Multivalued Attributes in DBMS
Multivalued Attributes
In this article, we will learn about Multivalued Attributes in DBMS. Attributes define what type of data is stored in a database table . Some times we need to store one or more values of a single attribute for that purpose multivalued attributes are used.

MULTIVALUED ATTRIBUTES IN DBMS
- Attributes define what type of data is stored in a database table for example student table stores details of Student name, roll no, marks, attendance, etc all these details corresponding the properties or attributes of the student table.
- A multivalued attributed in DBMS(Data Base Management System) is an attribute that can have multiple value for a single intance of an entity.
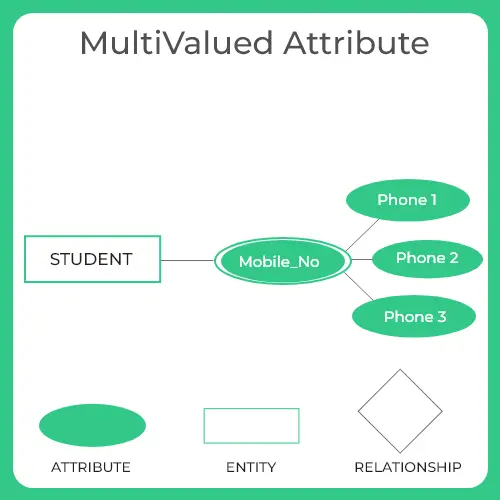
- For example, a person may have multiple phone numbers, so the “Phone Number” attribute for that person would be a multivalued attribute.
- In relational databases, multivalued attributes are typically represented by creating a separate table for the attribute, with a one-to-many relationship between the main entity and the new table.
Multi-valued attribute Definition
A multivalued attribute is capable of storing more than one value in a single attribute i.e nothing but it can hold multiple values for the single attribute.
Example for Multivalued attribute
Example 1
- In a Real-world scenario, a person can have more than one phone number hence “phone number attribute” will become a multivalued attribute
Example 2
- A person may have more than one address .hence address may become a multi-valued attribute
Representation of multivalued attribute
A multivalued attribute is represented using a double oval with the name of the attribute inside the oval.
Read more about Attributes:
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others





Login/Signup to comment