Stack using Linked List in Python
Implementation of Stack using Linked List in Python
To implement a Stack using Linked List in Python, you can modify the linked list code from the previous response. In a stack, elements are added and removed from the top, following the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle.
In this page, we will delve deep into the implementation of stacks using linked list in python, offering you a clear and detailed understanding of this topic.

Implementation of Stack using Linked List
Using a linked list for implementing a stack provides several advantages. Unlike arrays, linked lists allow for dynamic memory allocation, making it easier to manage the stack’s size.
- Additionally, linked lists are more flexible and efficient when it comes to inserting and deleting elements, which aligns with the nature of stack operations.
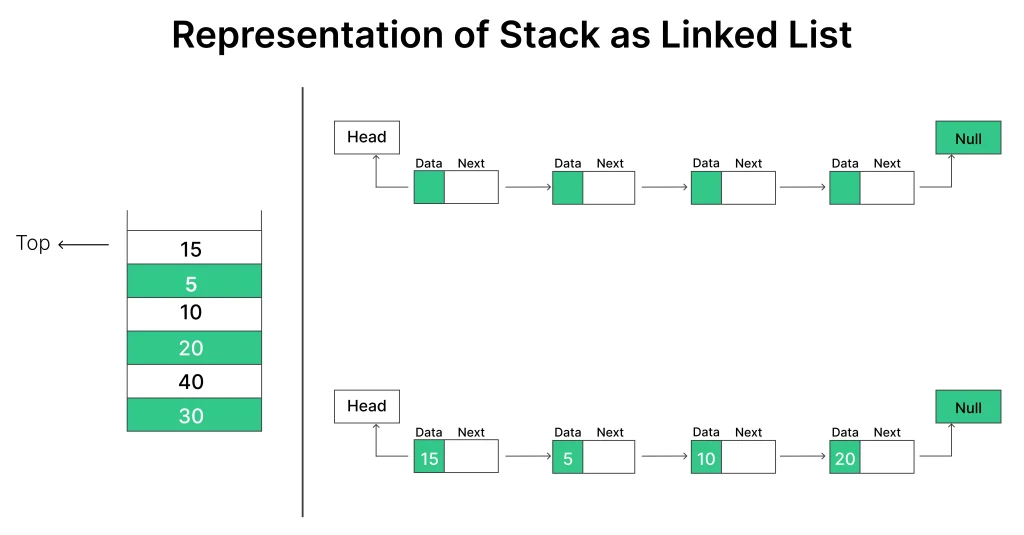
Implementing a Stack Using a Linked List in Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.top = None
self.size = 0
def push(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = self.top
self.top = new_node
self.size += 1
def pop(self):
if self.is_empty():
return None
popped = self.top.data
self.top = self.top.next
self.size -= 1
return popped
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Implementation of Stack using Linked List in Python
The implementation of a stack using a linked list in Python involves creating a Node class to store data and a reference to the next node, and a Stack class to manage stack operations like push, pop, and peek. This approach allows dynamic memory usage, ensuring efficient memory allocation without a predefined size limit.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.top = None # Initialize an empty stack
def is_empty(self):
return self.top is None # Check if the stack is empty
def push(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = self.top
self.top = new_node # Push data onto the stack
def pop(self):
if self.is_empty():
return None # Return None if the stack is empty
popped_data = self.top.data
self.top = self.top.next # Pop the top element from the stack
return popped_data
def peek(self):
if self.is_empty():
return None # Return None if the stack is empty
return self.top.data # Return the top element without removing it
# Example usage:
if __name__ == "__main__":
my_stack = Stack()
my_stack.push(5)
my_stack.push(10)
my_stack.push(15)
print("Top of the stack:", my_stack.peek()) # Output: Top of the stack: 15
popped_item = my_stack.pop()
print("Popped item:", popped_item) # Output: Popped item: 15
print("Top of the stack after popping:", my_stack.peek()) # Output: Top of the stack after popping: 10
Output:
Top of the stack: 15 Popped item: 15 Top of the stack after popping: 10
Explanation:
- Class Node is used to create each element in the linked list, where each node holds data and a pointer next to the next node.
- Class Stack manages the stack using the linked list:
- self.top keeps track of the top element in the stack.
- Push operations:
- push(5) → Stack becomes: 5
- push(10) → Stack becomes: 10 -> 5
- push(15) → Stack becomes: 15 -> 10 -> 5
- Peek operation:
- peek() returns 15, which is the current top of the stack.
- Pop operation:
- pop() removes and returns 15. Stack becomes: 10 -> 5
- Peek again:
- peek() now returns 10, which is the new top of the stack.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Push | O(1) | O(1) |
| Pop | O(1) | O(1) |
| Peek | O(1) | O(1) |
| Is Empty | O(1) | O(1) |
The key differences between implementing a stack using an array and using a linked list:
This table summarizes the main distinctions between using an array and a linked list for implementing a stack, highlighting factors such as dynamic sizing, memory allocation, time complexity, and more.
| Aspect | Stack Implementation with Array | Stack Implementation with Linked List |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Sizing | Fixed size, may require resizing | Dynamic sizing; grows or shrinks as needed |
| Memory Allocation | Contiguous block of memory | Non-contiguous, nodes scattered in memory |
| Insertion/Deletion | Push/pop operations have O(1) time complexity (amortized) | Push/pop operations have O(1) time complexity |
| Memory Overhead | Fixed size; may have unused space or lead to overflow | Each element has an associated node, leading to slightly higher memory overhead |
| Implementation Complexity | Simpler implementation | More complex due to node management |
Advantages of Using Linked Lists for Stacks
Using linked lists to implement a stack provides several advantages:
- Dynamic Size: Linked lists can grow or shrink dynamically, making them suitable for implementing a dynamic-sized stack.
- Efficient Operations: Push and pop operations have a time complexity of O(1) since they involve modifying only the top element.
- Ease of Implementation: Linked lists provide a straightforward way to manage stack operations without the need for fixed-size arrays.
Final Thoughts:
In this page, we’ve explored the concept of stacks, learned about linked lists, and seen how to implement a stack using linked lists in Python. Stacks are versatile data structures with a wide range of applications in computer science. Mastering the art of implementing stacks will undoubtedly enhance your programming skills.
FAQs
A stack is a linear data structure that follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle. Using a linked list, the push and pop operations are performed at the head node to ensure constant time complexity.
Linked lists provide dynamic memory allocation and avoid overflow unless memory is full, unlike arrays which have fixed size and may lead to overflow. Inserting and deleting elements is also faster as it avoids shifting.
In push(), a new node is created and inserted at the beginning of the list, making it the new top of the stack. This ensures O(1) time complexity for insertion.
To check if the stack is empty, simply verify if the top (head) pointer is None. If it is, there are no elements in the stack.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment