Find Second Smallest Element in an Array using Python

Second Smallest Element in an array using Python
Here, in this page we will discuss the program to find the second smallest element in an array using python programming language. We will discuss various method to find the second smallest element of the given array.
Various methods to discussed in this page are :
- Method 1 : Using two loops
- Method 2 : Using one loop
- Method 3 : Using sort() function.
Method 1 :
- Take a variable say first and set it to integer maximum value.
- Run a loop for range (0, len(arr))
- Check if first > arr[i], set first = arr[i]
- Now, declare a variable say second and set it to integer maximum value.
- Run a loop for range (0, len(arr))
- Check if ( arr[i] != first and arr[i]<second), set second = arr[i]
- Print(second)
Method 1 : Python code
Run
import math
arr = [10, 13, 17, 11, 34, 21]
first = math.inf
second = math.inf
for i in range(0, len(arr)):
if arr[i] < first:
first = arr[i]
for i in range(0, len(arr)):
if arr[i] != first and arr[i] < second:
second = arr[i]
print(second)
Output :
11
Method 2 :
- Take two variable say first and second, set them to integer maximum value.
- Run a loop for range (0, len(arr))
- Check if first > arr[i], set second = first and first = arr[i]
- Else Check if ( arr[i] != first and arr[i]<second), set second = arr[i]
- Print(second)
Method 2 : Python code
Run
import math
arr = [10, 13, 17, 11, 34, 21]
first = second = math.inf
for i in range(0, len(arr)):
if arr[i] < first:
second = first
first = arr[i]
elif (arr[i] < second and arr[i] != first):
second = arr[i];
print(second)Output :
11
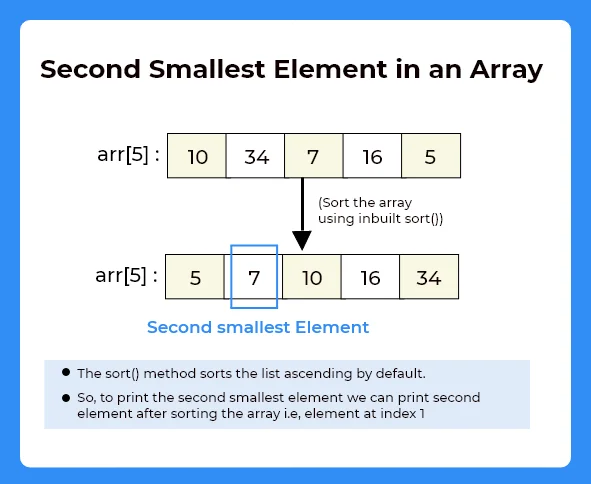
Method 3 :
- Sort the array using inbuilt sort() function.
- sort(), sort the array in ascending order.
- So, to print the second smallest element of the array print arr[1].
Method 3 : Python code
Run
import math arr = [10, 13, 17, 11, 34, 21] arr.sort(); print(arr[1])
Output :
11
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription




a=[11,13,14,11,3,4,32,5]
a.sort(reverse=True)
print(a[-2])
def second_smallest(array):
newlist=[]
for i in range(len(array)):
for j in range(len(array)-1):
if array[j]>array[j+1]:
array[j],array[j+1]=array[j+1],array[j]
for i in array:
if i not in newlist:
newlist.append(i)
return newlist[1]
ans=second_smallest([11,22,44,55,11])
print(ans)
arr = [10, 89, 9, 56, 4, 80, 8]
mini = arr[0]
arr.sort()
print(arr)
#maxi = arr[0]
for i in range(len(arr)):
if arr[i] < mini:
mini = arr[i]
arr.remove(mini)
arr.sort()
print(arr[0])
Join Here for your technical queries
size=int(input(“ENTER ARRAY SIZE”))
arr=[]
for i in range(size):
element=int(input())
arr.append(element)
arr.sort()
print(“THE 2 SMALLEST ARRY IS :– “,arr[1])
n = int(input())
arr = []
for i in range(n):
ele = int(input())
arr.append(ele)
print(arr)
arr.sort()
print(arr)
print(“the second smallest element is : “,arr[1])
x=int(input())
r=[]
for i in range(x):
y=int(input(“enter a number”))
r.append(y)
m=min(r)
r.remove(m)
print(min(r))
def sec_largest(arr):
for i in range(len(arr)):
for j in range(i+1,len(arr)):
if (arr[i]>arr[j]):
temp = arr[i]
arr[i] = arr[j]
arr[j] = temp
for i in range(1,len(arr)):
if arr[i]!= arr[0]:
return arr[i]
return -1
arr = [13, 6, 7, 10, 2, 13, 4, 10]
print(sec_largest(arr))
For C users..
#include
int main()
{
int n, arr[100];
printf(“Enter the length of the array.\n”);
scanf(“%d”, &n);
printf(“Enter array elements.\n”);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
}
int smallest = arr[0];
int Ssmallest = arr[1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < smallest)
{
smallest = arr[i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] smallest)
{
Ssmallest = arr[i];
}
}
printf(“Second %d”, Ssmallest);
return 0;
}
from array import *
a=array(“i”,[])
b=int(input(“enter size :”))
for x in range(b):
c=int(input())
a.append(c)
a1=sorted(a)
print(min(a))
print(a1[1])
a=list(map(int, input().split()))
k=int(input())
for i in range(k):
key=i
for j in range(i+1,len(a)):
if a[j]<a[key]:
key=j
else:
pass
a[i],a[key]=a[key],a[i]
print(a[k-1])
mylist=[11, 15, 2, 4, 91, 10, 20, 16, 14]
mylist.sort()
print (mylist)
print[“smallest number is:”,mylist[1])
Good but you have to store in an array as per these are in an array important questions
For people who are searching the code in C,
#include
void swap(int* xp, int* yp)
{
int temp = *xp;
*xp = *yp;
*yp = temp;
}
int main(void) {
// your code goes here
int arr[50]; int n= sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]); int min_idx;
printf(“size:\n”);
scanf(“%d”,&n);
printf(“arr: \n”);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
min_idx = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
// Swap the found minimum element
// with the first element
swap(&arr[min_idx], &arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("second smallest no: %d",arr[1]);
return 0;
}
Code given in the answer will give wrong output if entered element gets repeated
My code will do the job , nice and simple with o(n) complexity as same as the last two above me
n=int(input())
a=[]
for i in range(n):
a.append(int(input()))
print(“Array”,a)
s=set(a)
ln=list(a)
ln.sort()
print(“Second largerst :”,end=””)
print(ln[1])