Finding Repeating elements in an Array in Python
Repeating elements in an Array in Python
In this section we will discuss the program to find the repeating elements in an array in python programming language. We are given with an array and need to print the elements that occurs more than one times in the given input array.
Example
Input : arr[8] = [10, 20, 40, 30, 50, 20, 10, 20]Output : 10 20
Explanation : 40, 30 and 50 are occur 1 time in the given array, 10 occurs 2 times and 20 occurs 3 times.
Method Covered :
- Method 1 : Using Two loops
- Method 2 : Using hash Map
Method 1 :
In this method we will count the frequency of each elements using two for loops and print those elements which have frequency not equal to one.
- To check the status of visited elements create a array of size n.
- Run a loop from index 0 to n and check if (visited[i]==1) then skip that element.
- Otherwise create a variable count = 1 to keep the count of frequency.
- Run a loop from index i+1 to n
- Check if(arr[i]==arr[j]), then increment the count by 1 and set visited[j]=1.
- After complete iteration of inner for loop and check if count != 1 then print that element.
Time and Space Complexity
- Time Complexity : O(n2)
- Space Complexity : O(n)
Method 1 : Code in Python
Run
# Python 3 program to count unique elements
def count(arr, n):
# Mark all array elements as not visited
visited = [False for i in range(n)]
# Traverse through array elements
# and count frequencies
for i in range(n):
# Skip this element if already
# processed
if (visited[i] == True):
continue
# Count frequency
count = 1
for j in range(i + 1, n, 1):
if (arr[i] == arr[j]):
visited[j] = True
count += 1
if count != 1 :
print(arr[i]);
# Driver Code
arr = [10, 30, 40, 20, 10, 20, 50, 10]
n = len(arr)
count(arr, n)
Output
10 20
Method 2 :
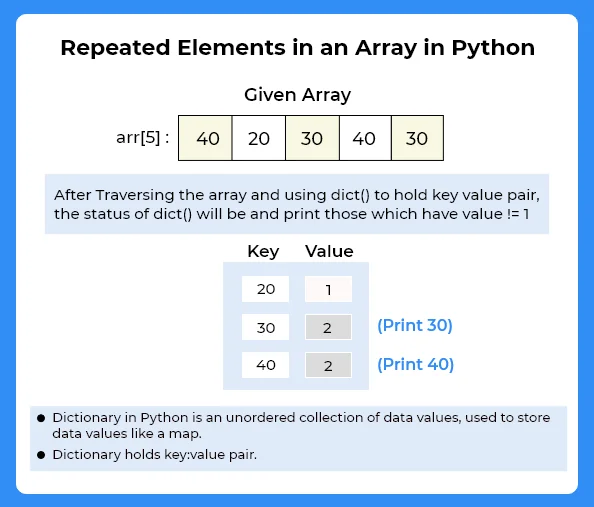
In this method we will count use dictionary to count the frequency of each elements and then check if that frequency is equal to 1 or not.
- Declare a dictionary dict().
- Start iterating over the entire array
- If element is present in map, then increase the value of frequency by 1.
- Otherwise, insert that element in map.
- After complete iteration over array, start traversing map and check if value is not equal to 1,then print the key value.
Time and Space Complexity
- Time Complexity : O(n)
- Space Complexity : O(n)
Method 2 : Code in Python
Run
def count(arr, n):
mp = dict()
# Traverse through array elements
# and count frequencies
for i in range(n):
if arr[i] in mp.keys():
mp[arr[i]] += 1
else:
mp[arr[i]] = 1
# Traverse through map and print
# frequencies
for x in mp:
if mp[x]!=1 :
print(x)
# Driver Code
arr = [10, 30, 40, 20, 10, 20, 50, 10]
n = len(arr)
count(arr, n)
Output
10 20
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Login/Signup to comment




arr = [10, 20, 40, 30, 50, 20, 10, 20]
dictionary={}
for i in arr:
dictionary[i]=dictionary.get(i,0)+1
for j in dictionary:
if dictionary[j]!=1:
print(j)
from collections import Counter
a=[10, 20, 40, 30, 50, 20, 10, 20]
result = [j for j,k in Counter(a).most_common() if k>1]
for j in result:
print(j)
lis1=[1,2,3,4,1,2,1,6,7,8,7,5]
lis2=[]
for i in range(len(lis1)):
for j in range(i+1,len(lis1)):
if lis1[i] == lis1[j]:
if lis1[i] not in lis2:
lis2.append(lis1[i])
print(lis2
arr = input().split(“,”)
a=set(arr)
b=””
for i in a:
if arr.count(i)>1:
b+=str(i)+” ”
for i in sorted(b.split(” “)):
print(i)