Juggling algorithm for array rotation C
Juggling-Algorithm for array rotation in C
Here in this program we’ll be learning about Juggling-Algorithm for array rotation in C. Juggling-algorithm is one of the efficient algorithms used for array rotation. Now, let’s discuss about juggling-algorithm and a program to rotate an array using the juggling-algorithm.

Keypoint
In this section we will learn about basic knowledge which we need to know before coding the above Program. So we must have knowledge of what is an array?
What is an array?
An array is a data structure, it is collection of similar data elements which is stored at contiguous memory locations in which each data element can be accessed directly by only using its index number.
How to declare an array?
To declare an array in C,a programmer specifies the type of the elements and the number of elements required by an array as follows − This is called a single-dimensional array. The arraySize must be an integer constant greater than zero and type can be any valid C data type. For example, to declare a 10-element array called balanceof type double, use this statement − Here balanceis a variable array which is sufficient to hold up to 10 double numbers.
Algorithm :
- In this method, divide the array into M sets, where M = GCD (n, k), and then rotate the elements in each set.
- From the number of elements ( n ) of the array and number of rotations ( k ) to be made to the array, the GCD(n, k) number of blocks are made.
- Then in each block, shifting will take place to the corresponding elements in the block.
- After all the elements in all the blocks are shifted, the array will be rotated for the given number of times.
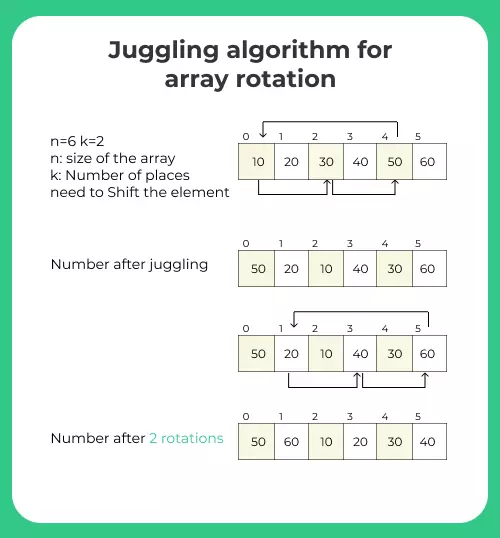
- Example: If we want to rotate the array Arr : {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60} by 2 positions :
- M = GCD(60, 20) = 20
- Initial Array : 10 20 30 40 50 60
- First Set Moves : 50 20 10 40 30 60
- Second Set Moves : 50 60 10 20 30 40
Juggling algorithm for array rotation C
#include<stdio.h>
int gcd(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0)
return a;
else
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
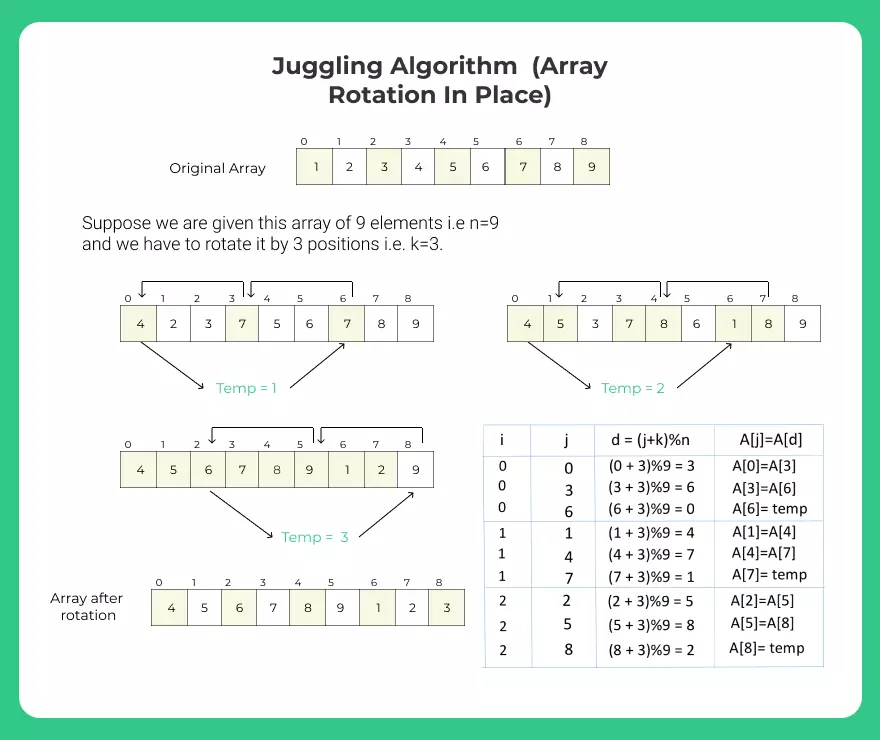
void ArrayRotate(int A[], int n, int k) {
int d = -1, i, temp, j;
for (i = 0; i < gcd(n, k); i++) {
j = i;
temp = A[i];
while (1) {
d = (j + k) % n;
if (d == i) break;
A[j] = A[d];
j = d;
}
A[j] = temp;
}
}
void displayArray(int A[], int n) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) printf("%d ", A[i]);
printf("
");
}
int main() {
int n = 9, i, k = 3;
printf("The size of the Array %d", n);
int A[n] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
printf("The Array elements");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) printf("%d ", A[i]);
printf("The value of k %d", k);
displayArray(A, n);
ArrayRotate(A, n, k);
displayArray(A, n);
return 0;
}Output:
The size of the Array 9
The Array elements
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
The value of k 3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
4 5 6 7 8 9 1 2 3




Login/Signup to comment