Java program for finding the second smallest element in an array
Second Smallest Element in an array in Java
Here, in this page we will discuss the program to find the second smallest element in an array using java programming language. We are given with an array and need to print the second smallest element among them.

Various Method Discuss in this page are :
- Method 1 : Using two loops
- Method 2 : Using one loop
Method 1 :
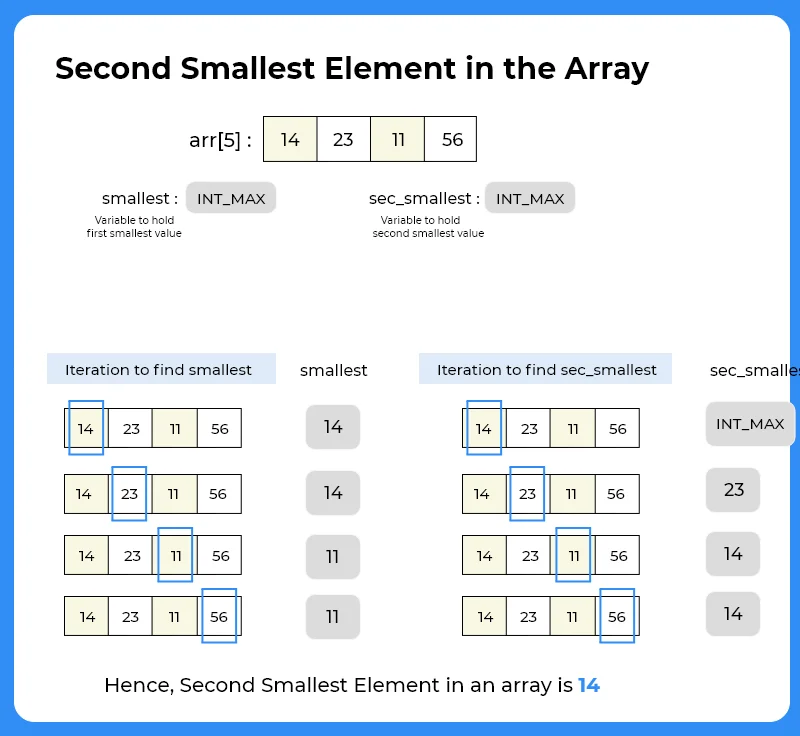
- Take a variable say smallest = Integer.MAX_VALUE
- Run a loop over the entire array and check if (arr[i]<smallest)
- Then set smallest = arr[i].
- Declare another variable say sec_smallest = Integer.MAX_VALUE
- Run a loop and check if arr[i] != smallest and arr[i] < sec_smallest
- Then print(sec_smallest) after completing the iteration.
Method 1 : Code in Java
Run
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int secSmallest(int arr[], int n)
{
// assigning first element as smallest temporarily
int smallest = arr[0];
// we find the smallest element here
for (int i=0; i < n; i++){
if(arr[i] < smallest)
smallest = arr[i];
}
// temporarily assinging largest max value
int sec_smallest = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// finding second smallest here
for (int i=0; i < n; i++){
if(arr[i] != smallest && arr[i] < sec_smallest)
sec_smallest = arr[i];
}
return sec_smallest;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = {12, 13, 1, 10, 34, 10};
int n = arr.length;
System.out.print(secSmallest(arr, n));
}
}Output :
10
Method 2 :
- Declare two variables say first = INT_MAX and second = INT_MAX to hold the first and second smallest elements respectively.
- Now, iterate over the entire array i.e, from index 0 to n-1
- Inside the loop check if (arr[i]<first) then set second = first and first = arr[i].
- Else check if(second > arr[i]) then set second = arr[i]
- After complete iteration print the value of second.
Method 2 Code in Java
Run
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int secSmallest(int arr[], int n)
{
int first = Integer.MAX_VALUE, second = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i=0; i < n; i++){
if(arr[i] < first){ second = first; first = arr[i]; } else if(second>arr[i])
second = arr[i];
}
return second;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = {12, 13, 1, 10, 34, 10};
int n = arr.length;
System.out.print(secSmallest(arr, n));
}
}
Output :
10
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Login/Signup to comment



public class SecondSmallestElement {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {12,32,14,45,36,74,34};
int temp;
for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){
for (int j=i+1; j arr[j]){
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
System.out.println("second smallest element = " + arr[1]);
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.*;
class A{
int function(int arr[]){
Arrays.sort(arr);
int n=arr.length;
int c=0;
for(int i=n-1;i>0;i–){
if(arr[i]>arr[i-1]){
c++;
}
if(c==2){
return arr[i];
}
}
return -1;
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter the elements in an arrray “);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
A obj=new A();
int a= obj.function(arr);
System.out.println(a);
}
}
//the most easiest way is this guys
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class secondlargestno {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
TreeSet v=new TreeSet();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
v.add(sc.nextInt());
}
Object f[]=v.toArray();
System.out.println(f[v.size()-2]);
}
}
import java.util.*;
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[]={3,5,2,1};
Arrays.sort(arr);
System.out.println(arr[1]);
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Second_Smallest_Element_in_an_array {
static void sec(int size,int[]a)
{
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;ja[j])
{
int temp=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=temp;
}
}
}
System.out.print(“Second smallest number is : “+a[1]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
{
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(“Size : “);
int size=in.nextInt();
System.out.println(“Numbers are “);
int[]a=new int[size];
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
a[i]=in.nextInt();
}
sec(size,a);
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SecondSmallest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n;
System.out.println(“Enter the size of array :”);
n = sc.nextInt();
int a[] = new int[n];
System.out.println(“Enter array elements : “);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Array elements are :");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println(" ");
int min = a[0];
int sm = a[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] < min) {
min = a[i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] != min && a[i] < sm) {
sm = a[i];
}
}
System.out.println("Second smallest element is " + sm);
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scn=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=scn.nextInt();
int[] arr=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
arr[i]=scn.nextInt();
}
int val=arr[0];
int min=arr[0];
int i=1;
while(iarr[i] && val>arr[i]){
val=min;
min=arr[i];
}
else if(arr[i]<val){
val=arr[i];
}
i++;
}
System.out.print(val);
}
}
Integer arr[] = { 12, 13, 1, 10, 34, 10 };
Arrays.sort(arr, Collections.reverseOrder());
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] < arr[0]) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
break;
}
}
public class Secondsmallest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[]= {7,5,12,3,45,7,90};
Arrays.sort(arr);
System.out.println(arr[1]);
}
}
public class Second {
static void fun() {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int arr[]=new int[20];
System.out.println(“enter the size of the array :”);
int n=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(“enter the elements of the array :”);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
int min, sm;
if(arr[0]<arr[1])
{
min=arr[0];
sm =arr[1];
}
else
{
min=arr[1];
sm =arr[0];
}
for(int i=2;i<n;i++)
{
if(arr[i]<min)
{
sm =min;
min=arr[i];
}
else if(arr[i]< sm)
{
sm =arr[i];
}
else
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("the second min element is :"+ sm);
}
}
SECOND APPROACH FOR FINDING THE SECOND ELEMENT:-
int min=a[0];
for(int i=0;i<Size;i++) {
if(a[i]<min) {
min=a[i];
a[i]=a[i+1];
}
Size–;
}
thats dumbbbbbbb!!!!
it is an example of bubble sort.below is a modified version which will simplify your understanding.
package com.company;
class test {
public static int prep(int[] a, int total){
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j a[j+1])
{
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j+1];
a[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
return a[1] ;//2nd element because index starts from 0
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int a[]={7,-3,9,0,2};
System.out.println(“Second smallest: “+prep(a,5));
}}
int max1,max2;
max1=max2=A[0];
for(int i=0; imax1)
{
max2=max1;
max1=A[i];
}
else if(A[i]>max2)
{
max2=A[i];
}
A
S.O.P(max2);