Binary to decimal conversion using Java
Binary to decimal conversion
In this article we will discuss binary to decimal conversion using java. For this purpose we need to ask a binary number from user and convert that binary number to its decimal equivalent form and then print the converted number on to the screen.

Working :
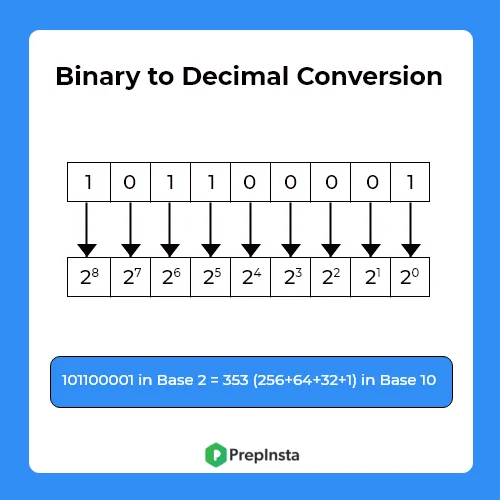
A Decimal number can be calculated by multiplying every digits of binary number with 2 to the power of the integers
starts from 0 to n-1 where n refers as the total number of digits present in a binary number and finally add all of them.
Algorithm :
- While num is greater then zero
- Store the unit place value of num to a variable (rem)
- Calculate rem with base and add it to answer
- Completely divide Num by 10 and multiply base with 2
Java Code :
Run
//Java program to convert Binary number to decimal number
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter a binary number : ");
int binary = sc.nextInt();
//Declaring variable to store decimal number
int decimal = 0;
//Declaring variable to use in power
int n = 0;
//writing logic for the conversion
while(binary > 0)
{
int temp = binary%10;
decimal += temp*Math.pow(2, n);
binary = binary/10;
n++;
}
System.out.println("Decimal number : "+decimal);
//closing scanner class(not compulsory, but good practice)
sc.close();
}
}Output :
Enter a binary number : 111001 Decimal number :
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription



package pripInsta;
public class BinarytoDecimal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String str=”1110″;
System.out.println(“in Binary: “+str);
int n=Integer.parseInt(str, 2);
System.out.println(“in Decimal: “+n);
}
}
Hey there, Kindly join our Discord server for all the technical and subject related queries.
package pripInsta;
public class BinarytoDecimal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String str=”1110″;
System.out.println(“in Binary: “+str);
int n=Integer.parseInt(str, 2);
System.out.println(“in Decimal: “+n);
}
}
Hey there, Kindly join our Discord server for all the technical and subject related queries.
class BinaryToDecimal {
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int binary=101101,mod=0;
double sum=0, length=len(binary)-1;
double k=0;
for(int j=0;j<=length;j++) {
mod=binary%10;
k= Math.pow(2, j);
sum=sum+(mod*k);
binary=binary/10;
}
System.out.println((int)sum);
}
public static int len(int n) {
int mod,le=0;
while(n!=0) {
mod=n%10;
n=n/10;
le++;
}
return le;
}
}
Hey!! Join Here
import java.util.*;
public class Binary_Decimal
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter a Binary number : “);
String binary=sc.nextLine();
int decimal=Integer.parseInt(binary,2);
System.out.println(“Decimal version is : “+decimal);
}
}
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(“Enter a binary number : “);
int binary = sc.nextInt();
Integer.toBinaryString(
import java.util.*;
class main{
static String decimal (int binary){
int a = binary;
int decimal = 0;
for(int i=0;a>0;i++,a/=10){
decimal += (a%10)*Math.pow(2, i);
}
return “Binary :”+binary +” == “+”Decimal : “+decimal;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int binary = 101110;
System.out.println(decimal(binary));
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int rem,sum=0;
System.out.println(“Enter a binary number :”);
int n = scan.nextInt();
int i=0;
while(n>0)
{
rem=n%10;
sum=(int) (sum+rem*Math.pow(2,i));
n=n/10;
i++;
}
System.out.print(sum);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(btoc(111001,0));
}
static int btoc(int n , int d){
if(n==0){
return 0;
}
int rem=n%10;
n/=10;
return rem*(int)Math.pow(2,d) + btoc(n,++d);
}
package com.company;
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“enter the binary number”);
int n=input.nextInt();
int l=0,a=n,b=0,sum=0;
System.out.println(l);
while(a!=0)
{
b=a%10;
a=a/10;
sum=sum+(b*((int)Math.pow(2,l)));
System.out.println(sum);
l++;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
//Java program to convert Binary number to decimal number
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Binary_To_Decimal
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int Decimal=0;
int i=1,j=1;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(“Enter a binary number : “);
int binary = sc.nextInt();
while(binary > 0)
{
int temp = binary%10;
Decimal = Decimal + (temp*(j));
System.out.println(Decimal+”=”+Decimal+”+(“+temp+” * “+j+”)”);
j=i+i;
binary = binary/10;
i=j;
}
System.out.println(“Decimal number : “+Decimal);
sc.close();
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter a binary number : “);
int binary = sc.nextInt();
//Declaring variable to store decimal number
int decimal = 0;
//Declaring variable to use in power
int n = 0;
//writing logic for the conversion
while(binary > 0)
{
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println(i+" Iteration");
int temp = binary%10;
System.out.print("temp="+temp+"\t");
decimal += temp*Math.pow(2, n);
System.out.print("decimal="+decimal+"\t");
binary = binary/10;
System.out.print("binary="+binary+"\t");
n++;
System.out.print("n="+n+"\n");
}
}
System.out.println("Decimal number : "+decimal);
//closing scanner class(not compulsory, but good practice)
sc.close();
}
}