SQL IS NULL and IS NOT NULL

Introduction
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a programming language that enables users to manage data stored in relational databases. SQL uses various operators to perform various operations, including data retrieval and manipulation.
let’s first understand the concept of NULL in SQL. In SQL, NULL represents the absence of a value or an unknown value. It is not the same as zero or an empty string; it signifies the absence of any data.
Working with IS NULL
The IS NULL operator allows us to check whether a column contains NULL values. It returns true if the value is NULL and false otherwise. It can be used in conjunction with the WHERE clause to filter records based on NULL values.
Implementing IS NOT NULL
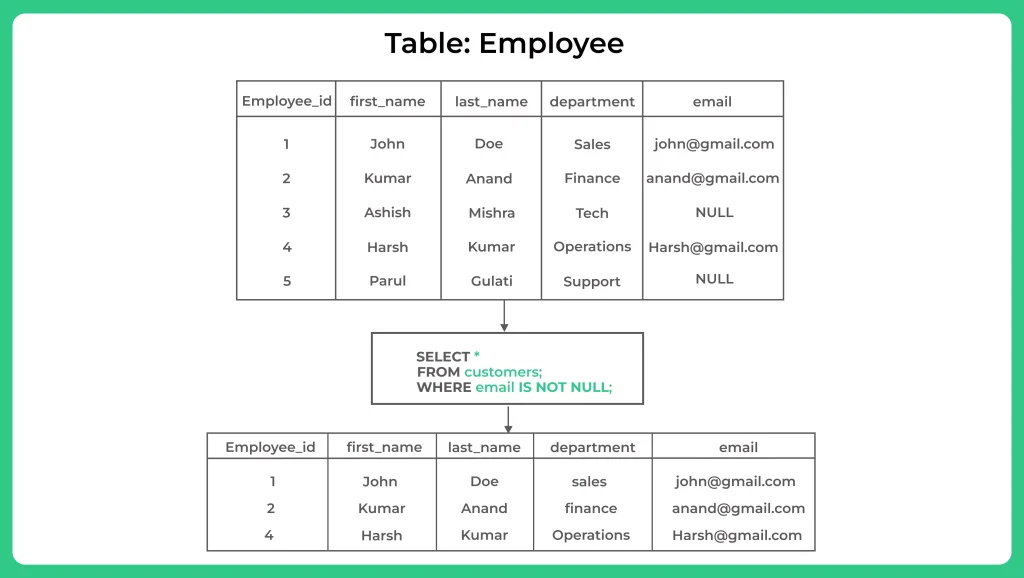
On the other hand, the IS NOT NULL operator is used to verify if a column does not contain NULL values. It returns true if the value is not NULL and false if it is NULL. Similar to IS NULL, IS NOT NULL can be combined with the WHERE clause to filter out records that are not NULL.
SELECT first_name, last_name FROM customers WHERE country = 'USA' AND last_name = 'Doe';
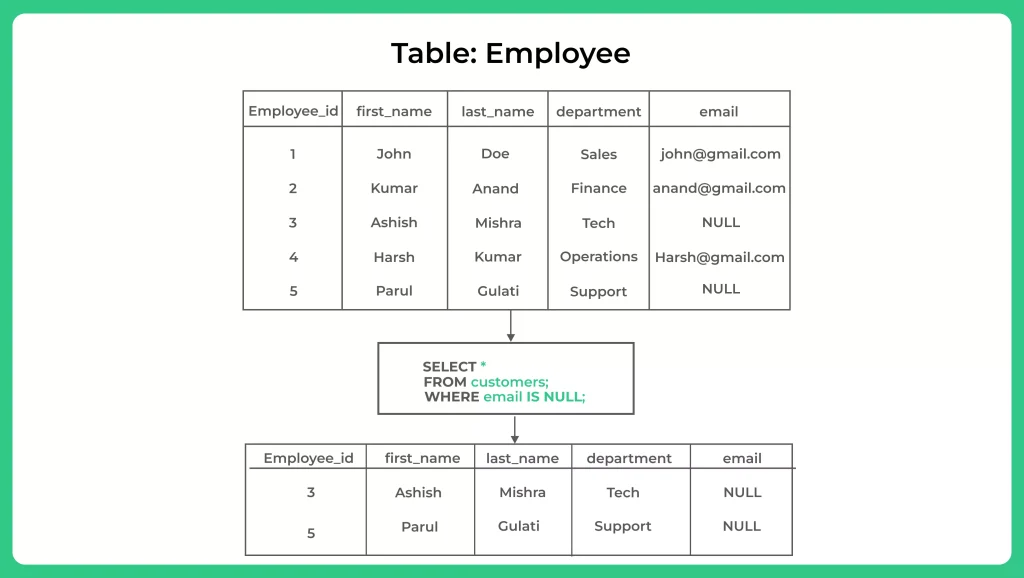
Differences between IS NULL and IS NOT NULL
While IS NULL checks for the presence of NULL values, IS NOT NULL checks for the absence of NULL values. These operators are complementary and can be used together to cover all possible scenarios involving NULL.
Common Use Cases
Understanding when to use IS NULL and IS NOT NULL is essential in various scenarios. Some common use cases include filtering records with missing values, handling optional fields, identifying incomplete data, and performing data validation.
SELECT first_name, last_name FROM Customers WHERE country = 'USA' OR last_name = 'Doe';
What is “IS NOT NULL”?
In SQL, “IS NOT NULL” is a condition used to filter data and retrieve only non-null values from a table or a specific column. It acts as a criterion in SQL queries to exclude rows that contain null values, ensuring that only meaningful and complete data is returned.
The Importance of “IS NOT NULL” Condition
The “IS NOT NULL” condition plays a vital role in data analysis and management. By excluding null values, it helps ensure data accuracy and integrity, allowing us to work with meaningful information. Furthermore, it assists in data validation, identifying incomplete records, and improving overall query efficiency.
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name WHERE column_name IS NOT NULL;
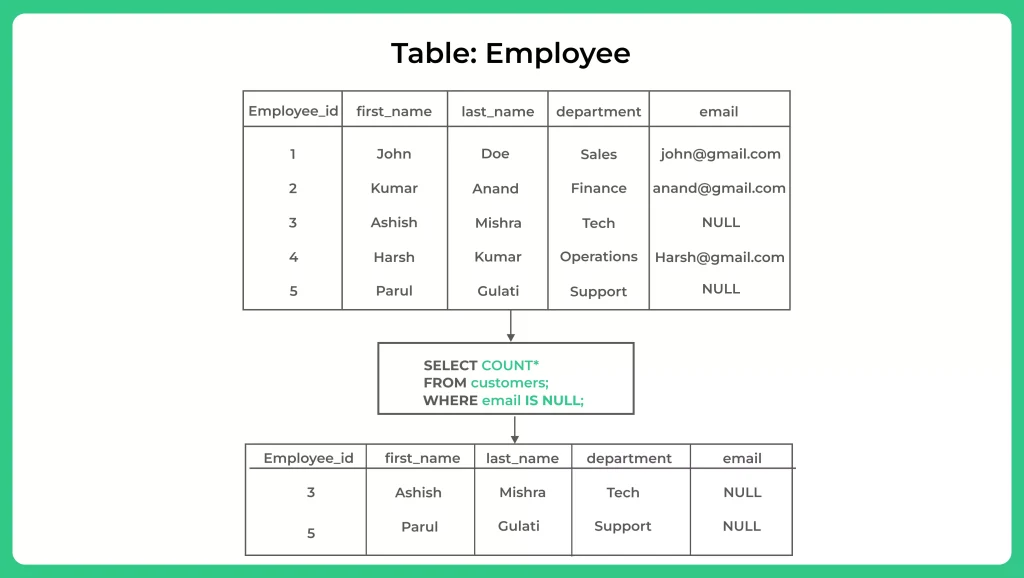
IS NULL With COUNT()
In SQL, the “IS NULL” operator is used to check if a column value is NULL. When combined with the “COUNT()” function, it can be used to count the number of NULL values in a column.
SELECT COUNT(*) AS null_count FROM table_name WHERE column_name IS NULL;
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




