C Program to Reverse a linked list in groups of given size
Reverse a linked list in groups of given size
C Program to Reverse a linked list in groups of given size. In this we will reverse the sub-nodes of the linked list according to the user given size, it is somehow same as reverse the nodes of the linked list which is not a big deal to reverse nodes of the linked list.
For Example:-
- Input:- 31 -> 12 -> 4-> 24 -> 65 -> 76 ->7 -> 18; m = 2(given size by user)
- Output:- 12 -> 31 -> 24 -> 4 -> 76 -> 65 -> 18 -> 7; reverse of nodes as per user group size is 2.
- To learn more about this steps and code are given in C Programming Language.

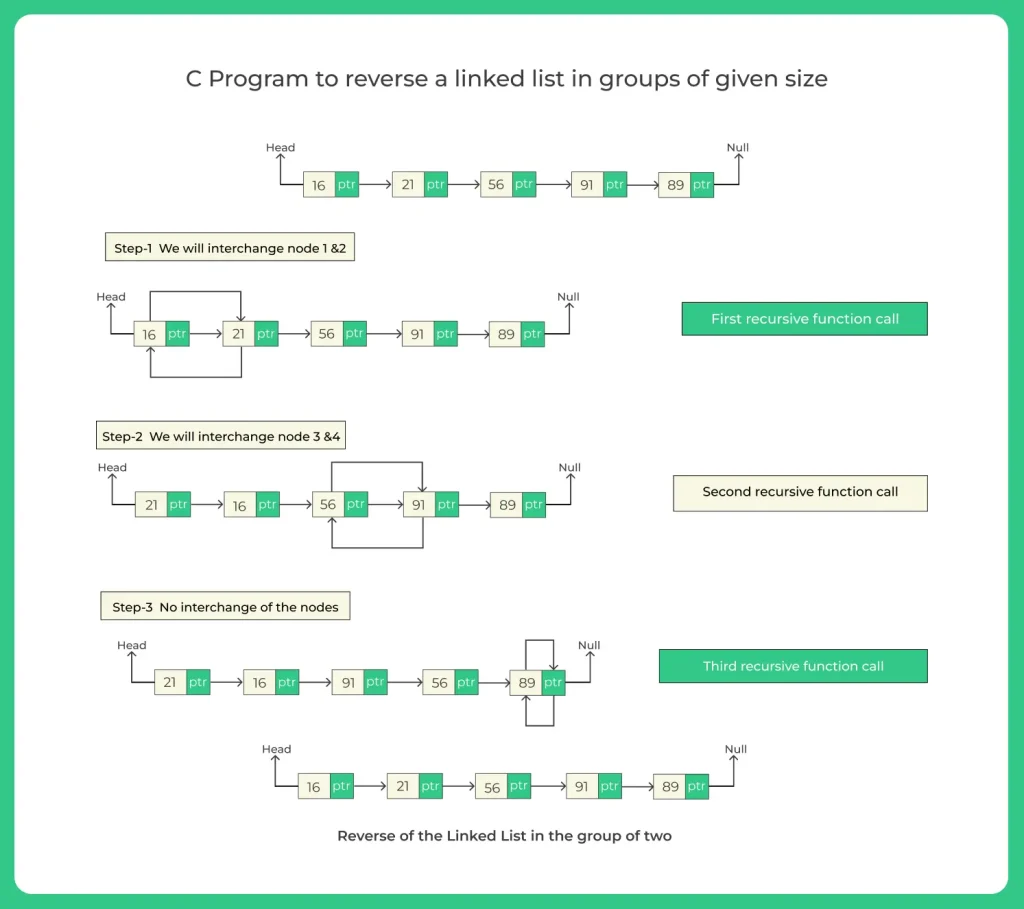
Steps required for Reverse a linked list in groups of given size:-
- First of all we have to reverse the first sub nodes of the size m according to the user requirement.
- While reversing the linked list keep observe the next node and previous node.
- Now lets take the pointer to the next node be next and pointer to the previous node be prev.
- Then take as head -> next = reverse (next, m).
- Return prev.
Structure for creating node in the singly linked list:-
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
C Program to Reverse a linked list in groups of given size
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node // Structure of node
{
int item;
struct Node *next;
};
/* this function reverses the linked list in groups of size m and
returns the pointer to the new head node*/
struct Node *reverse (struct Node *head, int m)
{
struct Node *current = head;
struct Node *next = NULL;
struct Node *previous = NULL;
int counter = 0;
//reverse first m nodes of the linked list
while (current != NULL && counter < m) { next = current->next;
current->next = previous;
previous = current;
current = next;
counter++;
}
if (next != NULL)
head->next = reverse (next, m);
return previous;
}
void print_List (struct Node *node) //print function of the list
{
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->item);
node = node->next;
}
}
void insert (struct Node **head_ref, int new_data) //insert the data
{
struct Node *new_node = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
new_node->item = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
insert (&head, 91);
insert (&head, 58);
insert (&head, 17);
insert (&head, 45);
insert (&head, 53);
insert (&head, 1);
insert (&head, 8);
insert (&head, 64);
insert (&head, 15);
insert (&head, 20);
printf ("The linked list is: \n");
print_List (head);
head = reverse (head, 4);
printf
("\nReverse a Linked List in groups of given size like m = 4 here: \n");
print_List (head);
return (0);
}
Output:- The linked list is: 20 15 64 8 1 53 45 17 58 91 Reverse a Linked List in groups of given size like m = 4 here: 8 64 15 20 17 45 53 1 91 58
Final Thoughts
Reversing a linked list in groups of a given size is a common interview question that helps you understand how to work with pointers and recursion in C. By breaking the list into smaller chunks and reversing each group, we make the problem more manageable and learn how to handle linked lists in parts. This technique is especially useful in real-world problems like batch processing or memory-efficient data handling.
Once you understand the logic and practice it a few times, you’ll see that it’s not as difficult as it looks. Just take it step by step – reverse a group, connect it with the next, and keep going until the end of the list.
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Frequently Asked Questions - FAQs
It means breaking the linked list into smaller parts (groups) of a specific size (say k), then reversing the nodes inside each group, while keeping the rest of the list structure intact.
Yes, if the total number of nodes isn’t a perfect multiple of the group size, the last group may have fewer nodes. In most cases, it’s still reversed normally.
Both methods can be used. In our blog, we mainly used recursion because it makes the code cleaner and easier to understand for group-wise reversal.
If the group size is 1, the list remains the same after reversal because each node is considered its own group. If it’s less than 1, the logic may break — so we should always check for valid group sizes.
This technique is useful in situations like processing data in batches, handling limited memory chunks, or implementing operations in stages like in networking or streaming applications.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others



Login/Signup to comment