Python Program to find Power of a number

Find the Power of a Number in Python Language
Given two integer input numbers, the objective is to find the power of the number raise to the power variable. Therefore, we’ll write a code to Find the Power of a Number in Python Language.
Example
Input : 2 3
Output : 8 Find the Power of a Number in Python Language
Given two integer inputs the objective is to Find the Power of a Number in Python Language. We usually multiply the number with itself for power number of times to get the power of a the number using loops and recursion. In Python language there are two other methods we can use to find the power of a Number. Here are some of the method we can use to Find the power of a Number in Python,
- Method 1: Using Pow() Function
- Method 2: Using Simple Iteration
- Method 3: Using Python Operator
- Method 4: Using Recursion
We’ll discuss the above mentioned methods in the sections below.
Method 1: Using pow() Function
Working
In this method we’ll use the inbuilt function pow() to find the power of a Number. The function takes the number and the power as the argument and returns the number raised to the power.
For the given two integers as inputs, we perform the following operations
- Call the pow() function and print the output.
Let’s implement the above mentioned logic in Python Language.
Python Code
num, power = 3, 2 print(pow(num,power))
Output
9
Method 2: Using Simple Iteration
Working
In this method we’ll use the loops to iterate through the number of multiplications required to raise the input number to the given power. Here we’ll use the for loop and run it until the power is reaches, meanwhile we multiple the number with itself with each iteration.
For a given integer variables as inputs, we perform the following operations,
- Run a for loop from 0 to power.
- Keep multiplying the number with itself with each iteration.
- Print the final output.
Let’s implement the above mentioned logic in Python Language.
Python Code
num, power = 3, 2 output = 1 for i in range(power): output*=num print(output)
Output
9
Method 3: Using Python Operator
Working
In this method we’ll use the python operator ** to calculate the power of a Number.
Given two integer variables as inputs, We perform the following operations,
- Print number**power.
Let’s implement the above logic in Python Language.
Python Code
num, power = 3, 2 print(num**power)
Output
9
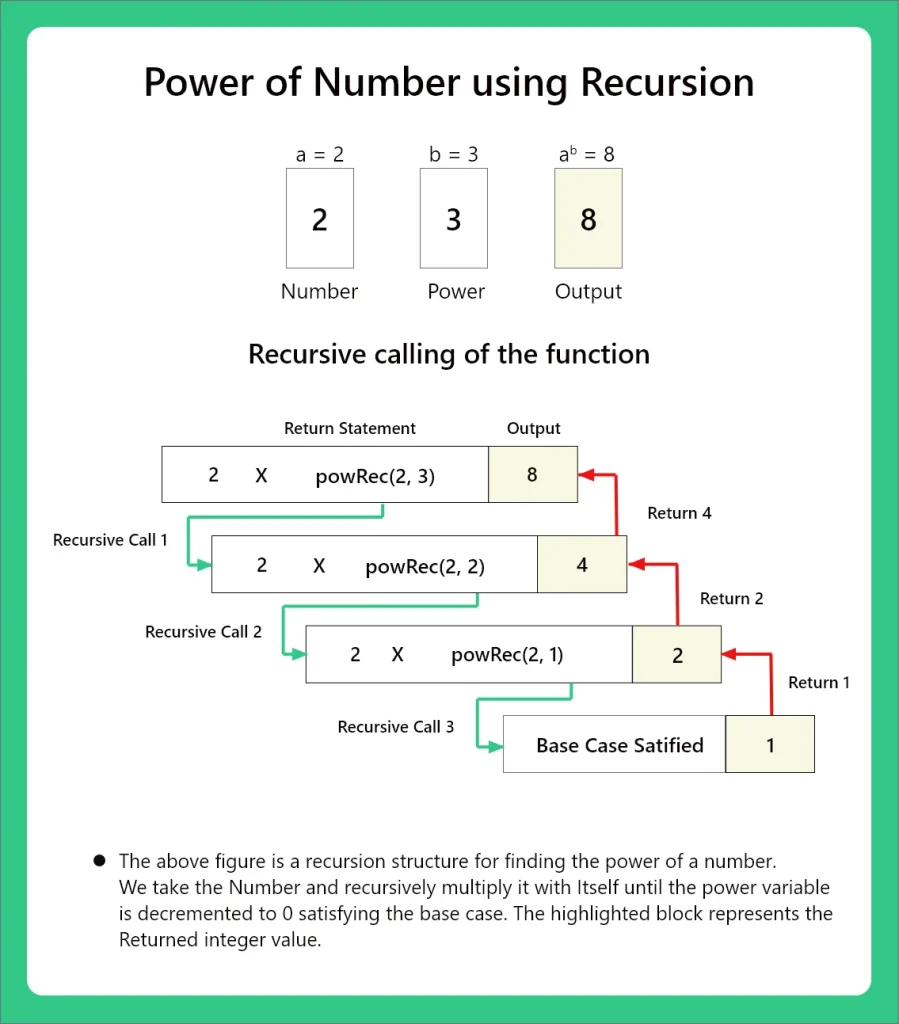
Method 4: Using Recursion
Working
In this method we’ll use recursion to calculate the power of a Number. To know more about recursion, check out our page Recursion in Python.
For the given two inputs, we’ll perform the following operations,
- Define a recursion function with base case as power == 0.
- Set recursive step call as num * powerrecur(num, power -1).
- Print the returned value.
Let’s implement the above logic in Python Language.
Python Code
num, power = 3, 2
def powerrecur(num,power):
if power == 0:
return 1
return num * powerrecur(num,power-1)
print(powerrecur(num,power))Output
9






n=int(input())
print(“power of number{}”.format(n**2))
Easy for Beginners
n=int(input())
m=int(input())
power=1
for i in range(m) :
power=power*n
print(power)
import math
k=int(input())
l=int(input())
p=math.pow(k,l)
print(int(p))
import math
k=int(input())
j=int(input())
l=math.pow(k,j)
print(l)
import math
base = int(input(“Enter Base number:”))
expo = int(input(“Enter Expo Number:”))
print(math.pow(base,expo))
base = int(input(“Enter Base number:”))
expo = int(input(“Enter Expo Number:”))
temp = 1
for i in range(0, expo):
temp = temp * base
print(temp)
the current solution
base = int(input(“Enter Base number:”))
expo = int(input(“Enter Expo Number:”))
temp = 1
for i in range(0, expo):
temp = base ** expo
print(temp)
base = int(input(“Enter Base number:”))
expo = int(input(“Enter Expo Number:”))
base = base ** expo
print(base)
Do u have code for Bucket,mug problem in TCS NQT2021 ????
I’m posting it here in python please check
#CODE ANSWER……
n=int(input());m=int(input())
if m>=n:
print(“INVALID INPUT”)
s=int((n-1)//m);count=0
r=int((n*0.80))
for i in range(int(r+1),n):
if i%m==0:
count+=1
print(s+count)
temp = base ** expo
print(temp)
If you want to do shortcuts in one line,then using math library
import math
x=int(input(“Enter the base value”))
n=int(input(“Enter the exponential value”))
power=math.pow(x,n)
print(power)
Input -3,4
Output- 81
x=int(input(“Enter the base value”))
n=int(input(“Enter the exponential value”))
def power(x,n):
ans=1
for i in range(0,n):
ans=ans*x
return ans
print(power(x,n))
Input- 2,4
Output- 16