Stock Span Problem in Python
Introduction to Stock Span Problem in Python
The stock span problem in Python is a classic algorithmic challenge that involves calculating the “span” of stock prices over a series of days. The span of a stock on a particular day is defined as the maximum number of consecutive days (including the current day) for which the stock price is less than or equal to the price on that day.
In this page, we will delve into this problem, exploring stock span problem (naive and optimized approach) in python.

What is the Stock Span Problem in Python?
The Stock Span Problem revolves around calculating the span of stock’s price for a given day. The span of a stock’s price on a particular day is defined as the maximum number of consecutive days just before the current day for which the price of the stock is less than or equal to the current day’s price.
- In simpler terms, it helps us determine how many days a stock’s price remained consistent or rose leading up to a given day.
- This information is valuable for assessing trends and volatility in the stock market.
Calculating Stock Span
The stock span of a particular day can be calculated using a simple algorithm. For each day, we start from that day and move backward in time, checking how many consecutive days the stock price was less than or equal to the current day’s price. This process continues until we find a day where the stock price exceeds the current day’s price or until we reach the first day of available data.
Pseudo Code : Stock Span Problem in Python
- Here’s a Python implementation of the Stock Span Problem:
def calculate_span(prices):
stack = []
span = []
for i in range(len(prices)):
while stack and prices[i] >= prices[stack[-1]]:
stack.pop()
if not stack:
span.append(i + 1)
else:
span.append(i - stack[-1])
stack.append(i)
return span
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Stock Span Problem (Naïve and Optimized Approach) in Python
The Naïve Approach
The naive approach to solving the Stock Span Problem involves iterating through the stock prices for each day and, for each day, going back to the previous days to count how many consecutive days have lower or equal prices. Here’s a simplified Python implementation of the naive approach:
def calculate_span(prices):
n = len(prices)
span = [1] * n # Span for each day initialized to 1
for i in range(1, n):
span[i] = 1
j = i - 1
while j >= 0 and prices[j] <= prices[i]:
span[i] += 1
j -= 1
return span
# Example
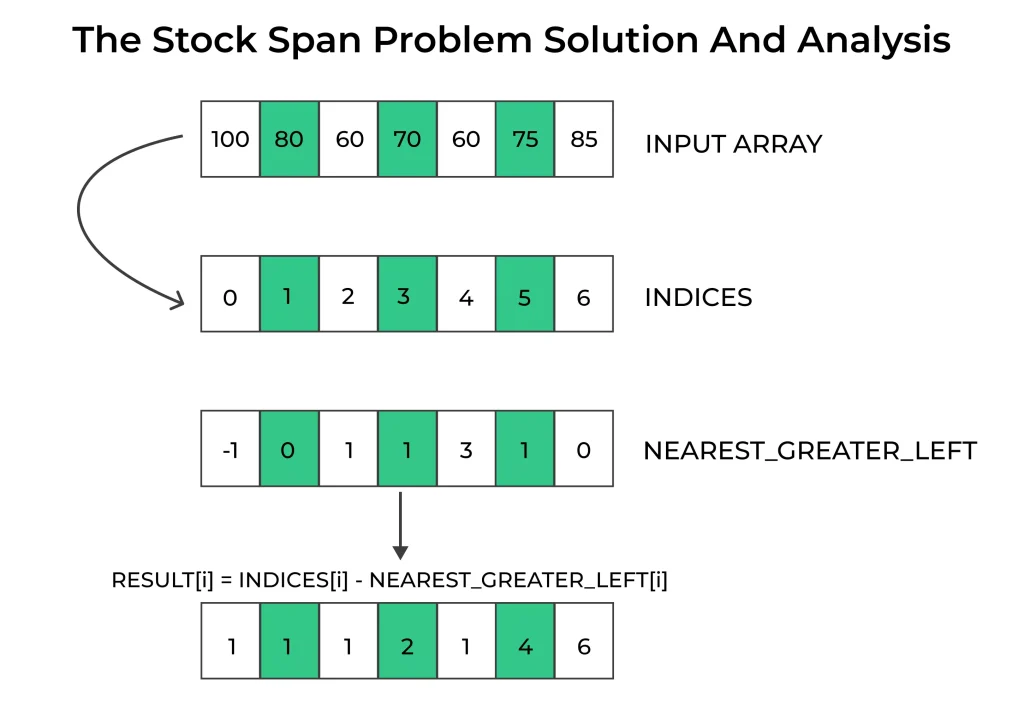
prices = [100, 80, 60, 70, 60, 75, 85]
span = calculate_span(prices)
print("Stock Prices:", prices)
print("Span:", span)
Output:
Stock Prices: [100, 80, 60, 70, 60, 75, 85] Span: [1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 4, 6]
Explanation:
- Span is the count of consecutive days with price less than or equal to today’s price.
- For each day, we loop backward and count such days.
- The span of the first day is always 1.
- This method is slow due to nested loops.
- Time Complexity: O(n^2) – For each element, we may traverse all previous elements in the worst case.
- Space Complexity: O(n) – For storing the span array of size n.
The Optimized Approach
To overcome the inefficiency of the naive approach, we can employ a more optimized solution using a stack data structure. This approach has a time complexity of O(n) and is much more efficient.
def calculate_span_optimized(prices):
n = len(prices)
span = [0] * n
stack = []
for i in range(n):
while stack and prices[stack[-1]] <= prices[i]:
stack.pop()
span[i] = i + 1 if not stack else i - stack[-1]
stack.append(i)
return span
# Example
prices = [100, 80, 60, 70, 60, 75, 85]
span = calculate_span_optimized(prices)
print("Stock Prices:", prices)
print("Span:", span)
Output:
Stock Prices: [100, 80, 60, 70, 60, 75, 85] Span: [1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 4, 6]
Explanation:
Use a stack to track indices of days with higher stock prices.
Pop from the stack while the top’s price is ≤ current day’s price.
Span is the distance between current index and top of the stack (or full span if stack is empty).
Push current index to stack after processing.
- Time Complexity: O(n) – Each element is pushed and popped at most once.
- Space Complexity: O(n) – For storing the stack and output span list.
Advantages of Mastering the Stock Span Problem
- Informed Decision-Making : By understanding the Stock Span Problem, you can make data-driven decisions when buying or selling stocks, increasing your chances of profitability.
- Risk Mitigation : Identify stocks with consistent upward trends to minimize your exposure to market volatility.
- Algorithm Development : Build sophisticated trading algorithms that leverage the Stock Span Problem to execute profitable trades.
Takeaway:
In the world of stock trading, understanding the historical performance of a stock is essential. The Stock Span Problem offers a valuable tool to assess the continuity and trends in stock prices. While the naive approach provides accurate results, the optimized approach is far more efficient, making it a preferred choice for analyzing large datasets.
In conclusion, whether you’re a seasoned trader or a budding investor, mastering algorithms like the Stock Span Problem can provide you with a competitive edge in the world of finance.
FAQs
The Stock Span Problem involves calculating how many consecutive days before the current day the stock price was less than or equal to today’s price. It’s commonly used in financial analysis to track price trends.
The naive approach compares each day’s price with all previous days until it finds a higher price. This takes O(n²) time, which is inefficient for large inputs.
The optimized approach uses a stack to keep track of indices, enabling computation in O(n) time. It skips unnecessary comparisons by using previous computations stored in the stack.
It reduces repeated scanning by storing potential spans in a LIFO structure, checking only the latest relevant prices. This saves time and speeds up processing significantly.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment