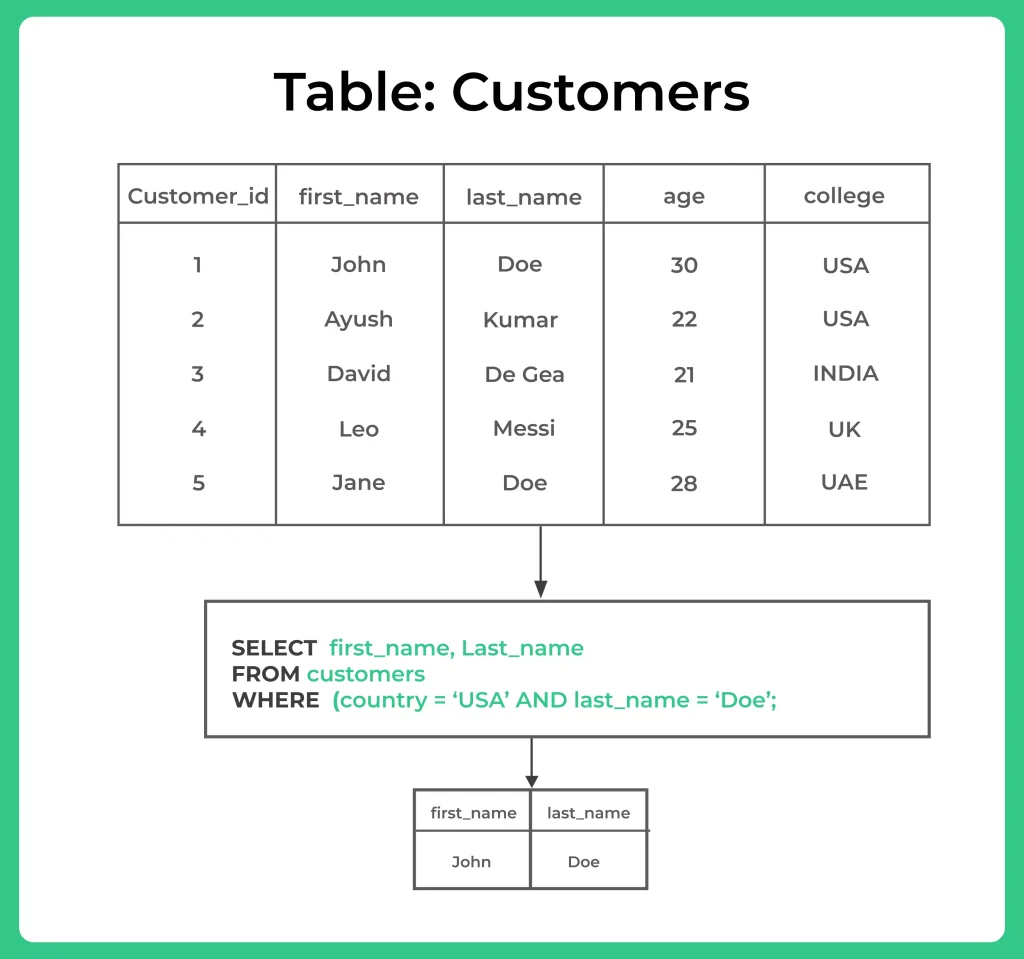
AND: The AND operator returns true if both conditions are true.
- For example, if we want to find all customers who are from the USA and last name is Doe, we can use the following query:
SELECT first_name, last_name FROM customers WHERE country = 'USA' AND last_name = 'Doe';
What is the OR Operator?
The OR operator is a logical operator used to combine two or more conditions in a WHERE clause to retrieve records that meet at least one of the conditions. The OR operator returns records where at least one condition is true.
Examples of OR Operator
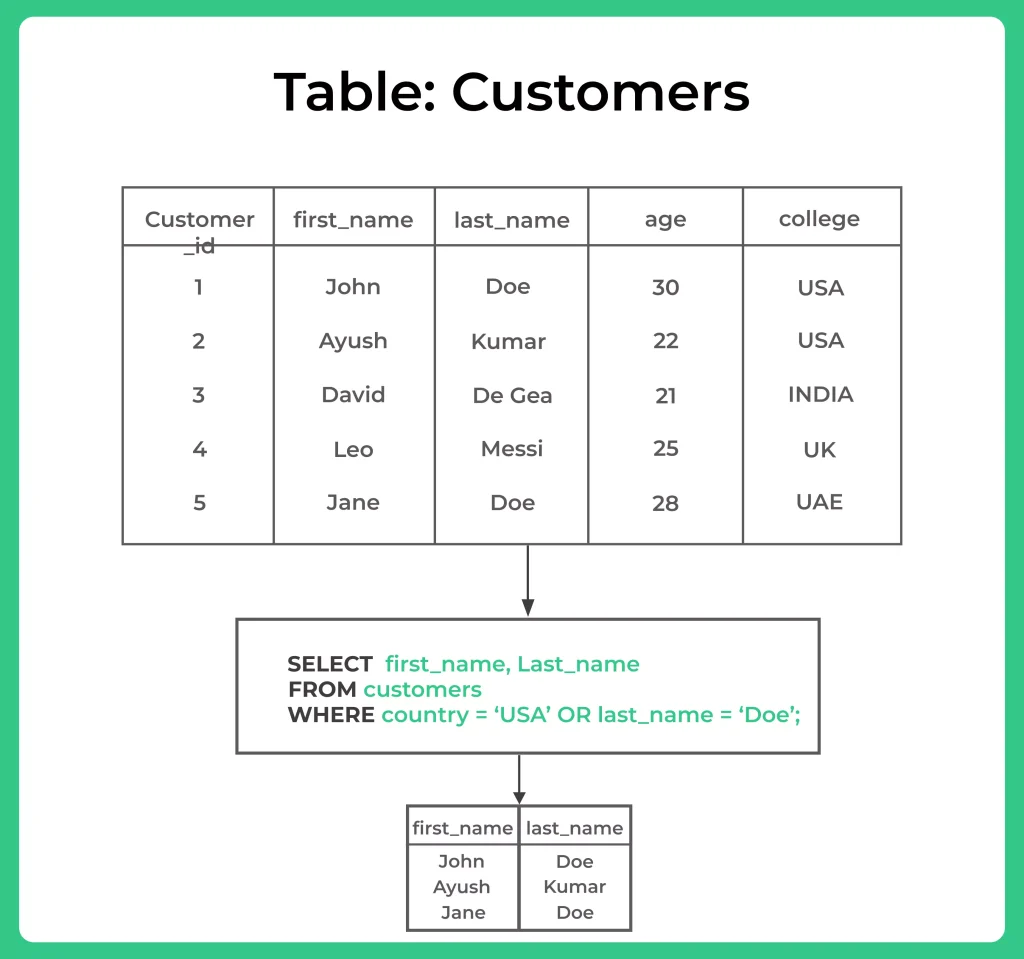
The OR operator returns true if either condition is true. For example, if we want to find all customers who are from the USA or last name Doe, we can use the following query:
sql
SELECT first_name, last_name FROM Customers WHERE country = 'USA' OR last_name = 'Doe';
What is the NOT Operator?
The NOT operator is a logical operator used to negate a condition in a WHERE clause. The NOT operator returns records where the condition is false.
Examples of NOT Operator
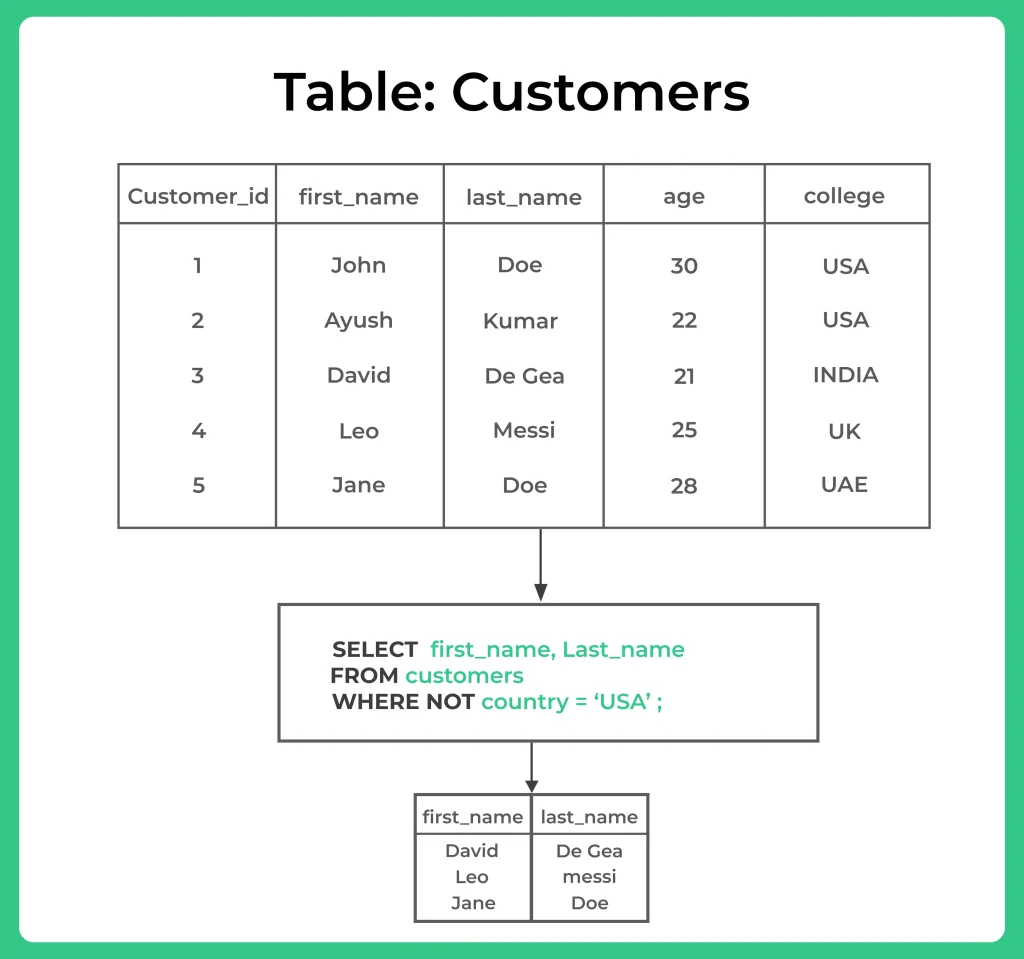
NOT: The NOT operator returns true if the condition is not true. For example, if we want to find all customers who are not from the USA, we can use the following query:
SELECT first_name, last_name FROM Customers WHERE NOT country = 'USA';
Combining Operators: OR and NOT
We can combine the AND, OR, and NOT operators to create more complex conditions in a WHERE clause. When combining operators, it’s important to use parentheses to ensure that the conditions are evaluated in the correct order.
Examples of OR and NOT Operator
NOT: The NOT operator returns true if the condition is not true. For example, if we want to find all customers who are not from the USA, we can use the following query:
SELECT first_name, last_name
FROM Customers
WHERE NOT country = ('USA'OR 'UK')AND AGE<26; 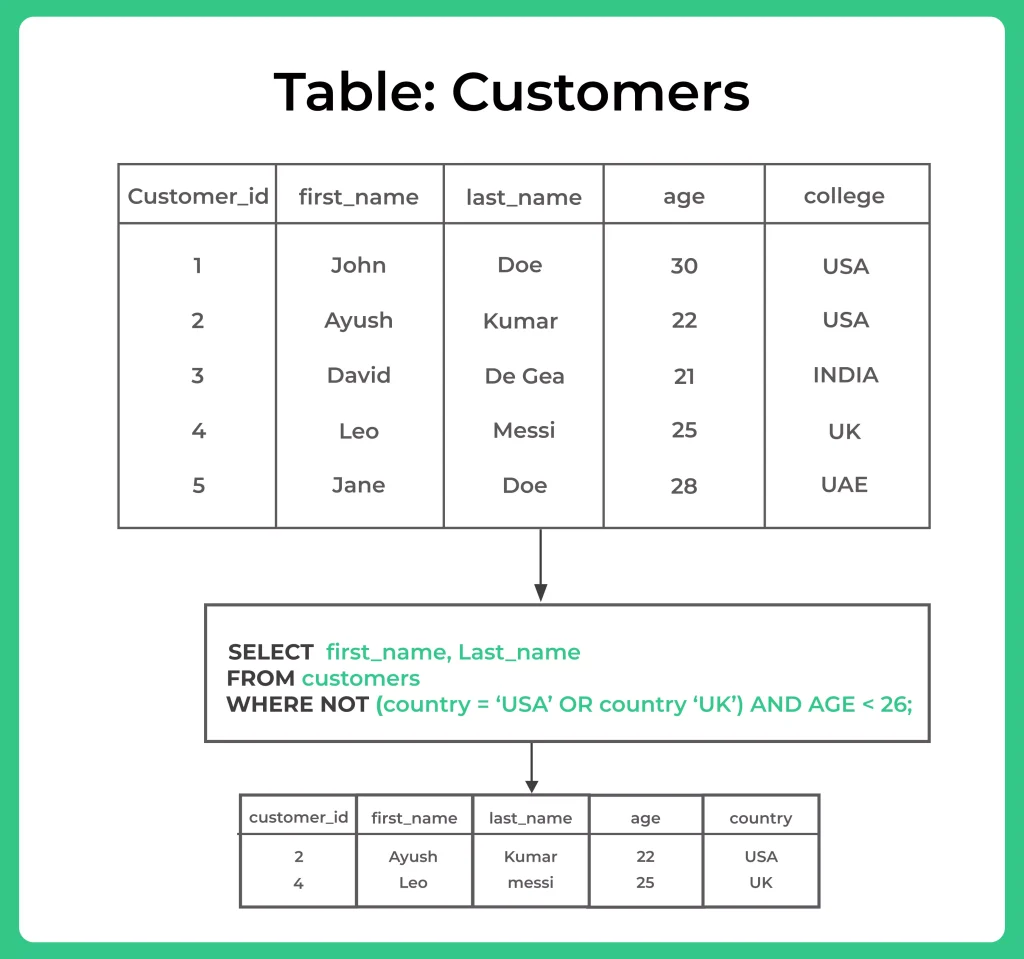
Examples of OR and NOT Operator
NOT: The NOT operator returns true if the condition is not true. For example, if we want to find all customers who are not from the USA, we can use the following query:
SELECT first_name, last_name FROM Customers WHERE NOT country ='USA' AND NOT 'last_name'= 'Doe';
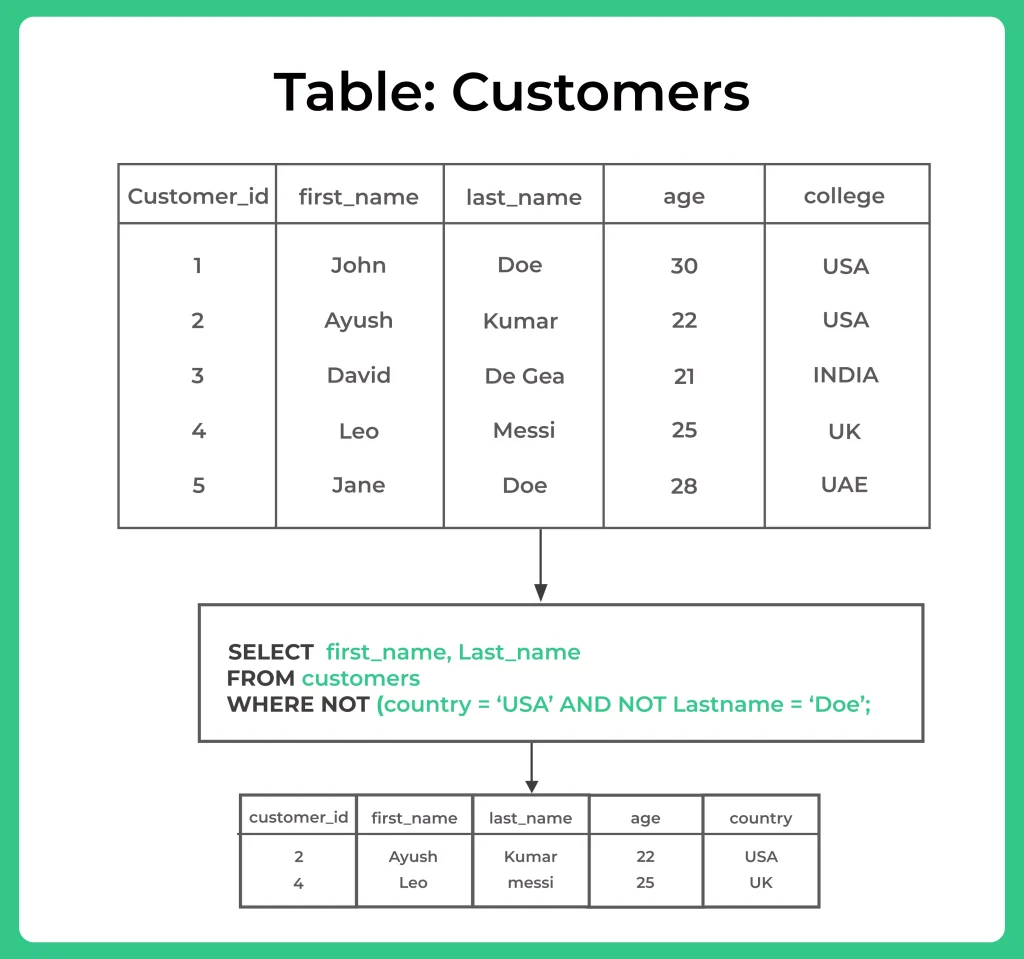
Conclusion AND,OR and NOT Operators:
In conclusion, understanding how to use the SQL AND, OR, and NOT operators is crucial for anyone working with databases. These operators allow for flexible and precise querying of data, which is essential for data analysis and decision-making.
By mastering the use of these operators, one can create more efficient and effective SQL queries, leading to improved database performance and more accurate data analysis.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others





Login/Signup to comment