Operation Of Trie Data Structure
Operation Of Trie Data Structure
The operation of a Trie data structure lies at the heart of its remarkable utility in handling strings and efficiently solving various problems involving words, prefixes, and pattern matching.
Operation Of Trie Data Structure refers to how we manage and manipulate words using a tree-like structure that supports efficient insertion, search, and prefix matching. A Trie (pronounced “try”) is a tree-based data structure designed for storing strings, where each node represents a character of a word.
In this article, we will delve into the world of Trie in Python, exploring their structure, applications, and how to implement them
What is the Operation Of Trie Data Structure?
- A Trie (pronounced “try”) is a tree-like data structure used for efficiently storing and searching a dynamic set of strings or keys, typically associated with text-based data.
- The name “Trie” comes from the word “retrieval,” as it excels at retrieving data based on a prefix or a sequence of characters. Tries are commonly used in various applications, such as autocomplete systems, spell checkers, IP routing, and more.
Basic Trie Structure
- A Trie consists of nodes, where each node represents a character in a word or string. These nodes are connected in a hierarchical manner, forming a tree-like structure.
- The root node represents an empty string, and as you traverse down the Trie, you build words character by character.

Operation Of Trie Data Structure
Trie Operations
Implementation Of Trie in Python
let’s see how we can implement a Trie in Python. We will create a basic Trie structure and demonstrate insertion and search operations.
class TrieNode:
def __init__(self):
self.children = {}
self.is_end_of_word = False
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.root = TrieNode()
def insert(self, word):
node = self.root
for char in word:
if char not in node.children:
node.children[char] = TrieNode()
node = node.children[char]
node.is_end_of_word = True
def search(self, word):
node = self.root
for char in word:
if char not in node.children:
return False
node = node.children[char]
return node.is_end_of_word
Advantages of Trie in Python
Tries in Python offer several advantages:
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
What is the time complexity of trie operations?
| Operations | Time Complexity |
|---|---|
| Insertion | O(K), where K is the length of the string being inserted. |
| Search | O(K), where K is the length of the string being searched. |
| Prefix Search | Searching for a key in a trie has a time complexity of O(L), where L is the length of the key. |
| Deletion | O(K), where K is the length of the string being deleted. |
| Counting Words with a Prefix: | O(P), where P is the length of the prefix being counted. |
Python trie dictionary
- A Python Trie Dictionary, often referred to as a TrieMap or TrieDict, is a data structure that combines the characteristics of a trie and a dictionary (or hashmap).
- It allows you to efficiently store key-value pairs, where the keys are strings, and provides fast retrieval and insertion of these pairs.
Here’s an example of Operation in trie in python example:
class TrieNode:
def __init__(self):
self.children = {}
self.is_end_of_word = False
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.root = TrieNode()
def insert(self, word):
node = self.root
for char in word:
if char not in node.children:
node.children[char] = TrieNode()
node = node.children[char]
node.is_end_of_word = True
def search(self, word):
node = self.root
for char in word:
if char not in node.children:
return False
node = node.children[char]
return node.is_end_of_word
def starts_with_prefix(self, prefix):
node = self.root
for char in prefix:
if char not in node.children:
return False
node = node.children[char]
return True
# Create a trie and insert some words
trie = Trie()
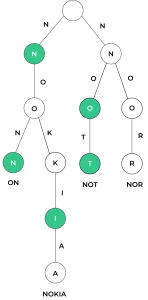
trie.insert("NOKIA")
trie.insert("NOR")
trie.insert("NOT")
trie.insert("ON")
# Search for words in the trie
print(trie.search("NOKIA")) # True
print(trie.search("NOR")) # True
print(trie.search("NOKIAS")) # False
print(trie.search("ban")) # False
# Check if prefixes exist in the trie
print(trie.starts_with_prefix("Nokia")) # True
print(trie.starts_with_prefix("NOT")) # True
print(trie.starts_with_prefix("NOR")) # True
print(trie.starts_with_prefix("batman")) # False
Python trie library
- To get started, you’ll need to install the pytrie library if you haven’t already. You can install it using pip:
pip install pytrie
- Once you have pytrie installed, you can use it to create and manipulate trie data structures. Here’s a basic example of how to use it:
from pytrie import StringTrie
# Create a trie
trie = StringTrie()
# Insert keys into the trie
trie["apple"] = 1
trie["app"] = 2
trie["banana"] = 3
trie["bat"] = 4
# Check if a key exists in the trie
print("Is 'apple' in trie?", "apple" in trie) # True
print("Is 'apricot' in trie?", "apricot" in trie) # False
# Retrieve values associated with keys
print("Value of 'apple':", trie.get("apple")) # 1
print("Value of 'app':", trie.get("app")) # 2
# Find keys with a common prefix
print("Keys with prefix 'ap':", list(trie.keys(prefix="ap"))) # ['app', 'apple']
print("Keys with prefix 'ba':", list(trie.keys(prefix="ba"))) # ['banana', 'bat']
# Delete a key from the trie
del trie["apple"]
print("Is 'apple' in trie after deletion?", "apple" in trie) # False
- In this example, we create a StringTrie, insert keys with associated values, and perform various operations like checking for key existence, retrieving values, and finding keys with common prefixes.
The pytrie library is a convenient tool for working with trie data structures in Python, making it easier to implement tasks like autocompletion, searching for words with common prefixes, and more.
Does Python have a trie data structure?
Python does not have a built-in trie data structure in its standard library. However, you can implement a trie data structure in Python using classes and data structures available in the language.
Final Analysis
The operation of Trie data structure is key to efficiently handling strings, especially when dealing with word searches and prefix matches. It makes tasks like autocomplete and spell check much faster.
Using Python, Tries can be implemented from scratch or through libraries like pytrie, making them easy to use in real-world applications where fast lookups are needed.
FAQs
Insertion, search, deletion, and prefix matching are the core operations supported by a Trie.
All major operations take O(K) time, where K is the length of the input string.
Tries are more efficient for prefix-based queries as they store shared prefixes, reducing redundancy.
No, Python doesn’t have a built-in Trie, but you can create one manually or use libraries like pytrie.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment