Insertion in a Binary Tree (Level Order) in C
Insertion in a binary tree
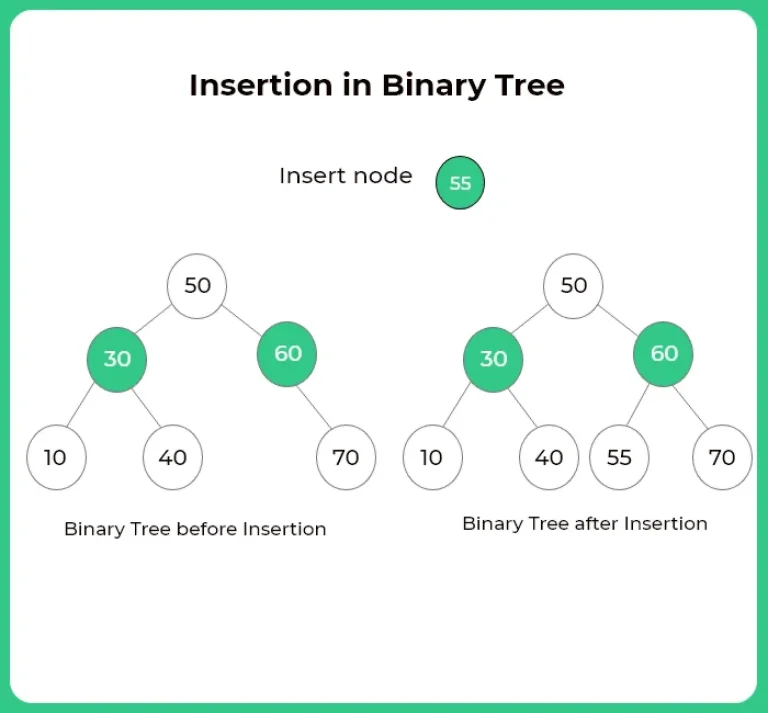
Given a tree and a key, add a node in the first available node in the tree. After adding the node, print the level order traversal. In this article, Queue data structure is used to add a node.

Insertion in a Binary Tree In C
Algorithm :
- Create a queue q.
- If root is NULL, add node and return.
- Else continue until q is not empty.
- If a child does not exists, add the node there.
- Otherwise add the node to the leftmost node.
C code for insertion a node in binary tree
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left;
struct Node *right;
};
struct Node *newNode (int data)
{
struct Node *Node = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return (Node);
};
void printCurrentLevel (struct Node *root, int level);
int height (struct Node *node);
int height (struct Node *node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
else
{
/* compute the height of each subtree */
int lheight = height (node->left);
int rheight = height (node->right);
/* use the larger one */
if (lheight > rheight)
return (lheight + 1);
else
return (rheight + 1);
}
}
void printLevelOrder (struct Node *root)
{
int h = height (root);
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= h; i++)
printCurrentLevel (root, i);
} /* Print nodes at a current level */
void printCurrentLevel (struct Node *root, int level)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (level == 1)
printf ("%d ", root->data);
else if (level > 1)
{
printCurrentLevel (root->left, level - 1);
printCurrentLevel (root->right, level - 1);
}
}
struct Node *insert (struct Node *root, int val)
{
if (root == NULL)
return newNode (val);
if (root->data < val)
root->right = insert (root->right, val);
else if (root->data > val)
root->left = insert (root->left, val);
return root;
}
// Driver code
int main ()
{
struct Node *root = newNode (10);
root->left = newNode (11);
root->left->left = newNode (7);
root->right = newNode (9);
root->right->left = newNode (15);
root->right->right = newNode (8);
printf ("Level order traversal before insertion: ");
printLevelOrder (root);
printf ("\n");
int key = 12;
root = insert (root, key);
printf ("Level order traversal after insertion: ");
printLevelOrder (root);
printf ("\n");
return 0;
}
Output :
Level order traversal before insertion : 10 11 9 7 15 8
Level order traversal after insertion : 10 11 9 7 15 8 12



Login/Signup to comment