Introduction to Arrays in C
Introduction to Arrays in C Language
On this page we will discuss about introduction to arrays in C . Arrays are the kind of data structure which can be defined as the collection of similar type of elements arranged in contiguous memory allocation.
Arrays in C are used to store multiple values of the same data type in a single variable, making data handling more efficient. They help manage large sets of data using a single name with index-based access.

Introduction To Arrays In C Programming
- Arrays are the derived data types in C programming Language.
- Array can store the elements of all primitive data type such as int, char, float, double etc.
- Arrays can also store the collection of derived data types such as pointers, structures etc.
- While Storing the elements in contiguous fashion the lowest address corresponds to the first element of array
Why should we use array in Programming
Let us consider a scenario where you have to store the marks of 5 students, you can use 5 float variables as student1, student2, and so on. But, if you have to store the marks of 100 students this method would takes a lot of time.
The most efficient way to get this task done is to create an float array with name as student and size as 100.
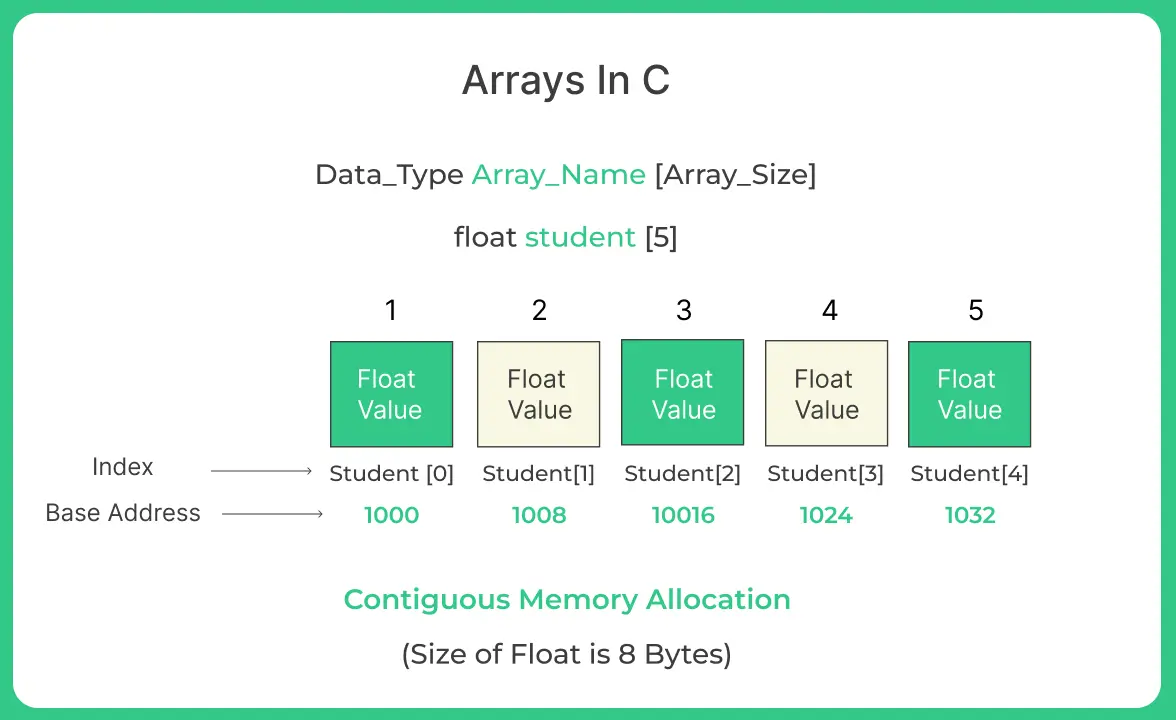
Declaration of Arrays in C Programming Language
Declaration of Array can be done by the following way in C Languge:
Syntax : Data_type array_name [Array_size] ;
Example :
integer Array : int student [50];
char Array : char student [50]; (Character Array is also known as String in C Programming Language)
float Array : float student [50];
double Array : double student [50];
Initialization of Arrays in C Programming Language
Array can be initialized in C programming language in the compile time or in the run time.
Initialization of Array in Compile Time
Initialization of Array at compile means declaring the elements of array before running the code at the time of declaration which can be done as follow:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
//integer array
int student[5] = {60, 70, 65, 80, 85};
//float array
float student[5] = {60.0, 75.5, 80.0, 67.0, 83.5};
return 0;
} Initialization of Array in Run Time
Initialization of Array at Run Time means declaring the elements of array after running the code. Here, elements are taken from user.
we can also set the the size of array when we initialize array at run time.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n; //size of array
scanf("%d",&n);
int student[n]; //array
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
scanf("%d",&student[i]);
return 0;
} Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Accessing the elements of Arrays in C Programming Language
The elements of array can be accessed by programmer with the help of index number of the element.
Note: 1st element is present at the 0th index, 2nd element is present at the 1st index, and so on.
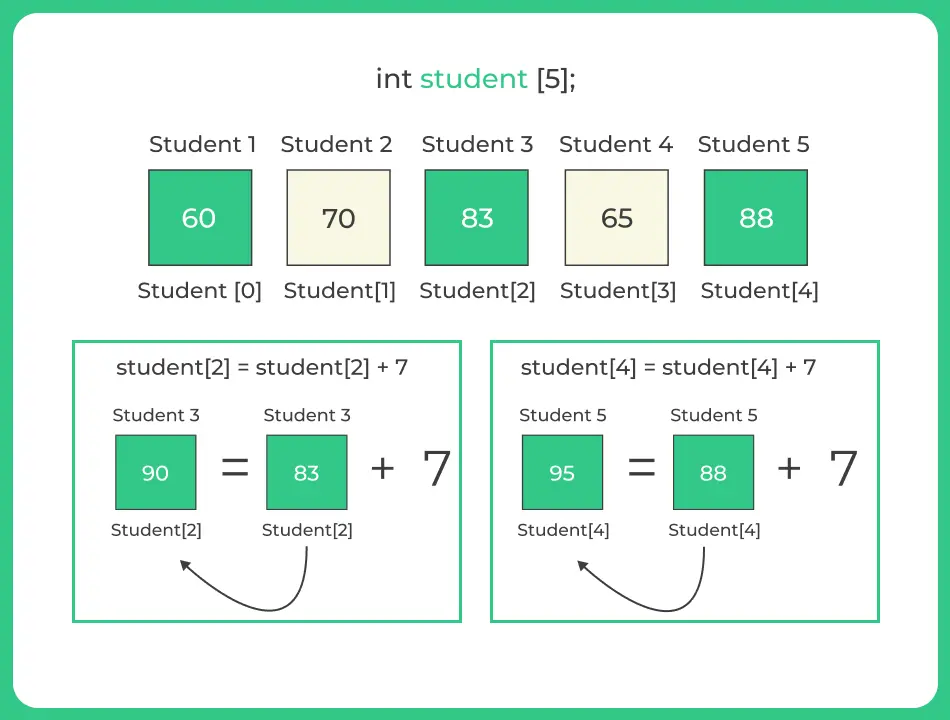
Let us consider another scenario where teacher has to input marks of 5 students, and has to calculate the average of marks, but before calculating the average teacher notice that the marks of 3rd and 5th student needs to incremented by 7.
This can be solved in C programming Language as follows
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n; //size of array
scanf("%d",&n);
int student[n]; //decleration of array
int average, sum=0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&student[i]); //initialization of array
}
student[2] = student[2] + 7; //accessing 3rd element
student[4] = student[4] + 7; //accessing 5th element
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
sum = sum + student[i]; //accessing elements via loop
}
average = sum / n; //calculating average
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
printf("Marks of student %d : %d\n", i+1,student[i]);
}
printf("Sum is : %d\n",sum);
printf("Average is : %d",average);
return 0;
}
Output
5
60 70 83 65 88
Marks of student 1 : 60
Marks of student 2 : 70
Marks of student 3 : 90
Marks of student 4 : 65
Marks of student 5 : 95
Sum is : 380
Average is : 76
Key Concepts of Arrays in C
| Concept | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Declaration | Defines an array with a specific size | int student[50]; |
| Compile-Time Initialization | Assigns values at the time of declaration | int student[5] = {60, 70, 80, 90, 100}; |
| Run-Time Initialization | User inputs values during program execution | scanf("%d", &student[i]); |
| Element Access | Accessing/modifying using index (starting from 0) | student[2] = student[2] + 7; |
| Memory Allocation | Array elements are stored in contiguous memory | Proved using &student[i] |
| Data Type Flexibility | Arrays can be of any data type like int, float, char | float marks[100]; |
Proving Array follows Contagious Memory Allocation
The program given below proves that the Array follows contagious memory allocation
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int student[5] = {60, 70, 83, 65, 88};
printf("Size of integer in this compiler is %d\n",sizeof(int));
for(int i=0 ;i<5 ;i++)
{
printf("Address student[%d] is %d\n", i, &student[i]);
}
return 0;
}Output
Size of integer in this compiler is 4
Address student[0] is 6422280
Address student[1] is 6422284
Address student[2] is 6422288
Address student[3] is 6422292
Address student[4] is 6422296
- Array size must be a constant value in standard C (unless using dynamic memory).
- Index out of bounds access (like arr[10] in an array of size 5) results in undefined behavior.
- Arrays can be of any data type: int, float, char, etc.
Closing Remarks
Arrays in C provide a structured way to store and access multiple values of the same data type efficiently using index based referencing. They significantly reduce the complexity of managing large datasets in programs.
With their ability to store elements in contiguous memory, arrays improve both speed and organization in programming. Whether it’s compile-time or run-time initialization, mastering arrays is essential for any C programmer.
FAQs
Arrays help manage multiple variables of the same type using a single identifier, making code simpler and more memory efficient.
In C, arrays are zero indexed, meaning the first element is accessed with index 0.
No, an array can only store elements of a single data type, though that type can be a derived one like struct or pointer.
Array elements are stored in contiguous memory locations, which can be verified by printing the address of each element.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment