Two Dimensional Array in C
Two Dimensional Array in C
On this page we will discuss about two dimensional array in C .The Representation of matrix i.e with the help of rows and column in C programming language is known as two dimensional matrix Array.
A matrix is a representation of rows and column. While Declaring 2d Array, we must declare the size of column. Same as single dimensional Array, Indexing of rows and column starts with 0 and goes till one less than the size of array.
why should we use 2d array in programming ?
Remember the scenario we had taken while learning single dimensional array (introduction of arrays in C) where you have to store the marks of 50 students. So, you can take the array of float or integer type array with size 50. But, if you have to enter the marks of 50 students in 5 subjects. Then, the first method is to create 50 array like float stduent1 [5], float student2 [5], float student3 [5] and so on.
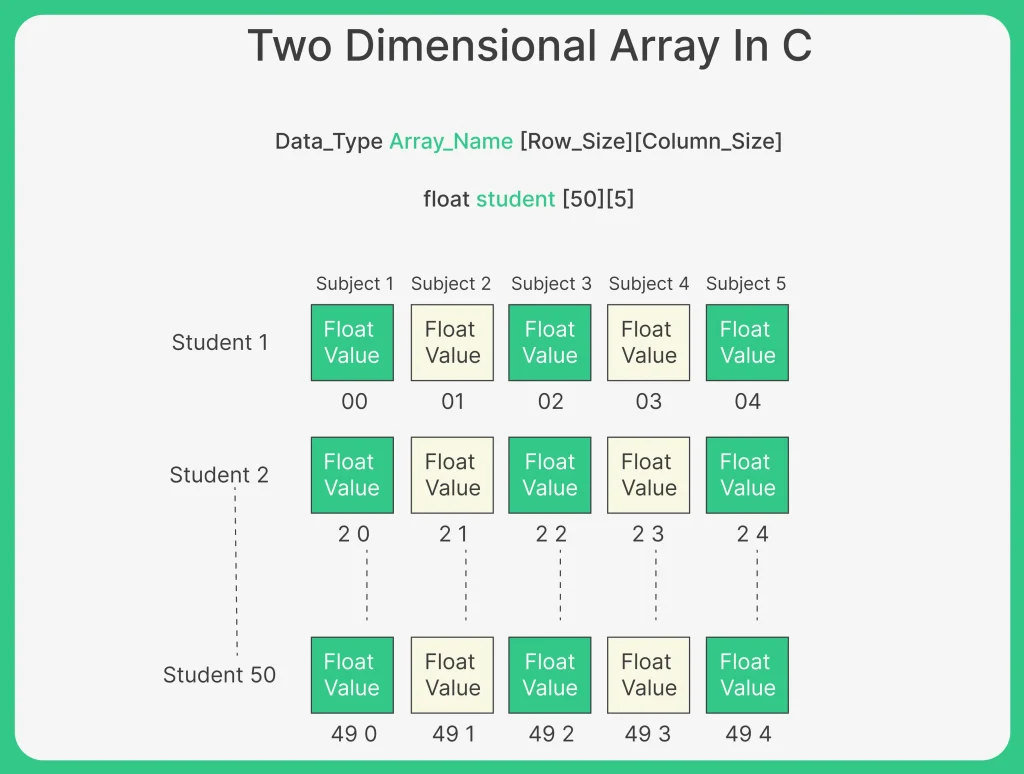

The better and the most efficient way is to create 2 dimensional array in the form of matrix where each row represent student number and each column represent subject number. The size of rows would be 50 while the size of column would be 5
Declaration of two dimensional array in C
Declaration of two dimensional array in C programming language can be done in following ways.
Syntax : Data_type array_name [Row_size][Column_size] ;
Note : While Declaring the two dimensional array we must declare the size of column, while the size of row can be blank.
Example :
Correct Declaration
integer Array : int student [50][5]; or int student [ ][5];
float Array : float student [50][5]; or float student [ ][5];
Incorrect Declaration
int student [ ][ ]; or int student [50][ ];
float student [ ][ ]; or float student [ ][ ];
We can also declare the 2d array after taking size the size of row and column from user itself.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n, m;
printf("enter number of rows : ");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter number of columns : ");
scanf("%d",&n);
int student[n][m];
return 0;
}Initialization of two dimension array in C programming Language
we can initialize the two dimensional array in C programming language at the compile time or at the run time.
Initialization of two dimensional array at compile time
Initialization of Array at compile means declaring the elements of array before running the code.
The code given below contains two array first is integer array with name student and the second array of integer type with name teacher.
The initialization of elements of array is done while writing the code itself.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
//Initialization type - 1
int student [3][3] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
//Initialization type - 2
int teacher [3][3] = {{11,12,13},{14,15,16},{17,18,19}};
return 0;
}
Initialization of two dimensional array at run time
Initialization of Array at run time means declaring the elements of array after running the code.
The code given contains a two dimensional integer array with name student with 3 rows and 3 columns while the element of array will be taken as input from the user.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int student [3][3];
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<3; j++)
{
scanf("%d",&student[i][j]);
}
}
return 0;
}
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Accessing two dimension array in C programming Language
we can access the two dimensional array in C programming language by using the index number of the element
NOTE : index number is 1 less than the element number because indexing starts from 0 for both rows and column.
let us consider the scenario where teacher has to enter the marks of n number of students in m number of subject, now teacher has to calculate the sum of marks of each student and print it one after the other.
C code
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n, m;
printf("Enter number of students : ");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Enter number of subjects : ");
scanf("%d",&m);
int student [n][m];
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<m; j++)
{
printf("Enter student %d subject %d marks : ",i+1, j+1);
scanf("%d",&student[i][j]);
}
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
sum = 0;
for(int j=0; j<m; j++)
{
sum = sum + student[i][j];
}
printf("Total marks of %d student is : %d\n",i+1, sum);
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter number of students : 3 Enter number of subjects : 4 Enter student 1 subject 1 marks : 60 Enter student 1 subject 2 marks : 73 Enter student 1 subject 3 marks : 88 Enter student 1 subject 4 marks : 84 Enter student 2 subject 1 marks : 90 Enter student 2 subject 2 marks : 65 Enter student 2 subject 3 marks : 78 Enter student 2 subject 4 marks : 80 Enter student 3 subject 1 marks : 82 Enter student 3 subject 2 marks : 76 Enter student 3 subject 3 marks : 79 Enter student 3 subject 4 marks : 84 Total marks of 1 student is : 305 Total marks of 2 student is : 313 Total marks of 3 student is : 321
In closing
Two dimensional arrays in C offer a powerful and efficient way to manage and organize data in matrix form. They simplify handling complex data like student marks or tabular data structures, making programs cleaner and more scalable.
By understanding how to declare, initialize, and access 2D arrays, you’re equipped to solve real-world problems with more flexibility. Mastering these fundamentals forms a strong base for advanced programming in C.
FAQs
A two dimensional array is a collection of elements arranged in rows and columns, like a matrix. It is used to store data in table format, such as marks of students in multiple subjects.
You can declare it using the syntax: data_type array_name[row_size][column_size];. The column size is mandatory, but the row size can be omitted during declaration.
Elements are accessed using two indices: one for the row and one for the column, starting from 0. For example, arr[1][2] refers to the element in the second row and third column.
Yes, using Variable Length Arrays (VLA), you can take row and column sizes at runtime. However, this feature requires C99 or above for support.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment