Breadth First Search (BFS) In C
Tree Traversal : Breadth First Search (BFS)
Breadth-first search (BFS) in C is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree data structures. It starts at the tree root (or some arbitrary node of a graph, sometimes referred to as a search key and explores all of the neighbor nodes at the present depth prior to moving on to the nodes at the next depth level.
Breadth First Search (BFS) In C
Steps for Breadth First Search Tree Treaversal
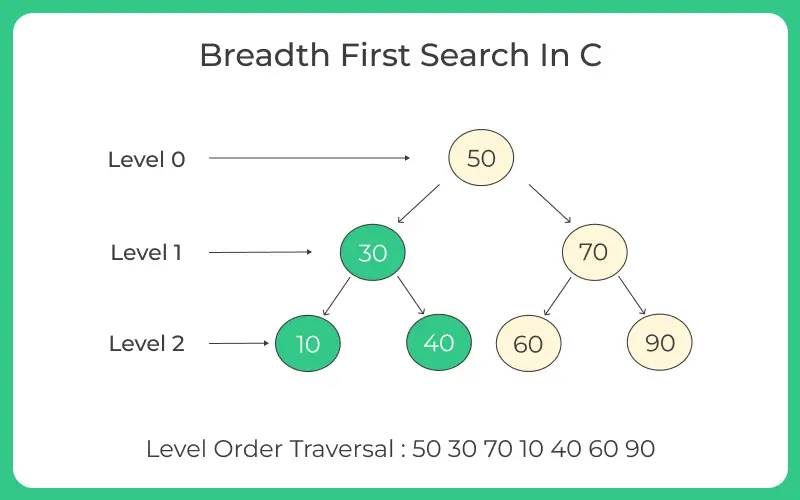
- Step 1 : Push the root i.e. 50 to the queue.
- Step 2 : Pop the element 50 from the queue and print it.
- Step 3 : Now, Add it’s left and right child i.e. add 30 and 70 to queue.
- Step 4 : Again pop the front element i.e. 30 from queue and print it .
- Step 5 : Add it’s left and right child i.e. 10 and 40 in the queue.
- Step 6 : Pop the element 70 from the queue and print it.
- Step 7 : add it’s left and right child i.e. 60 and 90.
- Step 8 : Now pop all the elements from the queue and print them as there is no child of these elements.
Therefore the printing sequence will be 50 30 70 10 40 60 90 .
Algorithm
- If the root is NULL, return.
- Otherwise push the root in queue.
- Pop the node from the queue.
- Print the node’s data and add its left and right child.
- Repeat until the queue is empty.
Implementation of Breadth First Search In C
Run
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 100
typedef struct Node
{
int value;
struct Node *left;
struct Node *right;
} Node;
typedef struct Queue
{
Node *items[MAX_QUEUE_SIZE];
int front;
int rear;
} Queue;
void enqueue (Queue * q, Node * item)
{
if (q->rear == MAX_QUEUE_SIZE - 1)
{
printf ("Queue Overflow\n");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
q->rear++;
q->items[q->rear] = item;
}
Node *dequeue (Queue * q)
{
if (q->front == q->rear)
{
printf ("Queue Underflow\n");
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
q->front++;
return q->items[q->front];
}
int
is_empty (Queue * q)
{
return q->front == q->rear;
}
void bfs (Node * root)
{
Queue q;
q.front = -1;
q.rear = -1;
enqueue (&q, root);
while (!is_empty (&q))
{
Node *current = dequeue (&q);
printf ("%d ", current->value);
if (current->left != NULL)
{
enqueue (&q, current->left);
}
if (current->right != NULL)
{
enqueue (&q, current->right);
}
}
}
int main ()
{
Node *root = (Node *) malloc (sizeof (Node));
root->value = 1;
Node *node1 = (Node *) malloc (sizeof (Node));
node1->value = 2;
Node *node2 = (Node *) malloc (sizeof (Node));
node2->value = 3;
Node *node3 = (Node *) malloc (sizeof (Node));
node3->value = 4;
Node *node4 = (Node *) malloc (sizeof (Node));
node4->value = 5;
Node *node5 = (Node *) malloc (sizeof (Node));
node5->value = 6;
root->left = node1;
root->right = node2;
node1->left = node3;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node5;
node2->right = NULL;
node3->left = NULL;
node3->right = NULL;
node4->left = NULL;
node4->right = NULL;
node5->left = NULL;
node5->right = NULL;
bfs (root);
return 0;
}
Output:
1 2 3 4 5 6



Login/Signup to comment