Circular Queue in C++
Circular queue in C++
A Circular Queue in C++ is a special type of linear queue where the last position is linked back to the first, forming a circular structure. It follows the FIFO (First In First Out) principle but uses memory more efficiently by reusing empty spaces created after deletions. This is why it is also known as a Ring Buffer.
Circular queues are commonly used in scenarios like task scheduling, buffering, and managing real-time data, making them a practical and optimized version of a standard queue.

Why Circular Queues?
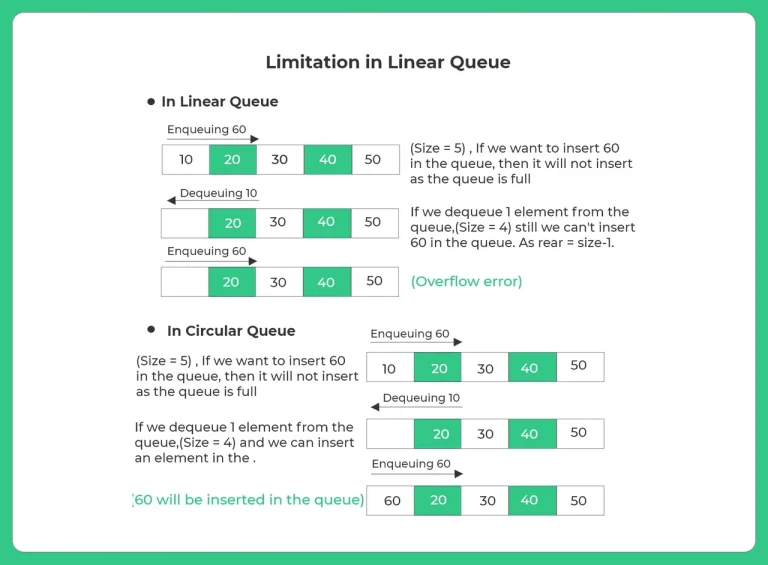
Once the queue becomes full, we can not insert more elements. Even though we dequeue few of the elements.
Because the following code –
//Overflow check condition
if (rear == SIZE-1)
cout<<"Overflow condition";
- After each enqueue, rear value is incremented & once queue is full rear value becomes equal to size – 1
//Enqueue function
void Enqueue(){
rear++;
}
//Dequeue Function
void Dequeue(){
front–;
}
- So no more elements can be entered & even if dequeue happens, as it only changes the front value & not rear value.
Operations on circular queue :
- front : Get the front item from the queue.
- rear : Get the last item from the queue.
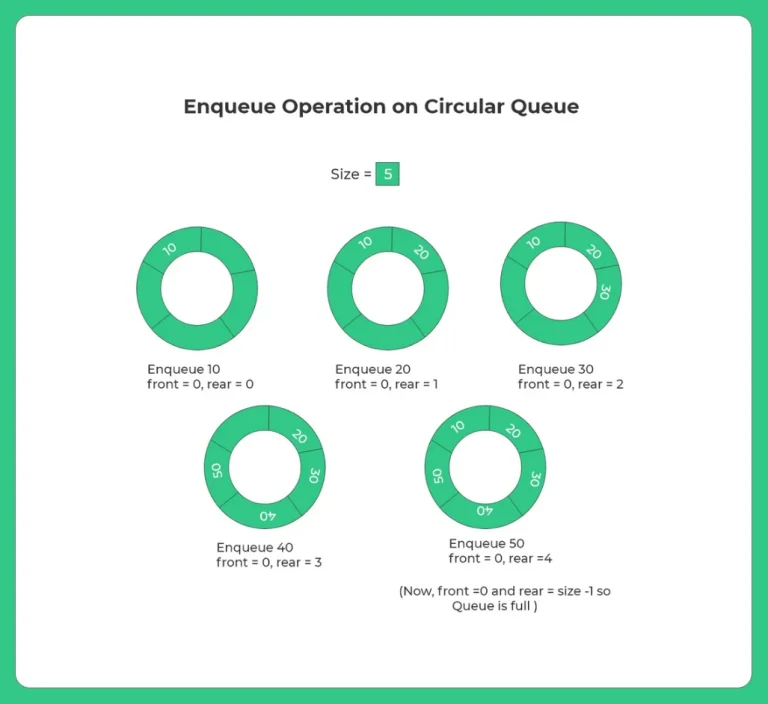
- enQueue() : This function is used to enqueue the element into the circular queue. New element will be added at the rear end of the queue.
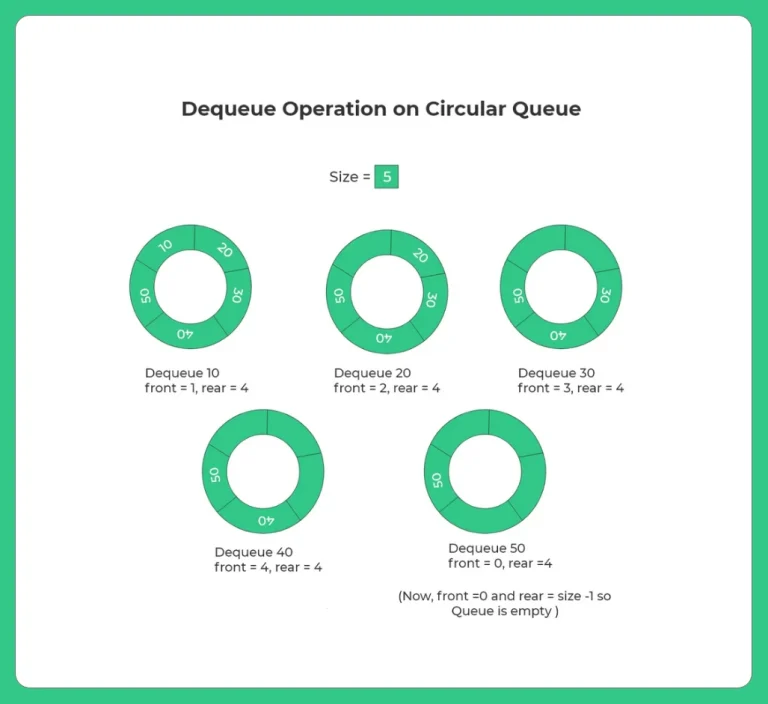
- deQueue() : This function is used to delete the element from the circular queue. Delete operation is done from the front end of the queue.
C++ Program for the implementation of circular queue given below:
A C++ program for implementing a circular queue demonstrates how elements are stored in a circular manner, allowing efficient use of memory without shifting elements. It uses front and rear pointers to manage insertions and deletions in a FIFO order.
- Circular queues prevent overflow by reusing empty spaces using modular arithmetic.
- They offer efficient enqueue and dequeue operations with constant time complexity.
Run
//Circular queue C++ program
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Queue
{
// Initialize front and rear
int rear, front;
// Circular Queue
int size;
int *arr;
Queue (int s){
front = rear = -1;
size = s;
arr = new int[s];
}
void enQueue (int value);
int deQueue ();
void displayQueue ();
};
/* Function to create Circular queue */
void Queue::enQueue (int value)
{
if ((front == 0 && rear == size - 1) || (rear == (front - 1) % (size - 1)))
{
cout << "\nQueue is Full";
return;
}
else if (front == -1) /* Insert First Element */
{
front = rear = 0;
arr[rear] = value;
}
else if (rear == size - 1 && front != 0)
{
rear = 0;
arr[rear] = value;
}
else{
rear++;
arr[rear] = value;
}
}
// Function to delete element from Circular Queue
int Queue::deQueue ()
{
if (front == -1)
{
cout << "\nQueue is Empty";
return INT_MIN;
}
int data = arr[front];
arr[front] = -1;
if (front == rear)
{
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
else if (front == size - 1)
front = 0;
else
front++;
return data;
}
// Function displaying the elements
// of Circular Queue
void Queue::displayQueue ()
{
if (front == -1)
{
cout << "\nQueue is Empty";
return;
}
cout << "\nElements in Circular Queue are: ";
if (rear >= front)
{
for (int i = front; i <= rear; i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
}
else
{
for (int i = front; i < size; i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
for (int i = 0; i <= rear; i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
}
}
int main ()
{
Queue q (5);
// Inserting elements in Circular Queue
q.enQueue (10);
q.enQueue (20);
q.enQueue (30);
q.enQueue (40);
// Display elements present in Circular Queue
q.displayQueue ();
// Deleting elements from Circular Queue
cout << "\nDeleted value = " << q.deQueue ();
cout << "\nDeleted value = " << q.deQueue ();
q.displayQueue ();
q.enQueue (50);
q.enQueue (60);
q.enQueue (70);
q.displayQueue ();
return 0;
}Output:
Elements in circular queue are : 10 20 30 40 Deleted element = 10 Deleted element =20 Elements in circular queue are : 30 40 Elements in circular queue are : 30 40 50 60 70
Explanation:
- The circular queue uses a fixed-size array that wraps around when the rear pointer reaches the end, ensuring efficient utilization of space.
- The enQueue() function checks overflow accurately and updates the rear pointer by either incrementing or wrapping it to zero.
- The deQueue() function prevents underflow and resets both front and rear to -1 when the last element is removed.
- The front pointer is updated correctly by either moving forward or wrapping back to zero based on its current position.
- The displayQueue() function prints elements in the correct sequence even when the queue structure has wrapped around the array.
Time & Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Enqueue (Insert) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Dequeue (Delete) | O(1) | O(1) |
| Display Queue | O(n) | O(1) |
| Overall Space Used | — | O(n) |
To wrap it up:
A circular queue in C++ offers an efficient way to manage data using a fixed size structure where the last position connects back to the first. This design removes unnecessary shifting of elements and ensures smooth, continuous insertion and deletion. It is widely used in scenarios like buffering, scheduling, and memory-optimized operations.
Understanding the working of enQueue(), deQueue(), and wrap-around logic helps you build faster and more reliable programs. With its efficient use of space and constant-time operations, a circular queue becomes an essential tool for anyone aiming to strengthen their DSA and C++ programming skills.
FAQs
A circular queue is a linear data structure where the last position connects back to the first, forming a loop. It efficiently utilizes space by preventing unused gaps after deletions.
Circular queues avoid the problem of wasted space that occurs in regular queues after multiple deletions. They allow both insertion and deletion to happen smoothly using the same fixed-size array.
Overflow happens when the next position of rear equals front, indicating the queue is full. Underflow occurs when both front and rear are -1, meaning the queue is empty.
Both insertion and deletion operations take O(1) time. This makes circular queues highly efficient for real-time or repeated data processing tasks.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment