Java program for Insertion in a Sorted Linked List
Java Program for Insertion in a Sorted Linked List
Here, you will learn how Insertion in a Sorted Linked List in Java works with clear explanations, simple algorithms, and complete Java code. This problem is commonly asked in coding interviews because it tests your understanding of ordered insertion, traversal, and pointer manipulation.
Insertion in a Sorted Linked List in Java
What Does Inserting in a Sorted Linked List Mean?
In a sorted linked list, elements are already arranged in ascending order.
So when inserting a new value, you must place it at the correct position such that the list remains sorted.
Example:
Input list:
10 → 20 → 40 → 50
Insert 30
Output:
10 → 20 → 30 → 40 → 50
You are not allowed to sort after insertion. The new node must be placed correctly during the operation.
Learning Insertion in a Sorted Linked List helps with:
- Maintaining ordered data
- Real-time insertion without resorting
- Understanding pointer-based insert operations
- Strengthening DSA foundations
- Handling edge cases like inserting at the beginning or end
This is also useful in priority queues, ordered sets, and incremental data structures.
1. Create a new node with the given value.
2. If the list is empty or new value is smaller than the head, insert at the beginning.
3. Otherwise, traverse the list until you find a node whose value is greater than the new value.
4. Insert the new node just before that node by adjusting pointers.
5. If no such node exists, append at the end.
This entire logic depends on pointer traversal and position checking.
Insertion in a Sorted Linked List:
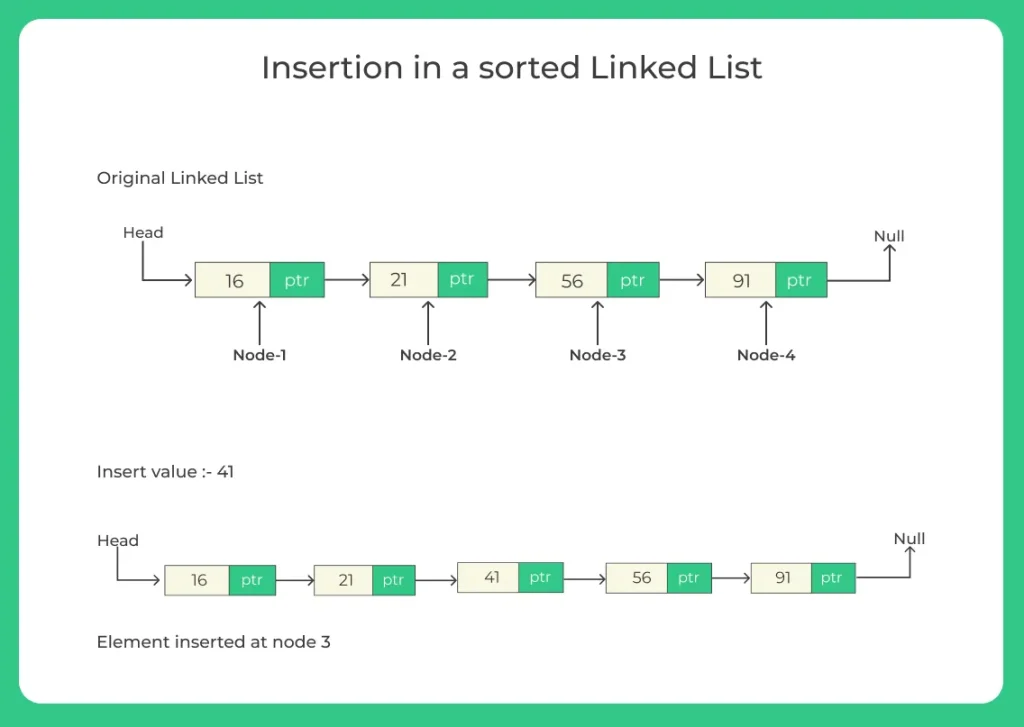
Methods for Insertion in a Sorted Linked List in Java
Here are the 2 methods for Insertion in a Sorted Linked List in Java:
Learn DSA
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Method for Insertion in a Sorted Linked List in Java
Method 1: Iterative Traversal
Algorithm:
Create a new node with the given value.
If head == null, return new node.
If new value is less than or equal to head.data, set new node as the new head.
Initialize pointer current = head.
Traverse while current.next != null and current.next.data < newValue.
Insert the node between current and current.next.
Return the head of the list.
Java Code:
class SortedInsert {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
public static Node insertSorted(Node head, int value) {
Node newNode = new Node(value);
if (head == null || value <= head.data) {
newNode.next = head;
return newNode;
}
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null && current.next.data < value) {
current = current.next;
}
newNode.next = current.next;
current.next = newNode;
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(10);
head.next = new Node(20);
head.next.next = new Node(40);
System.out.println("Before insertion:");
printList(head);
head = insertSorted(head, 30);
System.out.println("After insertion:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
10 20 40 Insert: 30
Output:
10 20 30 40
Space Complexity: O(1)
Method for Insertion in a Sorted Linked List
Method 2: Recursive Sorted Insertion
Algorithm:
If list is empty or value is smaller than head.data, return new node as new head.
Recursively call insertion on head.next.
Connect head.next to result of recursion.
Return head.
Java Code:
class SortedInsertRec {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) { this.data = data; }
}
public static Node insertSortedRecursive(Node head, int value) {
if (head == null || value <= head.data) {
Node newNode = new Node(value);
newNode.next = head;
return newNode;
}
head.next = insertSortedRecursive(head.next, value);
return head;
}
public static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(5);
head.next = new Node(15);
head.next.next = new Node(25);
System.out.println("Before insertion:");
printList(head);
head = insertSortedRecursive(head, 20);
System.out.println("After insertion:");
printList(head);
}
}
Input:
5 15 25 Insert: 20
Output:
5 15 20 25
Space Complexity: O(n)
Conclusion....
Insertion in a sorted singly linked list demonstrates how ordered data structures can be maintained using simple pointer adjustments.
| Method | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Iterative Traversal | O(n) | O(1) |
| Recursive Insertion | O(n) | O(n) |
Because the list is already sorted, the algorithm ensures the new value is inserted in the correct position while preserving the sorted order.
The iterative approach offers the most efficient solution with constant space, while the recursive method provides a cleaner but slightly more memory intensive alternative.
Understanding how Insertion in a Sorted Linked List in Java works helps build strong foundations for ordered data handling, priority structures, and efficient real time insert operations.
This concept also forms the basis for more advanced data structure problems such as merging sorted lists, implementing ordered queues, and maintaining dynamic sorted collections.
FAQ's related to Insertion in a Sorted Linked List in Java
Answer:
It means inserting a new value into the correct position in an already sorted list.
Answer:
Traverse until you find the correct position, then adjust pointers to place the new node.
Answer:
The new node becomes the new head of the list.
Answer:
Yes, but it uses extra stack space.
Answer:
The new node becomes the new head of the list.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others







Login/Signup to comment