Java program to check whether linked list is palindrome or not
Java Program to Check whether linked list is palindrome or not
Check out Java program to check whether the linked list is palindrome or not on this page. In this program, we have to check whether the given linked list is palindromic or not.
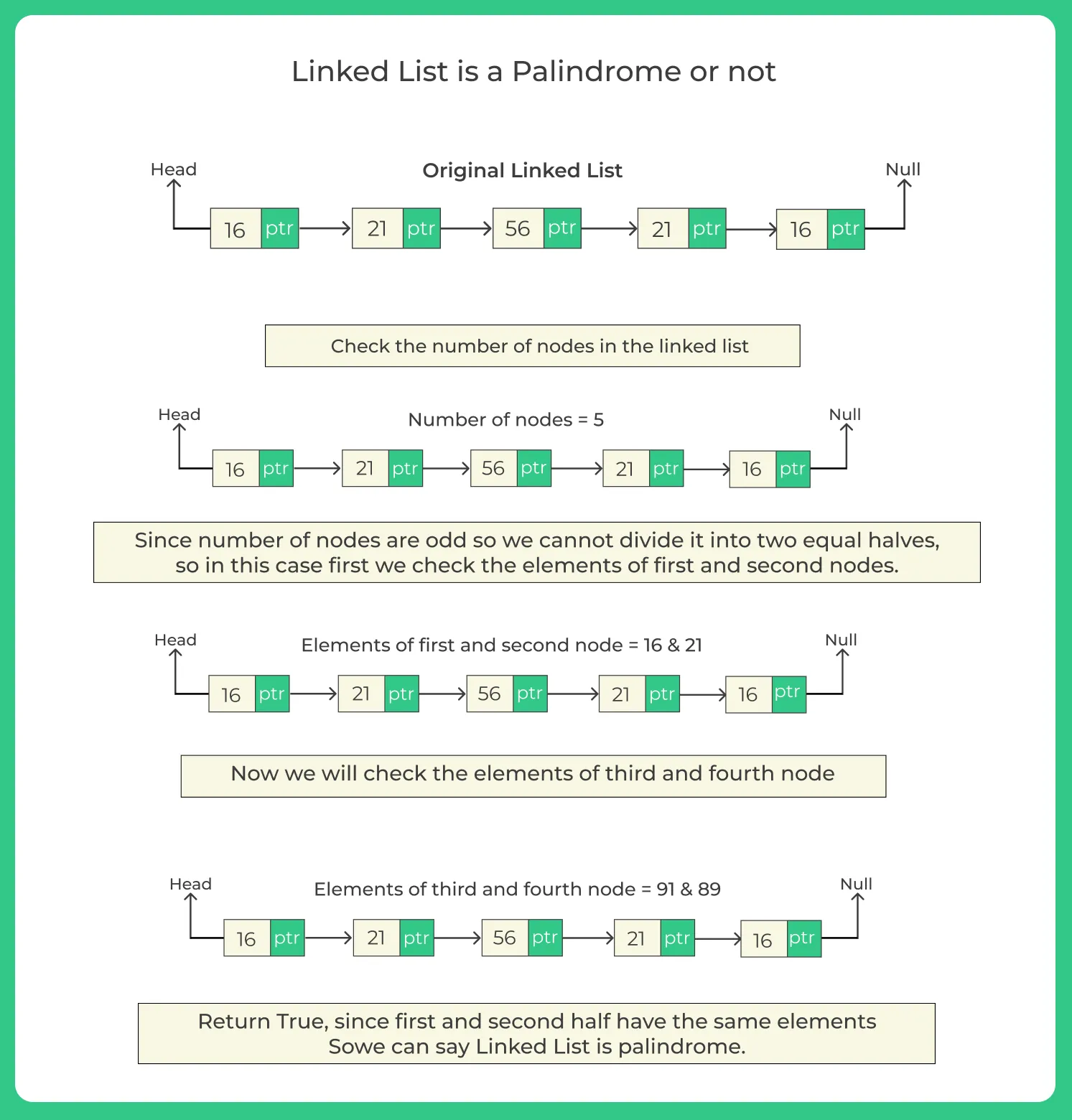
Palindrome is a list which has the property of reversing itself. To check whether a number is palindrome or not, we traverse the list and check if any element from the starting half doesn’t match with the ending half of a list then we say it’s not a palindrome number otherwise it is palindrome.

How to check whether linked list is palindrome or not?
When working with data structures, linked lists are a fundamental concept. They’re used to store and manipulate dynamic data efficiently.
One interesting and frequently asked interview question is: “How do you check if a singly linked list is a palindrome?”
This problem tests your understanding of linked lists, pointers, and algorithmic thinking. In this article, we’ll explore multiple ways to solve this problem using Java, breaking down each approach with clear steps, time and space complexity analysis, and code examples.
Example:
Input: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
Output: true (It's a palindrome)
Input: 1 -> 2 -> 3
Output: false (Not a palindrome)
Methods to Check if a Linked List is a Palindrome or not
We’ll explore 2 main methods to check if a linked list is a Palindrome or not:

Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Method 1: Using a Stack to check if a linked list is palindrome
Idea:
- Traverse the list and push each element into a stack.
- Traverse the list again and compare each node’s value with the top of the stack.
- If all values match, it’s a palindrome.
Algorithm Steps:
- Traverse the linked list and push all elements to a stack.
- Reset the current pointer to head.
- While traversing again, compare the current node’s value with the top of the stack.
- If all elements match, return true. Else, return false.
Space Complexity: O(n) (for the stack)
Java Code:
import java.util.Stack;
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public class PalindromeLinkedList {
public static boolean isPalindrome(Node head) {
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
Node current = head;
// Push all elements to stack
while (current != null) {
stack.push(current.data);
current = current.next;
}
// Compare again from start
current = head;
while (current != null) {
if (current.data != stack.pop()) {
return false;
}
current = current.next;
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next.next = new Node(1);
System.out.println("Is Palindrome: " + isPalindrome(head)); // Output: true
}
}
Method 2: Reversing the Second Half to check if a linked list is palindrome
Idea:
- Use the fast and slow pointer technique to find the middle.
- Reverse the second half of the list.
- Compare the first half and the reversed second half.
- Restore the list (optional) and return the result.
Algorithm Steps:
- Use slow and fast pointers to find the middle.
- Reverse the second half of the list.
- Compare the first and second halves node by node.
- Return true if all nodes match, else false.
Space Complexity: O(1) – no extra data structures
Java Code:
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public class PalindromeLinkedList {
public static boolean isPalindrome(Node head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return true;
// Step 1: Find the middle
Node slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// Step 2: Reverse second half
Node secondHalf = reverseList(slow);
// Step 3: Compare both halves
Node firstHalf = head;
Node secondHalfCopy = secondHalf; // To restore later if needed
while (secondHalf != null) {
if (firstHalf.data != secondHalf.data) {
return false;
}
firstHalf = firstHalf.next;
secondHalf = secondHalf.next;
}
return true;
}
// Helper to reverse a linked list
private static Node reverseList(Node head) {
Node prev = null, next = null, current = head;
while (current != null) {
next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
return prev;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(1);
System.out.println("Is Palindrome: " + isPalindrome(head)); // Output: true
}
}
Comparison between Space and Time Complexity
| Method | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stack Based | O(n) | O(n) | Simple but uses extra space |
| Reverse Second Half | O(n) | O(1) | More efficient |
To wrap it up with….
Checking if a linked list is a palindrome is a common interview question that tests your understanding of data structures and algorithmic logic.
We explored two approaches:
- Simple stack based method
- Efficient in place method using pointer reversal.
Understanding both will help you strengthen your grasp of linked lists and prepare you well for technical interviews.
FAQ's Related to Java Program To Check if a linked list is palindrome
Answer:
Most efficient approach is to reverse the second half of the list and compare it with the first half. It uses constant space and linear time.
Answer:
Yes, it’s even simpler with a doubly linked list. You can use two pointers from head and tail to compare elements directly.
Answer:
Fast and slow pointer technique helps to find the middle of the list in a single pass. It’s a standard approach in linked list problems.
Answer:
You can call the reverse method again on the reversed half to restore the list.
Answer:
Yes, the examples above are designed for singly linked lists, but similar logic can be adapted for doubly linked lists or circular lists.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






