Deletion in Doubly Linked List in Python
Deletion in Doubly Linked List in Python
Doubly linked lists are a fundamental data structure in computer science and are often used in various applications to efficiently manage and manipulate data.
In this page, we will explore how to perform deletion in doubly linked list using Python. We will cover different scenarios and techniques for deleting elements at various positions within the list

Understanding Deletion in Doubly Linked Lists in Python
A Doubly Linked List is a data structure that consists of a set of nodes, where each node contains both data and two pointers: one pointing to the next node and another pointing to the previous node. This bidirectional linking enables efficient traversal in both directions.
Deletion in Doubly linked list in Python involves removing a specific node from the list. Doubly linked lists consist of nodes, where each node contains two parts: data and a reference (or a pointer) to the next node in the list. To delete a node from a linked list, you typically need to update the references to ensure that the deleted node is no longer part of the list.
Elements of Doubly Linked List
Data : This is the actual information or value that the node holds. It can be of any data type, depending on the application’s requirements. For example, in a list of student records, the data may include the student’s name, ID, and grade.
Next Pointer : The “next” pointer, also known as the “forward” or “next node” pointer, points to the next node in the list. It helps in navigating from the current node to the next node when traversing the list in the forward direction.
Previous Pointer : The “previous” pointer, also known as the “backward” or “previous node” pointer, points to the previous node in the list. It facilitates traversal in the reverse direction, allowing you to move from the current node to the previous node.
Deleting Nodes in Python Doubly Linked Lists
Deleting a node from a doubly linked list involves a few essential steps.
Step 1: Locate the Node to Delete
- Before deleting a node, we must find the node we want to remove. This typically involves traversing the list using a loop until we find the node with the desired data value.
Step 2: Update Pointers
- Once we’ve located the node to delete, we need to update the pointers of the adjacent nodes to bypass the node we’re deleting. This includes changing the ‘next’ pointer of the previous node to point to the next node and the ‘previous’ pointer of the next node to point to the previous node.
Step 3: Delete the Node
- After updating the pointers, we can safely delete the node from memory. In Python, memory management is typically automatic through garbage collection.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Deletion in Doubly Linked-list in Python
For each deletion operation, we need to consider the three cases.
- Deletion at the beginning
- Deletion at Middle
- Deletion at End
Deletion at Beginning in Doubly Linked List in Python
Algorithm
- Check if there is only 1 node or not
- If there is one node
- Assign head to NULL
- Free memory
- Else
- Assign head to next node in the list
- Assign head->prev to NULL
- Free memory
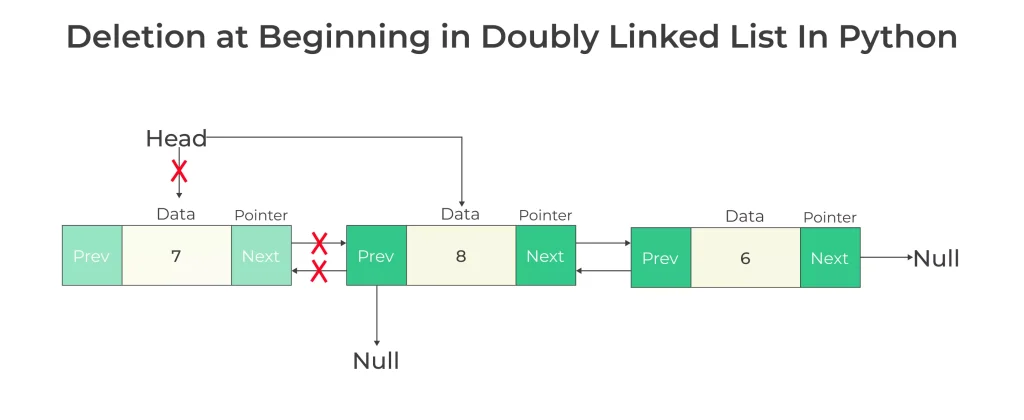
Function for deletion at beginning in doubly linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def insert_at_end(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
return
curr = self.head
while curr.next:
curr = curr.next
curr.next = new_node
new_node.prev = curr
def delete_at_beginning(self):
if self.head is None:
print("List is empty. Nothing to delete.")
return
if self.head.next is None:
self.head = None
else:
self.head = self.head.next
self.head.prev = None
def display(self):
curr = self.head
while curr:
print(curr.data, end=" <-> ")
curr = curr.next
print("None")
# Example usage
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
dll.insert_at_end(7)
dll.insert_at_end(8)
dll.insert_at_end(6)
print("Original List:")
dll.display()
dll.delete_at_beginning() # Deletes 7
print("After Deletion at Beginning (7 deleted):")
dll.display()
Output:
Original List: 7 <-> 8 <-> 6 <-> None After Deletion at Beginning (7 deleted): 8 <-> 6 <-> None
Explanation:
- We created a doubly linked list and inserted nodes 7, 8, and 6 at the end.
- The delete_at_beginning() method removes the first node (7) from the list.
- head is updated to the next node (8), and its prev is set to None.
- The updated list after deletion is printed: 8 <-> 6 <-> None.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at End | O(n) | O(1) |
| Deletion at Beginning | O(1) | O(1) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
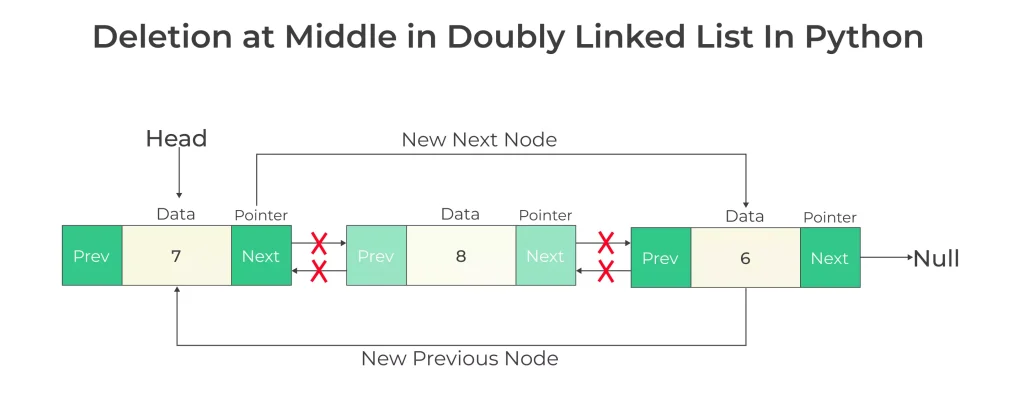
Deletion at Middle in Doubly Linked List in Python
Algorithm
- Traverse till the target node
- create a node called the previous storing previous node of the target node
- Assign previous node’s next pointer to the next node of the target node
- For the next node of the target node, its previous pointer is assigned to the targets node’s previous node’s address
- Free memory of target node
Function for deletion at Middle in doubly linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def insert_at_end(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
return
curr = self.head
while curr.next:
curr = curr.next
curr.next = new_node
new_node.prev = curr
def delete_node(self, key):
if self.head is None:
print("List is empty.")
return
curr = self.head
# If the node to be deleted is the head
if curr.data == key:
if curr.next:
self.head = curr.next
self.head.prev = None
else:
self.head = None
return
# Traverse to find the node to delete
while curr and curr.data != key:
curr = curr.next
if curr is None:
print(f"Node with value {key} not found.")
return
# If node is not last node
if curr.next:
curr.prev.next = curr.next
curr.next.prev = curr.prev
else:
# If node is the last node
curr.prev.next = None
def display(self):
curr = self.head
while curr:
print(curr.data, end=" <-> ")
curr = curr.next
print("None")
# Example usage
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
dll.insert_at_end(7)
dll.insert_at_end(8)
dll.insert_at_end(6)
print("Original List:")
dll.display()
dll.delete_node(8) # Deleting the middle node
print("After Deletion at Middle (8 deleted):")
dll.display()
Output:
Original List: 7 <-> 8 <-> 6 <-> None After Deletion at Middle (8 deleted): 7 <-> 6 <-> None
Explanation:
- A doubly linked list is created with elements 7, 8, and 6.
- The delete_node() method searches for the node with value 8 (middle node).
- If found:
- It updates prev.next to skip the current node.
- It updates next.prev to bypass the deleted node.
- The list after deletion is printed: 7 <-> 6 <-> None.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at End | O(n) | O(1) |
| Deletion at Middle | O(n) | O(1) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
Deletion at End in Doubly Linked List in Python
- Traverse till the target node
- Check if this is the last node i.e. if node->next = NULL, then its last node
- Assign last node’s previous node’s next pointer to the last node’s next node’s address, which basically is NULL in this case
- Free the memory
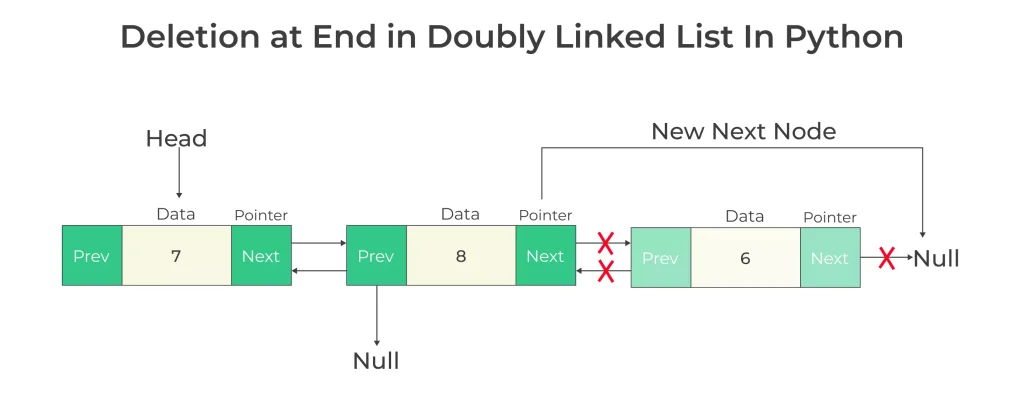
Function for deletion at End in doubly linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def delete_end(self):
if self.head is None:
print("Linked List Empty, nothing to delete")
return
temp_node = self.head
if temp_node.next is None:
print(f"{temp_node.data} deleted")
self.head = None
return
# Traverse to the last node
while temp_node.next is not None:
temp_node = temp_node.next
second_last = temp_node.prev
# Assign 2nd last node's next to None
second_last.next = None
print(f"{temp_node.data} deleted")
del temp_node
# Usage example:
# Create a doubly linked list
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
# Insert some nodes (you can add more if needed)
node1 = Node(1)
node2 = Node(2)
node3 = Node(3)
dll.head = node1
node1.next = node2
node2.prev = node1
node2.next = node3
node3.prev = node2
# Delete the last node
dll.delete_end()
Output:
Original List: 7 <-> 8 <-> 6 <-> None After Deletion at End (6 deleted): 7 <-> 8 <-> None
Explanation:
- We insert nodes 7, 8, and 6 into a doubly linked list.
- The delete_at_end() method is called:
- It checks if the list is empty or has one node.
- It then traverses to the last node (6).
- The second-last node’s next is set to None, effectively removing the last node.
- After deletion, the list becomes: 7 <-> 8 <-> None.
Time and Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion at End | O(n) | O(1) |
| Deletion at End | O(n) | O(1) |
| Display List | O(n) | O(1) |
Python Code for Deletion in a Doubly Linked List
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def insert_at_end(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
return
curr = self.head
while curr.next:
curr = curr.next
curr.next = new_node
new_node.prev = curr
def delete_at_end(self):
if self.head is None:
print("List is empty. Nothing to delete.")
return
if self.head.next is None:
self.head = None
return
curr = self.head
while curr.next:
curr = curr.next
curr.prev.next = None # Remove the last node
def display(self):
curr = self.head
while curr:
print(curr.data, end=" <-> ")
curr = curr.next
print("None")
# Example usage
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
dll.insert_at_end(7)
dll.insert_at_end(8)
dll.insert_at_end(6)
print("Original List:")
dll.display()
dll.delete_at_end() # Deletes 6
print("After Deletion at End (6 deleted):")
dll.display()
To wrap it up:
In this page, Deletion in Doubly Linked List in Python, we have discussed about the understanding the different scenarios for deletion and implementing them correctly is crucial for efficient data manipulation. Doubly linked lists provide an excellent foundation for various data-related tasks.
FAQs
Deletion in a doubly linked list can occur at the beginning, end, or any middle position using node references. Each type requires pointer adjustment of both prev and next nodes.
We move the head to the next node and set its prev to None. The previous first node becomes unreachable and gets deleted by the garbage collector.
The prev pointer of the next node and the next pointer of the previous node are updated to skip the target node. This isolates the middle node for deletion.
We traverse to the last node and move the prev node’s next pointer to None. This removes the last node from the list structure.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment