Octal to binary conversion using Java
Octal to Binary Conversion using Java
Here, on this page, we will discuss octal to binary conversion using java. For this purpose, we need to ask for an octal number from user and convert that octal number to its binary equivalent form and then print the converted number onto the screen.
For conversion, we first convert the octal number into decimal form and then convert the decimal number to a binary number.

Method 1:-
- Accept octal number
- Convert it into decimal Equivalent
- Convert this decimal value into Binary
Make sure you have visited these two pages before moving ahead with the code –
Method 1 Code in Java
Run
//Java program to convert octal number to binary number
class Main
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int octal = 12;
//Declaring variable to store decimal number
int decimal = 0;
//Declaring variable to use in power
int n = 0;
//writing logic for the octal to decimal conversion
while(octal > 0)
{
int temp = octal % 10;
decimal += temp * Math.pow(8, n);
octal = octal/10;
n++;
}
int binary[] = new int[20];
int i = 0;
//writing logic for the decimal to binary conversion
while(decimal > 0)
{
int r = decimal % 2;
binary[i++] = r;
decimal = decimal/2;
}
//printing result
System.out.print("Binary number : ");
for(int j = i-1 ; j >= 0 ; j--)
System.out.print(binary[j]+"");
}
} Output
Enter a octal number : 12
Binary number : 1010
Method 2
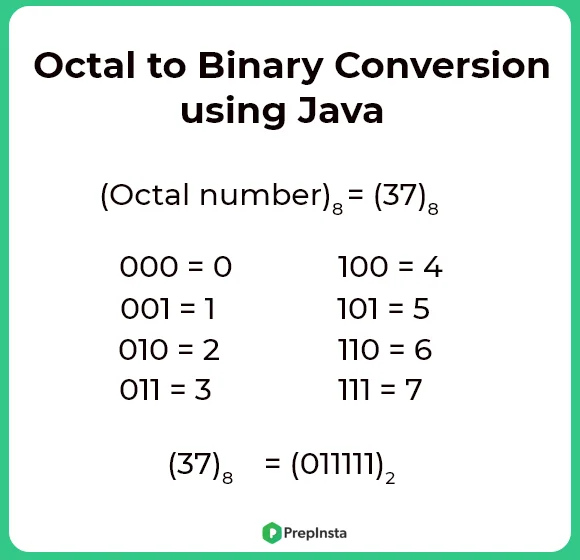
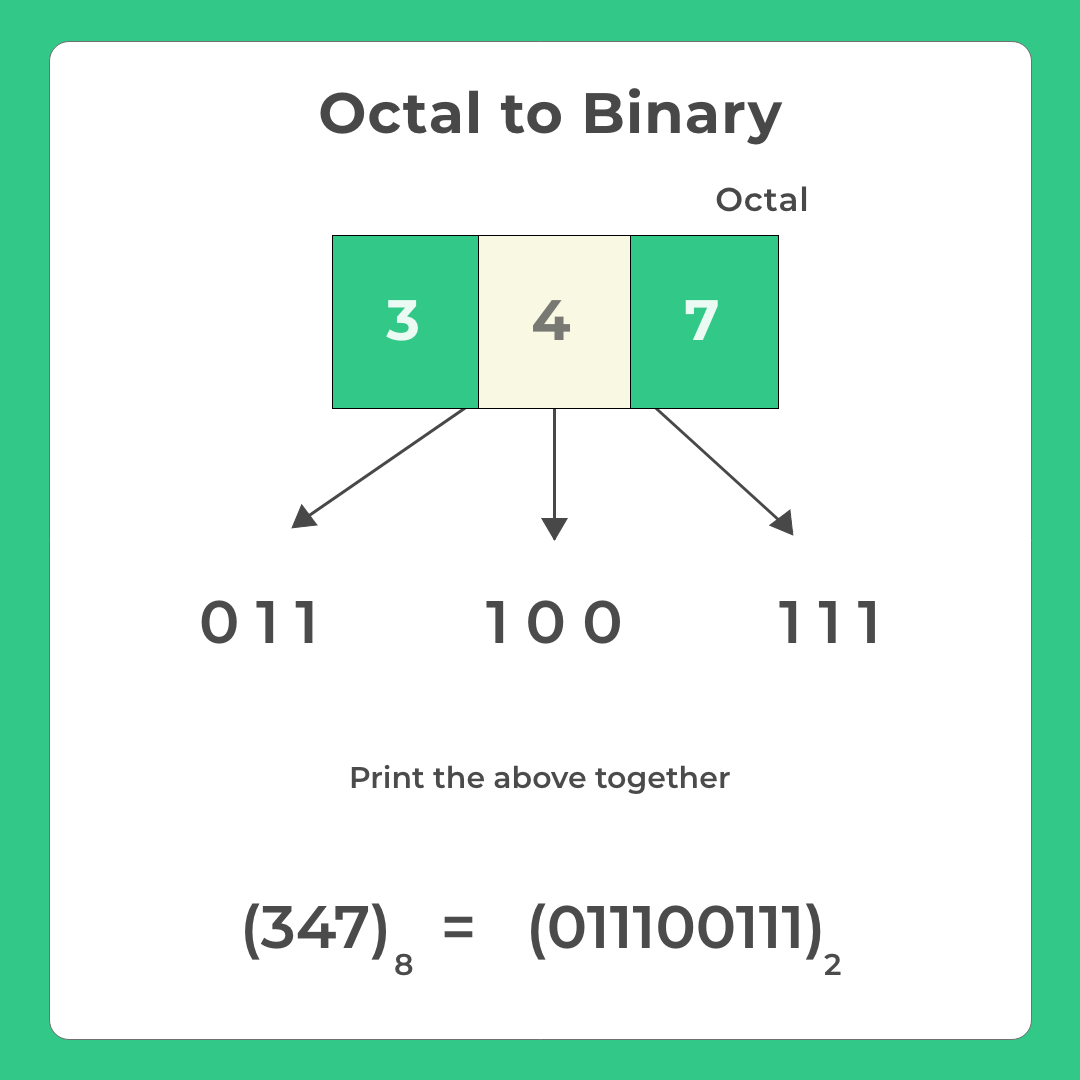
Each digit of an octal number can be converted into its binary Equivalent (see image)
Binary Representation for Octal digit:
- 0 => 000
- 1 => 001
- 2 => 010
- 3 => 011
- 4 => 100
- 5 => 101
- 6 => 110
- 7 => 111
Method 2 Code in Java:
Run
import java.util.HashMap;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
HashMap b =new HashMap();
b.put(0,"000");
b.put(1,"001");
b.put(2,"010");
b.put(3,"011");
b.put(4,"100");
b.put(5,"101");
b.put(6,"110");
b.put(7,"111");
String result =" ";
long num = 347;
long n=num;
while(n !=0)
{
int rem=0;
rem=(int)n%10;
if(n!=0)
{
result = b.get(rem)+result;
}
n=n/10;
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}Output
Enter a octal number : 347
Binary number : 011100111
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription



import java.util.*;
public class Octal_Binary
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter an octal number : “);
int num=Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine(),8);
String Binary=Integer.toBinaryString(num);
System.out.println(“Binary vesrion is : “+Binary);
}
}
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class octal_Binary {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap b =new HashMap();
b.put(0,”000″);
b.put(1,”001″);
b.put(2,”010″);
b.put(3,”011″);
b.put(4,”100″);
b.put(5,”101″);
b.put(6,”110″);
b.put(7,”111″);
Scanner s= new Scanner(System.in);
String result =” “;
long num = s.nextLong();
long n=num;
while(n !=0){
int rem=0;
rem=(int)n%10;
if(n!=0) {
result = b.get(rem)+result;
}
n=n/10;
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
correct “” (double coutes) and add System.out.println(“Enter a number “) after Scanner.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(“Enter a OCTAL number:”);
int octal=sc.nextInt();
int binary=0;
int i=1;
while(octal!=0) {
int decimal=octal%10;
while(decimal!=0) {
int temp=decimal%2;
binary=binary+temp*i;
decimal /=2;
i *=10;
}
octal /= 10;
}
System.out.println(binary);