Introduction to Priority Queues using Python
Introduction to Priority Queues using Python
Introduction to Priority Queues using Python enables us to perform various operations like insertion, deletion, and retrieval of data with optimal time complexity. Priority Queues ensure that elements with higher priority are served before those with lower priority. They are especially useful in scenarios like job scheduling and real time systems where task prioritization is crucial.
In this article, we’ll delve into the concept of Priority Queues, understand their significance, and explore how to implement them using Python.
Priority Queue Python
A Priority Queue is a type of data structure that stores elements with associated priorities. Unlike traditional queues, where elements are retrieved based on the order of insertion (FIFO),
- Priority Queues serve elements based on their priority values. Elements with higher priorities are dequeued before those with lower priorities.
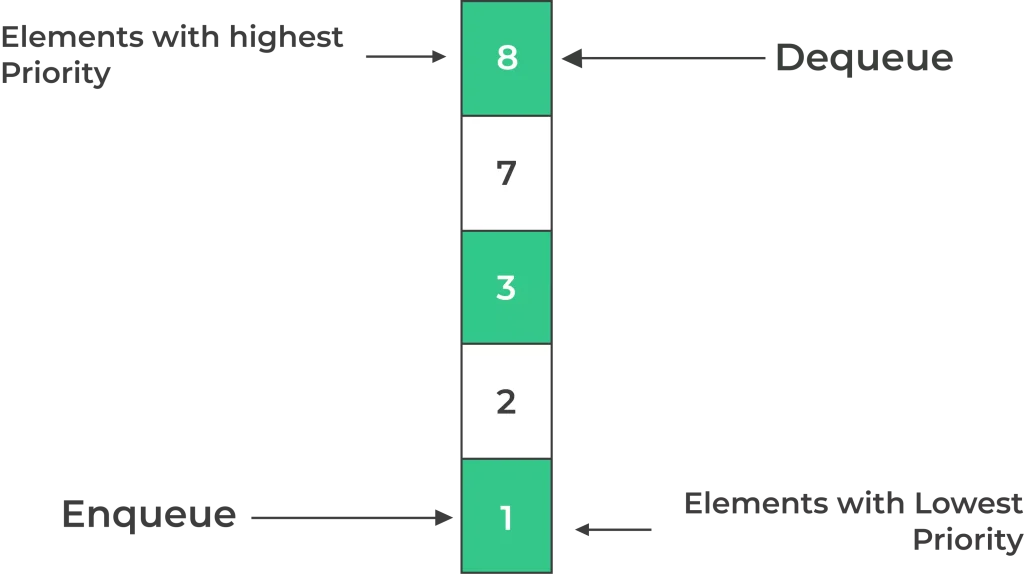
Types of Priority Queues
How to use Priority Queue in Python?
- Import the heapq module:
import heapq
- Create an empty list to represent your priority queue. You can use this list to store elements along with their priorities:
priority_queue = []
- Add elements to the priority queue using the heapq.heappush() function. Each element should be a tuple where the first element is the priority and the second element is the data:
heapq.heappush(priority_queue, (3, 'Task 1')) heapq.heappush(priority_queue, (1, 'Task 2')) heapq.heappush(priority_queue, (2, 'Task 3'))
- To retrieve the element with the highest priority, you can use the heapq.heappop() function:
highest_priority_task = heapq.heappop(priority_queue) print(highest_priority_task) # Output: (1, 'Task 2')
- You can continue adding elements and popping elements from the priority queue as needed.
- If you want to check if the priority queue is empty, you can use the len() function:
if len(priority_queue) == 0:
print("Priority queue is empty")
else:
print("Priority queue is not empty")
Recommended for you
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
How does Python priority queue sort?
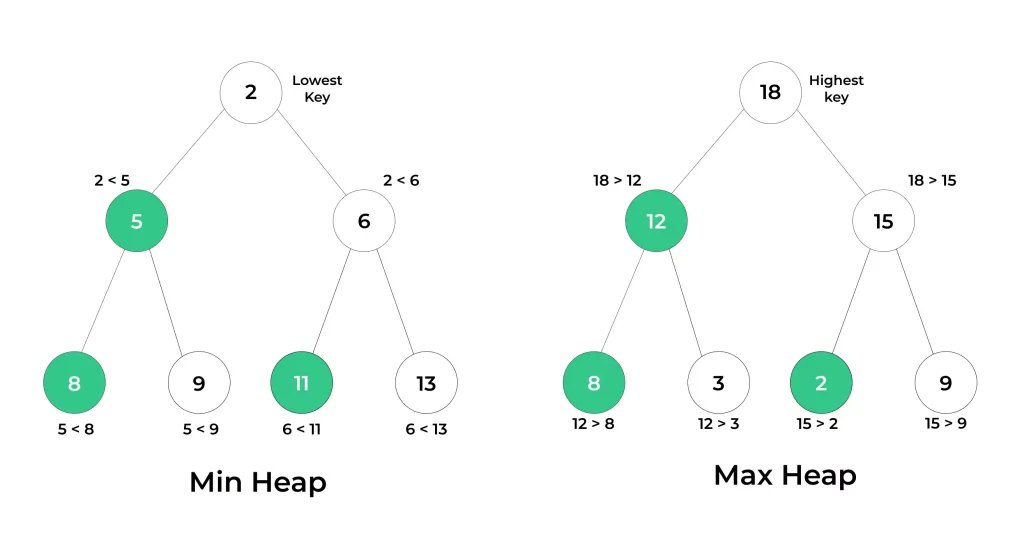
- In Python, a priority queue is typically implemented using the heapq module, which provides a heap-based priority queue.
- Python’s heapq module uses a min-heap to implement a priority queue. A min-heap is a binary tree where the parent node has a smaller (or equal) value than its children.
- When an element is inserted into a heapq priority queue, it is first added as a leaf node in the binary heap.
- The element is then "bubbled up" by swapping with its parent until the heap property is maintained.
- This process ensures that the smallest (highest priority) element remains at the root of the heap.
- To retrieve the highest priority (smallest) element in a min-heap, remove the root of the heap.
- The last leaf node is moved to the root position after removal.
- This node is then "bubbled down" by swapping with its smaller child until the heap property is restored.
What are the advantages of priority queues in Python?
Implementing Priority Queues in Python
Python offers multiple ways to implement Priority Queues. Let’s explore two common approaches:
- Using Lists
One straightforward way to create a Priority Queue in Python is by using lists. You can maintain a list of elements and sort them based on their priorities whenever necessary.
- Using Heaps
The heapq module in Python provides a convenient way to implement Priority Queues using binary heaps. Heaps ensure efficient operations, making them an ideal choice.
Using Lists:
A Priority Queue is a special type of queue where elements are dequeued based on their priority, not just their arrival order. Using lists, we can simulate this by inserting elements and sorting or picking the element with the highest or lowest priority.
Code:
class PriorityQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = []
def enqueue(self, data, priority):
self.queue.append((priority, data))
def dequeue(self):
if not self.queue:
return "Queue is empty"
# Find the element with the highest priority (lowest number)
self.queue.sort() # sort based on priority
return self.queue.pop(0)[1] # remove and return the highest priority data
def display(self):
for item in sorted(self.queue):
print(f"Data: {item[1]}, Priority: {item[0]}")
# Example Usage
pq = PriorityQueue()
pq.enqueue("Task 1", 3)
pq.enqueue("Task 2", 1)
pq.enqueue("Task 3", 2)
print("Priority Queue:")
pq.display()
print("\nDequeued element:", pq.dequeue())
print("\nPriority Queue after one dequeue:")
pq.display()
Output:
Priority Queue: Data: Task 2, Priority: 1 Data: Task 3, Priority: 2 Data: Task 1, Priority: 3 Dequeued element: Task 2 Priority Queue after one dequeue: Data: Task 3, Priority: 2 Data: Task 1, Priority: 3
Explanation:
- The queue stores tuples of the form (priority, data).
- enqueue() appends elements to the list.
- dequeue() sorts the list by priority and removes the element with the highest priority (lowest priority value).
- display() prints all items sorted by priority.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Enqueue | O(1) | O(n) |
| Dequeue | O(n log n) | O(n) |
| Display | O(n log n) | O(n) |
Using Heaps:
A Priority Queue is a special type of queue where each element is associated with a priority, and elements are served based on their priority (not just their insertion order). Using heaps, especially a min-heap, allows efficient implementation where the element with the highest priority (lowest value) is always at the top.
Code:
import heapq
class PriorityQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.heap = []
def push(self, item):
heapq.heappush(self.heap, item)
def pop(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return heapq.heappop(self.heap)
else:
return "Queue is empty"
def peek(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self.heap[0]
else:
return "Queue is empty"
def is_empty(self):
return len(self.heap) == 0
# Example usage
pq = PriorityQueue()
pq.push(10)
pq.push(5)
pq.push(15)
pq.push(1)
print("Top Element:", pq.peek()) # Should print 1
print("Removed:", pq.pop()) # Should remove 1
print("Removed:", pq.pop()) # Should remove 5
print("Is Empty?", pq.is_empty()) # Should print False
Output:
Top Element: 1 Removed: 1 Removed: 5 Is Empty? False
Explanation:
- The PriorityQueue class uses the built-in heapq module which provides an efficient implementation of a min-heap.
- The push() method adds an element while maintaining the heap property.
- The pop() method removes and returns the smallest element (highest priority).
- peek() gives the top element without removing it.
- is_empty() checks if the queue has any elements left.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion (push) | O(log n) | O(n) |
| Deletion (pop) | O(log n) | O(n) |
| Peek (peek) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Check Empty (is_empty) | O(1) | O(1) |
In Closing
In this article, we’ve introduced you to the world of Priority Queues. We’ve explored their significance, types, operations, and implementation in Python. Understanding Priority Queues can significantly enhance your ability to tackle complex problems in the realm of computer science and programming.
FAQs
A Priority Queue is a special type of queue in which each element is associated with a priority, and elements are served based on their priority. In Python, it can be implemented using heapq, which provides a min-heap by default.
In a regular queue, elements are dequeued in the order they were enqueued (FIFO), while in a priority queue, the element with the highest priority (lowest value in min-heap) is dequeued first.
Python’s heapq module allows implementation of a priority queue using lists. Functions like heapq.heappush() and heapq.heappop() manage insertion and removal efficiently.
Insertion and deletion in a priority queue implemented via a binary heap take O(log n) time, while peeking at the top priority element takes O(1) time.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment