Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes (Data reverse only)
Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes in Java
(Data reverse only)
Reversing a linked list is a classic data structure problem, in this guide you will learn how to Reverse a Linked List Without Changing Links Between Nodes in Java (Data Reverse Only).
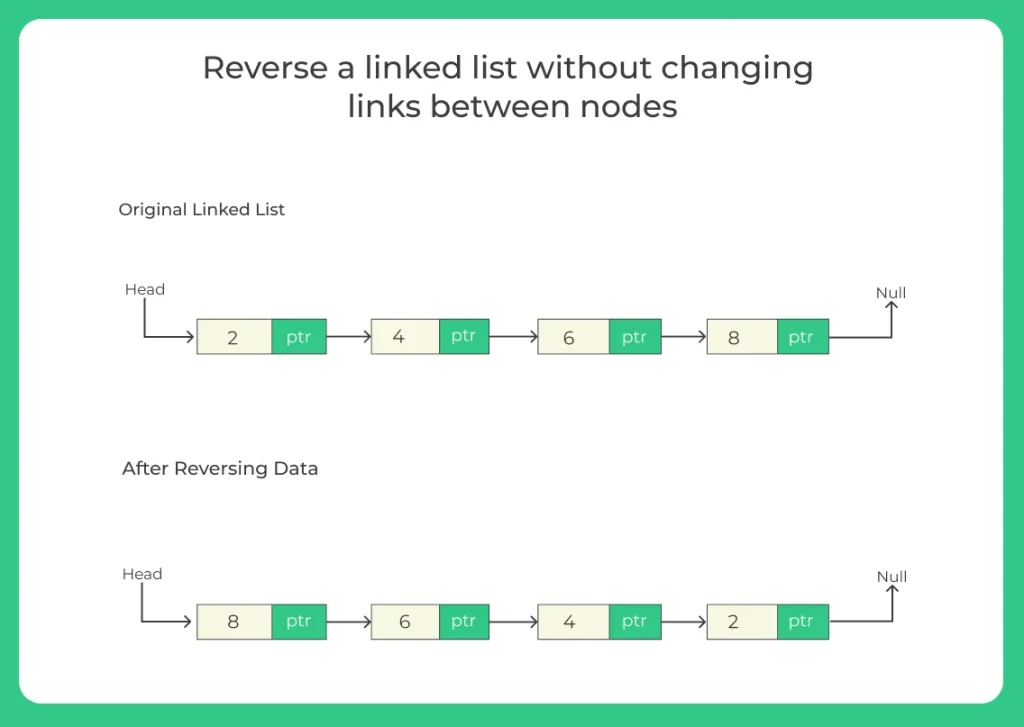
This version of reversal does not modify the node pointers. Instead, it reverses only the data inside the nodes, making it very useful when pointer manipulation is restricted or not preferred.
Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes in Java
What Does Data Reverse Mean?
Normally, reversing a linked list involves changing the next pointers of nodes. But in data reverse, you keep the links exactly the same and only swap the node values.
Example:
List:
5 → 10 → 20 → 40
Data Reverse Output:
40 → 20 → 10 → 5
The nodes remain in the same physical order; only data inside them is swapped.
Data reversal is useful when:
- You are not allowed to modify node pointers
- The list is part of a structure where node links cannot be changed
- You want a simpler version of reversal
- You want to practice list traversal and data manipulation
This operation is frequently asked in coding tests to differentiate between node reverse and data reverse.
1. Traverse the linked list and store all node values in a list or array.
2. Traverse the linked list again and overwrite its data from the end of the array.
Since node pointers remain untouched, this method is simpler but requires extra space.
Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes in Java:
Approaches to Reverse a linked list without changing links
We will use 2 methods to Reverse a linked list without changing links between nodes in Java:
Each method includes: Step by step algorithm, Full Java code, Example input/output, Time and space complexity.
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Methods to Reverse a Linked List Without Changing Links
Method 1: Using ArrayList
Algorithm:
- Initialize an empty ArrayList list.
- Traverse the linked list and add each node’s data into the list.
- Reverse the ArrayList or use two pointers to fetch from the end.
- Traverse the original linked list again.
- Assign each node’s data from the reversed list in order.
- Return the head.
Java Code:
import java.util.ArrayList;
class DataReverseList {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
public static Node reverseData(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
list.add(temp.data);
temp = temp.next;
}
int index = list.size() - 1;
temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
temp.data = list.get(index);
index--;
temp = temp.next;
}
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(5);
head.next = new Node(10);
head.next.next = new Node(20);
head.next.next.next = new Node(40);
System.out.println("Before Data Reverse:");
printList(head);
head = reverseData(head);
System.out.println("After Data Reverse:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
5 10 20 40
Output:
40 20 10 5
Space Complexity: O(n)
Methods to Reverse a Linked List Without Changing Links in Java
Method 2: Using Stack (Reverse Data Using LIFO)
Algorithm:
- Create an empty stack.
- Traverse the linked list and push all node data into the stack.
- Traverse the linked list again.
- Pop data from the stack and assign it to each node.
- Continue until stack becomes empty.
- Return the head.
Java Code:
import java.util.Stack;
class DataReverseStack {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
public static Node reverseData(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
stack.push(temp.data);
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
temp.data = stack.pop();
temp = temp.next;
}
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next = new Node(5);
System.out.println("Before Data Reverse:");
printList(head);
head = reverseData(head);
System.out.println("After Data Reverse:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
1 3 5
Output:
5 3 1
Space Complexity: O(n)
Conclusion....
Reversing a linked list without modifying node connections is a valuable technique when structural integrity of the list must remain unchanged. Instead of manipulating pointers, the algorithm focuses on reorganizing the data stored in each node.
| Method | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Using ArrayList | O(n) | O(n) |
| Using Stack | O(n) | O(n) |
This approach simplifies the logic and avoids pointer related errors but requires additional memory proportional to the number of elements.
Both methods discussed, using an ArrayList or using a stack, achieve the same result in linear time.
Understanding how to Reverse a Linked List Without Changing Links Between Nodes in Java (Data Reverse Only) is essential for mastering linked list transformations under constraints and learning the difference between physical node rearrangement and logical data reordering.
FAQ's related to Reverse a linked list without changing links
Answer:
It means the nodes stay in the same order but the values inside them are reversed.
Answer:
By storing all data in a list or stack and rewriting values in reverse order.
Answer:
Both take O(n) time, but pointer reverse uses O(1) space, while data reverse uses extra space.
Answer:
Yes, but ensure object references are handled correctly.
Answer:
Because a singly linked list does not have backward links, so traversal is required to reach the last node.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Login/Signup to comment






//in c//
#include
#include
//reverse a linked list//
struct node{
int val;
struct node* link;
};
struct node* insert(struct node* head,int val)
{
struct node* node=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->val=head->val;
node->link=head->link;
head->val=val;
head->link=node;
return head;
}
void display(struct node* head)
{
struct node* nodes=head;
while( nodes != NULL)
{
printf(“%d”,nodes->val);
nodes=nodes->link;
}
}
struct node* reverse(struct node* head)
{
struct node* temp=head;
struct node *nodes;
struct node* exp;
int n=6;
int i; //reverse the data of the linked list//
for(i=1;i<=3;i++) //three times running
{
int j;
nodes=temp;
for(j=i;jlink;
}
exp->val=temp->val;
temp->val=nodes->val;
nodes->val=exp->val;
–n;
temp=temp->link;
}
return head;
}
int main()
{
struct node * head =(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
head->val=12;
head->link=NULL;
insert(head,34);
insert(head,78);
insert(head,56);
insert(head,67);
insert(head,60);
reverse(head);
display(head);
}