Linked List in Python
Introduction to Linked List in Python
A linked list in Python is a data structure used for storing a collection of elements, where each element, known as a “node,” contains both data and a reference to the next node in the sequence.
In this page, we will dive deep into understanding linked lists in Python, exploring their types, operations, and practical applications.

What is a Linked List in Python?
A linked list is a linear data structure where elements, known as nodes, are connected together using pointers or references. Each node contains two components: data and a reference (or link) to the next node in the sequence.
- Linked lists are versatile and can be used to implement various data structures like stacks, queues, and symbol tables.
Types of Linked List in Python
- Singly Linked List :
In a singly linked list, each node points to the next node in the sequence. It is the simplest form of a linked list and is often used when we need to traverse the list in one direction.
- Doubly Linked List :
A doubly linked list extends the concept of a singly linked list by adding an additional reference to the previous node. This bidirectional connection allows for more versatile operations but consumes additional memory.
- Circular Linked List :
In a circular linked list, the last node points back to the first node, forming a closed loop. This structure is advantageous in scenarios where we need continuous access to elements.
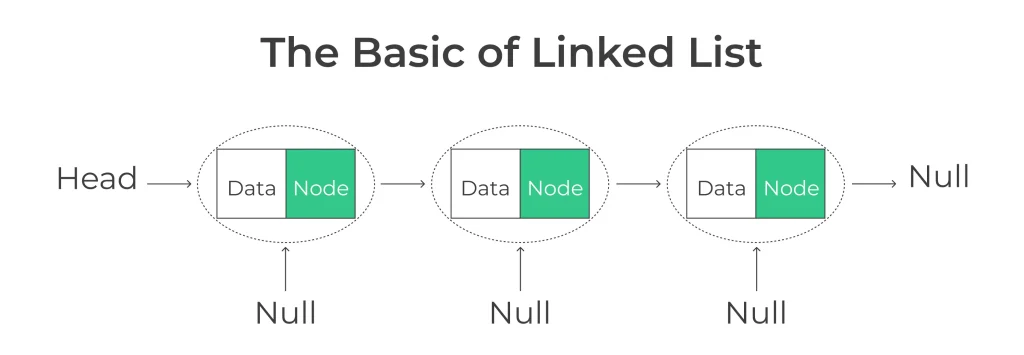
Creating a Linked List in Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Mastering Linked List Operations in Python
- Insertion Operation
- Deletion Operation
Insertion Operation
- Insertion at the Beginning : To insert a node at the beginning of the linked list, we modify the ‘head’ reference.
def insert_at_beginning(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
- Insertion at the End : To insert a node at the end, we traverse the list to find the last node:
def insert_at_end(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if not self.head:
self.head = new_node
return
current = self.head
while current.next:
current = current.next
current.next = new_node
Deletion Operations
- Deleting a Node by Value : To delete a node by its value, we find the node and update the references:
def delete_by_value(self, value):
current = self.head
if current and current.data == value:
self.head = current.next
current = None
return
prev = None
while current and current.data != value:
prev = current
current = current.next
if current is None:
return
prev.next = current.next
current = None
Understanding Singly vs. Doubly Linked Lists
| Aspect | Singly Linked List | Doubly Linked List |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A data structure where each node points to the next node in the list. | A data structure where each node points to both the next and the previous node in the list. |
| Nodes | Each node contains data and a reference (pointer) to the next node. | Each node contains data, a reference to the next node, and a reference to the previous node. |
| Traversing Forward | Easy and efficient. | Easy and efficient. |
| Traversing Backward | Not efficient; requires starting from the head and traversing the list. | Efficient; can traverse backward easily using the previous pointers. |
| Insertion/Deletion at Head | Efficient; O(1) complexity. | Efficient; O(1) complexity. |
| Insertion/Deletion at Tail | Inefficient; O(n) complexity as it requires traversing the entire list to reach the tail. | Efficient; O(1) complexity as the tail pointer is readily accessible. |
| Insertion/Deletion in Middle | Requires traversal to the insertion/deletion point; O(n) complexity. | Requires traversal to the insertion/deletion point; O(n) complexity. |
| Use Cases | Suitable for cases where forward traversal is the primary operation and memory efficiency is crucial. | Suitable for cases where both forward and backward traversal is required, and memory efficiency is not a significant concern. |
Advantages of Linked Lists in Python
- Dynamic Sizing: Linked lists can grow or shrink dynamically, optimizing memory usage.
- Efficient Insertions/Deletions: O(1) time complexity for inserting/deleting at the beginning.
- No Wasted Memory: Memory allocation only occurs when needed.
Conclusion
In this page, we’ve explored the world of linked lists in Python, covering their types, operations of linked list in python implementations, advantages, and real-world applications.
FAQs
A Python Linked List is a linear data structure where each element (node) points to the next, unlike Python lists which use contiguous memory. This allows for efficient insertions/deletions but slower indexing.
To create a Python Linked List, define a Node class with data and a pointer to the next node, and a Linked List class to manage the nodes. This setup enables dynamic memory usage for storing elements.
The time complexity depends on the position of insertion. In the worst case, it’s O(n) for singly linked lists and O(1) for doubly linked lists when inserting at the beginning.
Use a Python Linked List when frequent insertions/deletions are needed at arbitrary positions, as it’s more efficient than arrays in such cases. It’s especially useful in implementing stacks, queues, and graph algorithms.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment