Insertion at Beginning in Circular Linked List in Python
Insertion at Beginning in Circular Linked List in Python
In the realm of data structures, linked lists are fundamental. Among them, circular linked lists present a unique twist. They not only have the standard features of a singly linked list but also form a closed loop.
In this page, we will explore how to perform insertion at beginning in circular linked list using Python. We will cover different scenarios and techniques for inserting elements in terms of Naïve Approach and Optimized Approach.

Understanding Circular Linked List Insertion
Linked lists are fundamental data structures, but circular linked lists add an extra layer of complexity and versatility. Inserting a node at the beginning of a circular linked list may seem straightforward at first glance, but there are multiple ways to achieve this, each with its own advantages and drawbacks.
In a circular linked list, the last node is connected to the first node, forming a closed loop. This unique structure allows for efficient traversal and certain operations, making it particularly useful in specific scenarios.
Circular Linked List Algorithm :
- Initialize: Create a structure for the linked list node, including data and a pointer to the next node.
- Create an Empty Circular Linked List: Initialize a pointer, say head, to NULL to represent an empty list.
- Insertion at the Start: To insert a new node at the beginning of the circular linked list:
- Create a new node with the desired data.
- If the list is empty (head is NULL), set the new node’s next pointer to itself and update head to point to the new node.
- If the list is not empty, set the new node’s next pointer to the current head.
- Update the last node’s next pointer to the new node (making it circular).
- Update head to point to the new node.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
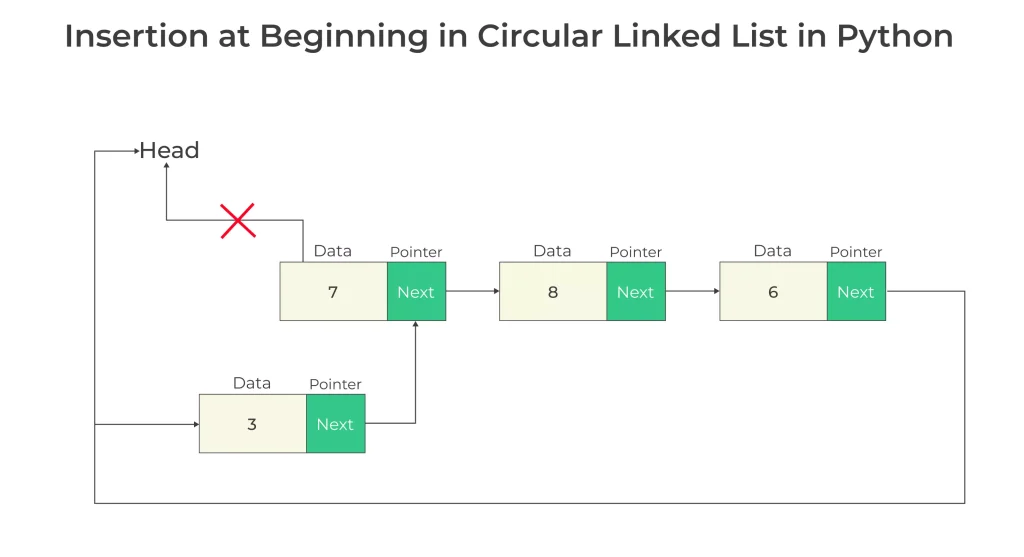
Circular Linked List Insertion at Beginning in Python
For each Insertion operation, we need to consider the two cases.
- Naïve Approach
- Optimized Approach
Naïve Approach for Insertion at Beginning in Circular Linked List
Step 1: Create a New Node
To add a new node at the start, first create a new node with the desired data
Step 2: Link the New Node
- Set the next pointer of the new node to the current head of the circular linked list.
Step 3: Update the Head
- Now, update the head pointer to point to the new node.
Implementation of Circular Linked List in Python(Naïve Approach) :
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class CircularLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def append(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if not self.head:
self.head = new_node
self.head.next = self.head # Point to itself
else:
temp = self.head
while temp.next != self.head:
temp = temp.next
temp.next = new_node
new_node.next = self.head
def display(self):
nodes = []
if not self.head:
print("List is empty")
return
temp = self.head
while True:
nodes.append(str(temp.data))
temp = temp.next
if temp == self.head:
break
print(" -> ".join(nodes) + " -> (back to head)")
# Example usage
cll = CircularLinkedList()
cll.append(10)
cll.append(20)
cll.append(30)
cll.display()
Output:
10 -> 20 -> 30 -> (back to head)
Explanation:
- Each node has data and a next pointer.
- Head points to the first node.
- If list is empty, new node points to itself.
- Otherwise, last node links to new node, and new node links to head.
- Display prints until it loops back to head.
- No None in the list — it’s fully circular.
Optimized Approach for Insertion at Beginning in Circular Linked List
Step 1: Create a New Node
Similar to the naïve approach, start by creating a new node with the desired data.
Step 2: Link the New Node
- Set the next pointer of the new node to the current head.
Step 3: Update the Last Node
- Find the last node in the circular linked list and update its next pointer to the new node.
Step 4: Update the Head
- Finally, update the head pointer to point to the new node.
Implementation of Circular Linked List in Python(Optimized Approach) :
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class CircularLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None # Keep track of the last node
def append(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if not self.head:
self.head = new_node
self.tail = new_node
new_node.next = self.head
else:
self.tail.next = new_node
self.tail = new_node
self.tail.next = self.head # Maintain circular link
def display(self):
if not self.head:
print("List is empty")
return
temp = self.head
result = []
while True:
result.append(str(temp.data))
temp = temp.next
if temp == self.head:
break
print(" -> ".join(result) + " -> (back to head)")
# Example usage
cll = CircularLinkedList()
cll.append(10)
cll.append(20)
cll.append(30)
cll.display()
Output:
10 -> 20 -> 30 -> (back to head)
Explanation:
- Each node stores data and next.
- Tail pointer avoids full traversal for insertion.
- First node links to itself; tail equals head.
- On new insertions, tail.next updated and tail moved.
- Circular link is maintained by tail.next = head.
- Display continues until loop returns to head.
To wrap it up:
In this page, we have discussed about concept of “Insertion at Beginning in Circular Linked Lists in Python” using both naïve and optimized approaches. While the naïve approach is simple to understand, the optimized approach offers improved efficiency with constant time complexity. Understanding the nuances of circular linked lists and their insertion methods can be invaluable in solving various programming challenges.
FAQs
To insert at the beginning, a new node is created and linked to the current head, while the last node’s next pointer is updated to point to the new node.
After inserting, the new node becomes the new head, and the previous last node is made to point to this new head to maintain the circular structure.
If the list is empty, the new node is made to point to itself and becomes both the head and tail of the circular linked list.
Yes, it’s efficient with O(1) time complexity as it involves only pointer adjustments without the need for traversal.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment