Construct A Binary Tree From Inorder And Postorder Traversals
Construct A Binary Tree From Inorder And Postorder Traversal
Suppose we have a inorder and postorder sequence of a binary tree . We have to generate tree from these sequences. In this article we will see if the inorder and postorder sequence is [10 30 40 50 60 70 90 ] and [10 40 30 60 90 70 50] , then the tree will be –
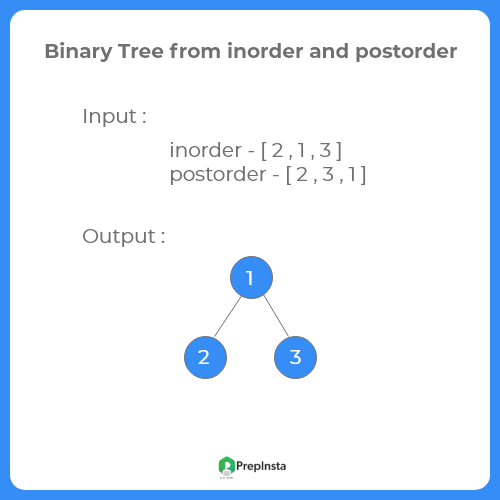
Example to construct a Binary Tree from Inorder And Postorder Traversal
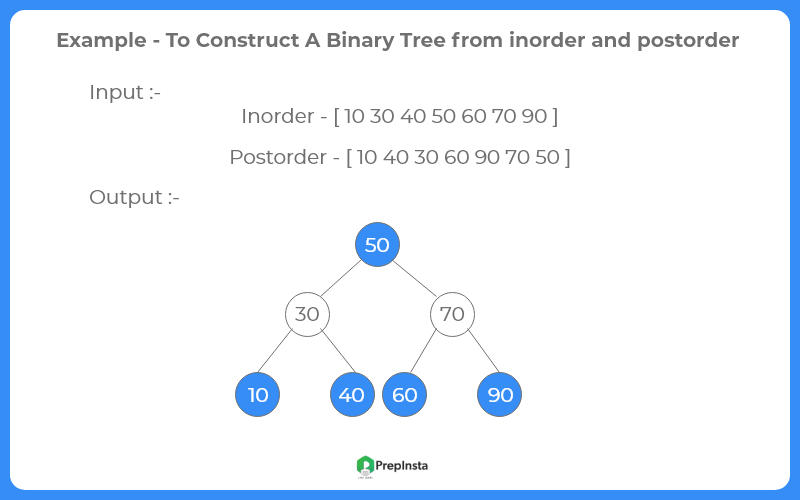
Let us see the process of constructing tree :-
inorder = [ 10 30 40 50 60 70 90]
postorder= [ 10 40 30 60 90 70 50 ]
- We first find the last node in postorder []. The last node is 50 , we know this value is root as root always appear in the end of postorder traversal.
- we search 50 in inorder [] to find left and right subtrees of root. Everything on left of 50 in inorder [] is in left subtree and everything on right is in right subtree.
- Recur the above process for following two. a) Recur for inorder[]=[ 10 30 40 ] and postorder = [ 10 40 30 ] . And make the created tree as left child of root. b) Recur for inorder = [ 60 70 90 ] and postorder [ 60 90 70]. And make the created tree as right child of root.
CODE FOR CONSTRUCTING A BINARY TREE IN JAVA
import java.util.*;
/*Representing Node of the Binary Tree */
class Node
{
int value;
Node left,right;
//constructor
Node(int value)
{
this.value=value;
left=right=null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
BinaryTree()
{
root=null;
}
/*inorder traversal of binary tree */
public void inorder(Node ptr)
{
if(ptr==null)
return ;
/*first traverse left child */
inorder(ptr.left);
/*then print the value of node */
System.out.print(ptr.value+" ");
/* now traverse the right child */
inorder(ptr.right);
}
/*preorder traversal of binary tree */
public void preorder(Node ptr)
{
if(ptr==null)
return ;
/*first print the value of node*/
System.out.print(ptr.value+" ");
/*then traverse the left child */
preorder(ptr.left);
/*now traverse the right child*/
preorder(ptr.right);
}
/*postorder traversal of binary tree */
public void postorder(Node ptr)
{
if(ptr==null)
return ;
/*first traverse left child*/
postorder(ptr.left);
/*then traverse the right child*/
postorder(ptr.right);
/*now print the value of node*/
System.out.print(ptr.value+" ");
}
//function to find index of values in inArr[start....end]
int search(int arr[],int start,int end,int value)
{
int i;
for( i=start;i<=end;i++)
if(arr[i]==value)
break;
return i;
}
Node createTree(int inArr[],int postArr[],int inStart,int inEnd,int postStart,int postEnd)
{
if(inEnd<inStart)
return null;
//Take the last node of postorder
Node ptr=new Node(postArr[postEnd]);
//if it has no child then simply returns
if(inEnd==inStart)
return ptr;
int index=search(inArr,inStart,inEnd,ptr.value);
/*create left and right subtree*/
ptr.left=createTree(inArr,postArr,inStart,index-1,postStart,postStart-inStart+index-1);
ptr.right=createTree(inArr,postArr,index+1,inEnd,postEnd-inEnd+index,postEnd-1);
return ptr;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree=new BinaryTree();
int inorder[]={10,30,40,50,60,70,90}; //given inorder of a binary tree
int postorder[]={10,40,30,60,90,70,50}; //given postorder of a binarytree
int length=inorder.length;
tree.root=tree.createTree(inorder,postorder,0,length-1,0,length-1);
System.out.println("Inorder of the tree:");
tree.inorder(tree.root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Preorder of the tree");
tree.preorder(tree.root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Postorder of the tree");
tree.postorder(tree.root);
}
}
Output:
Inorder of the tree:
10 30 40 50 60 70 90
Preorder of the tree
50 30 10 40 70 60 90
Postorder of the tree
10 40 30 60 90 70 50
Time Complexity For constructing A Binary Tree
Time Complexity :
O(n²)



Login/Signup to comment