Stack using Array in Python
Implementation of Stack Using Array in Python
Stack using Array in Python is a fundamental data structure in computer science that follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle.
Stacks are fundamental data structures in computer science, widely used for various applications. We will provide a comprehensive guide on creating a stack using array in python, covering the key concepts and operations involved.

Implementation of Stack using Array in Python
An array implementation of a stack is a way to create a stack data structure using a one-dimensional array or list in a programming language. In this implementation, the array is used to store the elements of the stack, and the stack operations (push, pop, peek, etc.) are performed using the array’s operations.
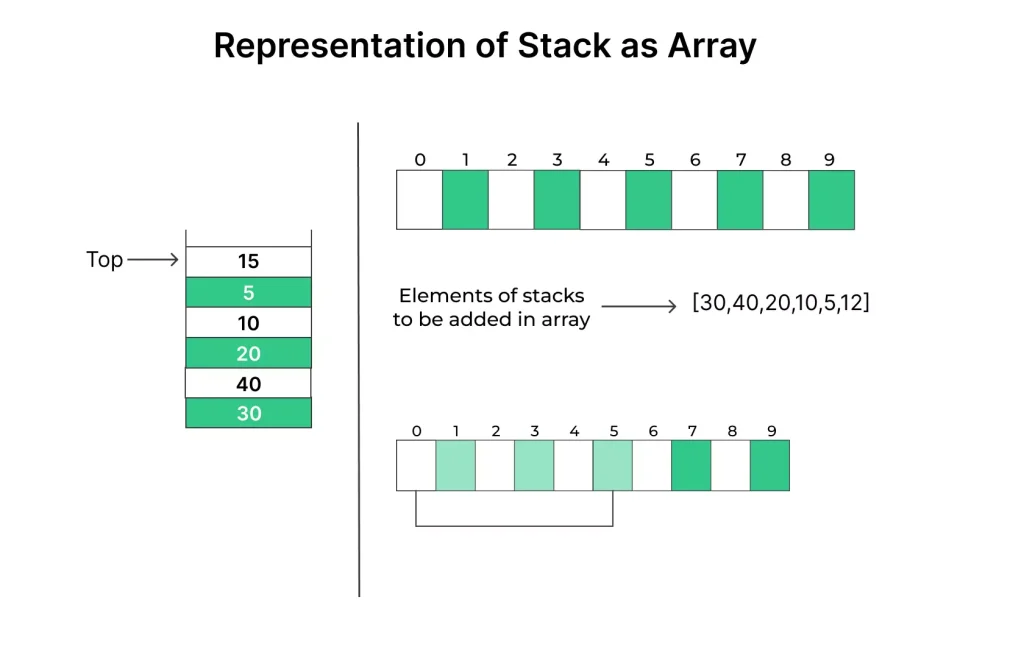
Array-Based Stack Implementation
Now, let’s delve into the core of our topic: implementing a stack using arrays.
class Stack:
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.capacity = capacity
self.stack = [None] * capacity
self.top = -1
def push(self, item):
if self.top == self.capacity - 1:
print("Stack Overflow")
return
self.top += 1
self.stack[self.top] = item
def pop(self):
if self.top == -1:
print("Stack Underflow")
return None
item = self.stack[self.top]
self.top -= 1
return item
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Example: Implementation of Stack using Array in Python
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
def is_empty(self):
return len(self.stack) == 0
def push(self, item):
self.stack.append(item)
def pop(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self.stack.pop()
else:
print("Stack is empty. Cannot pop.")
return None
def peek(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self.stack[-1]
else:
print("Stack is empty. Cannot peek.")
return None
def size(self):
return len(self.stack)
# Example usage:
stack = Stack()
stack.push(1)
stack.push(2)
stack.push(3)
print("Stack:", stack.stack) # Output: Stack: [1, 2, 3]
print("Peek:", stack.peek()) # Output: Peek: 3
print("Pop:", stack.pop()) # Output: Pop: 3
print("Stack:", stack.stack) # Output: Stack: [1, 2]
print("Is Empty?", stack.is_empty()) # Output: Is Empty? False
print("Stack Size:", stack.size()) # Output: Stack Size: 2
Output:
Stack: [1, 2, 3] Peek: 3 Pop: 3 Stack: [1, 2] Is Empty? False Stack Size: 2
Explanation:
- A custom Stack class is created using a list to store elements.
- push(item) adds an element to the top of the stack using append().
- pop() removes and returns the last item if the stack is not empty.
- peek() returns the last item without removing it, or shows a message if the stack is empty.
- is_empty() returns True if the stack has no elements.
- size() gives the total number of elements currently in the stack.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| push() | O(1) | O(1) |
| pop() | O(1) | O(1) |
| peek() | O(1) | O(1) |
| is_empty() | O(1) | O(1) |
| size() | O(1) | O(1) |
| Total Space (for n elements) | — | O(n) |
Advantages of Array-Based Stack
- Implementing a stack using arrays offers several advantages:
Final Thoughts:
Stack using Array in Python data structure is a fundamental concept in computer science and programming. Its implementation can vary, but the core principles of push, pop, and LIFO remain consistent. Understanding stacks and their applications is crucial for any programmer or computer scientist.
FAQs
You can implement a stack using a Python list, leveraging its append() method for push and pop() method for pop operations. This allows LIFO (Last In First Out) behavior efficiently.
You can check if the stack (list) is empty using len(stack) == 0 or simply not stack. Both return True when the stack has no elements.
Both push() (append) and pop() operations have O(1) time complexity in Python lists, making stack operations efficient.
To peek the top element without removing it, access stack[-1]. This returns the most recently added element if the stack is not empty.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others



