Insertion in Doubly Linked List in Python
Insertion in Doubly Linked List in Python
Doubly linked lists are a fundamental data structure in computer science and are often used in various applications to efficiently manage and manipulate data.
In this page, we will explore how to perform insertion in doubly linked list using Python. We will cover different scenarios and techniques for inserting elements at various positions within the list

Understanding Doubly Linked Lists in Python
A Doubly Linked List is a data structure that consists of a set of nodes, where each node contains both data and two pointers: one pointing to the next node and another pointing to the previous node. This bidirectional linking enables efficient traversal in both directions.
Elements of Doubly Linked List
Data : This is the actual information or value that the node holds. It can be of any data type, depending on the application’s requirements. For example, in a list of student records, the data may include the student’s name, ID, and grade.
Next Pointer : The “next” pointer, also known as the “forward” or “next node” pointer, points to the next node in the list. It helps in navigating from the current node to the next node when traversing the list in the forward direction.
Previous Pointer : The “previous” pointer, also known as the “backward” or “previous node” pointer, points to the previous node in the list. It facilitates traversal in the reverse direction, allowing you to move from the current node to the previous node.
Doubly Linked List
# Define a Node class to represent a doubly linked list node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.prev = None
- Always update both prev and next pointers when inserting a node
- Handle edge cases like inserting at head or tail carefully
- Validate the position before performing an insertion
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Insertion in Doubly Linked-list
For each insertion operation, we need to consider the three cases. These three cases also need to be considered when removing data from the doubly linked list.
- Insertion at the beginning
- Insertion at end
- Insertion at Nth position
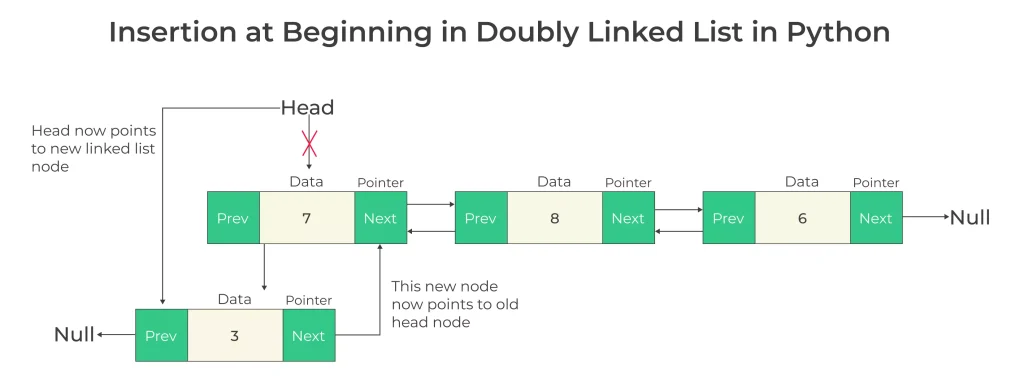
Insertion at Beginning in Doubly Linked List in Python
Create a new node with the desired data.
Update the pointers of the new node to point to the current first node and NULL for the previous node.
Update the previous pointer of the current first node to point to the new node.
Update the head pointer to point to the new node, making it the new first node.
# Function to create a new node
def createNode(data):
new_node = Node(data) # Assuming you have the Node class defined as shown earlier
return new_node
# Create a new node
newNode = createNode(data)
# Update pointers
newNode.next = head
newNode.prev = None
# Update the previous pointer of the current first node
if head is not None:
head.prev = newNode
# Update the head pointer
head = newNode
Python Code(Insertion at Beginning)
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def insert_at_beginning(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
else:
new_node.next = self.head
self.head.prev = new_node
self.head = new_node
def display(self):
temp = self.head
while temp:
print(temp.data, end=" <-> ")
temp = temp.next
print("None")
# Example usage
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
dll.insert_at_beginning(6)
dll.insert_at_beginning(8)
dll.insert_at_beginning(7)
dll.display()
Output:
7 <-> 8 <-> 6 <-> None
Explanation:
- A new node is created with the given value using the Node class.
- When inserting:
- If the list is empty, the new node becomes the head.
- If the list is not empty:
- The new node’s next points to the current head.
- The current head’s prev points back to the new node.
- The head is updated to the new node.
- This ensures constant-time (O(1)) insertion at the beginning.
- display() prints the list from start to end using the next pointers.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at Beginning | O(1) | O(1) |
| Traversal (Display) | O(n) | O(1) |
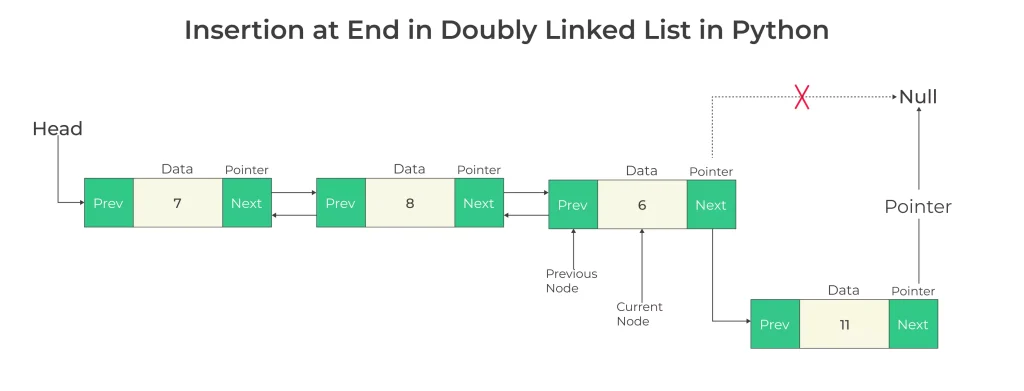
Insertion at End in Doubly Linked List in Python
Create a new node with the desired data.
Traverse the list to find the last node.
Update the pointers of the new node to point to the current last node as the previous node and NULL as the next node.
Update the next pointer of the current last node to point to the new node.
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
# Create a new node
newNode = createNode(data)
# Traverse to find the last node
current = head
while current.next is not None:
current = current.next
# Update pointers
newNode.prev = current
newNode.next = None
current.next = newNode
Python Code(Insertion at End)
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def insert_at_end(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
else:
temp = self.head
while temp.next:
temp = temp.next
temp.next = new_node
new_node.prev = temp
def display(self):
temp = self.head
while temp:
print(temp.data, end=" <-> ")
temp = temp.next
print("None")
# Example usage
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
dll.insert_at_end(7)
dll.insert_at_end(8)
dll.insert_at_end(6)
dll.display()
Output:
7 <-> 8 <-> 6 <-> None
- A new node is created using the Node class with the provided value.
- If the list is empty, the new node becomes the head.
- If the list already has nodes:
- Traverse to the last node using while temp.next.
- Set last_node.next to the new node.
- Set new_node.prev to the last node.
- This appends the new node at the end of the list.
- display() prints all nodes from head to tail.
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at End | O(n) | O(1) |
| Traversal (Display) | O(n) | O(1) |
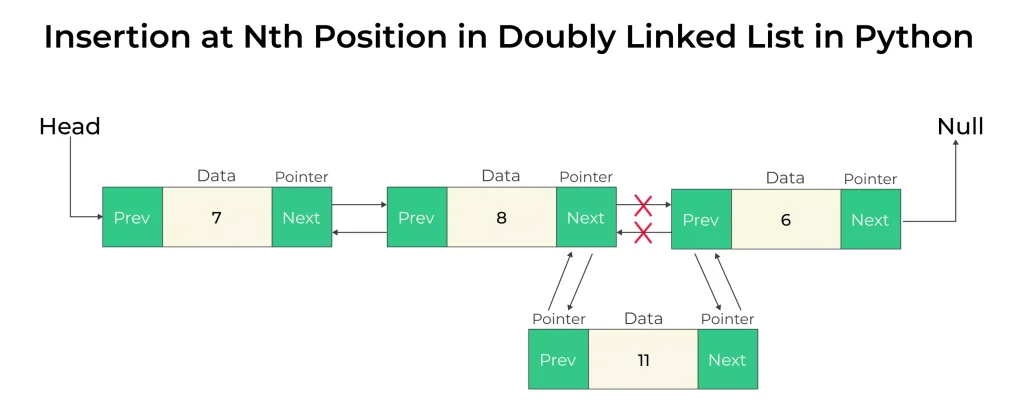
Insertion at Nth Position in Doubly Linked List in Python
- Calculate the size of the node
- If the position you want to enter is less than 1
- If the position you want to enter is greater than size then
- else create a temp node and assign it the address of the head
- Create a new node and assign it the data value Iterate to the position you want to enter after in the linked list
- Assign this new node’s next and previous nodes
- Assign previous node’s next to this new node
- Assign next node’s previous to this new node
- Invalid position But, if 0 then use insertAtStart method
- Invalid position, but if the position is equal to size then use insertLast method
Python Code(Insertion at Nth Position)
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def insert_at_position(self, data, position):
new_node = Node(data)
if position == 1:
if self.head:
new_node.next = self.head
self.head.prev = new_node
self.head = new_node
return
temp = self.head
for _ in range(position - 2):
if temp is None:
print("Position out of range")
return
temp = temp.next
if temp is None:
print("Position out of range")
return
new_node.next = temp.next
new_node.prev = temp
if temp.next:
temp.next.prev = new_node
temp.next = new_node
def display(self):
temp = self.head
while temp:
print(temp.data, end=" <-> ")
temp = temp.next
print("None")
# Example usage
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
dll.insert_at_position(7, 1) # Insert at position 1
dll.insert_at_position(8, 2) # Insert at position 2
dll.insert_at_position(6, 2) # Insert at position 2
dll.display()
Output:
7 <-> 6 <-> 8 <-> None
Explanation:
- A Node class is defined with data, prev, and next.
- The insert_at_position method inserts a new node at a given position:
- If inserting at position 1, it becomes the new head.
- Else, traverse the list to the (position – 1)th node.
- Adjust next and prev pointers of surrounding nodes to insert the new node.
- Proper boundary checks are added for invalid positions.
- The display() function shows the list from head to tail.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at Nth Position | O(n) | O(1) |
| Traversal (Display) | O(n) | O(1) |
Singly vs Doubly Linked List Insertion in python
| Property | Singly Linked List | Doubly Linked List |
|---|---|---|
| Data Structure | Each node contains data and a reference to the next node. | Each node contains data, a reference to the next node, and a reference to the previous node. |
| Insertion at the Beginning | O(1) | O(1) |
| Insertion at the End | O(n) – Requires traversing the entire list to find the last node. | O(1) – Can directly access the last node. |
| Insertion at a Specific Position | O(n) – Requires traversing the list to find the desired position. | O(n) – Requires traversing the list to find the desired position. |
| Insertion after a Node | O(1) if you have a reference to the node, O(n) if you need to find the node first. | O(1) if you have a reference to the node, O(n) if you need to find the node first. |
| Deletion Efficiency | O(n) – Requires traversing to find and remove the node. | O(1) – Can directly remove a node if you have a reference to it. |
| Traversal Efficiency | O(n) – Requires traversing the list from the beginning. | O(n) – Can traverse forward and backward. |
| Use Cases | Suitable when primarily dealing with forward traversal. Memory-efficient for simple scenarios. | Suitable when frequent forward and backward traversal is needed. Offers more flexibility but with higher memory overhead. |
To wrap it up:
In this page, we have discussed about insertion in doubly linked list in Python and concept of doubly linked lists and how to perform various insertion operations in python. We’ve covered inserting at the beginning, inserting at the end, and inserting at Nth position. These operations are crucial when working with doubly linked lists and can be adapted to suit your specific needs in different programming scenarios.
FAQs
Inserting at the beginning places the new node before the current head and updates the head pointer accordingly. Inserting at the end requires traversing the list to the last node and updating its next pointer to the new node.
To insert at a specific position, you traverse the list until the desired spot and adjust the prev and next pointers of surrounding nodes. This maintains the proper linking of the list and avoids breaking the sequence.
When the list is empty, the inserted node becomes both the head and tail of the list. Its prev and next pointers are set to None as it is the only node present.
In a doubly linked list, each node connects in both directions, so updating both pointers is necessary. This ensures the list can be navigated forward and backward without errors.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others



