C Program for Insertion at the nth node of Singly Linked List
Insertion at the nth node of the Singly Linked List
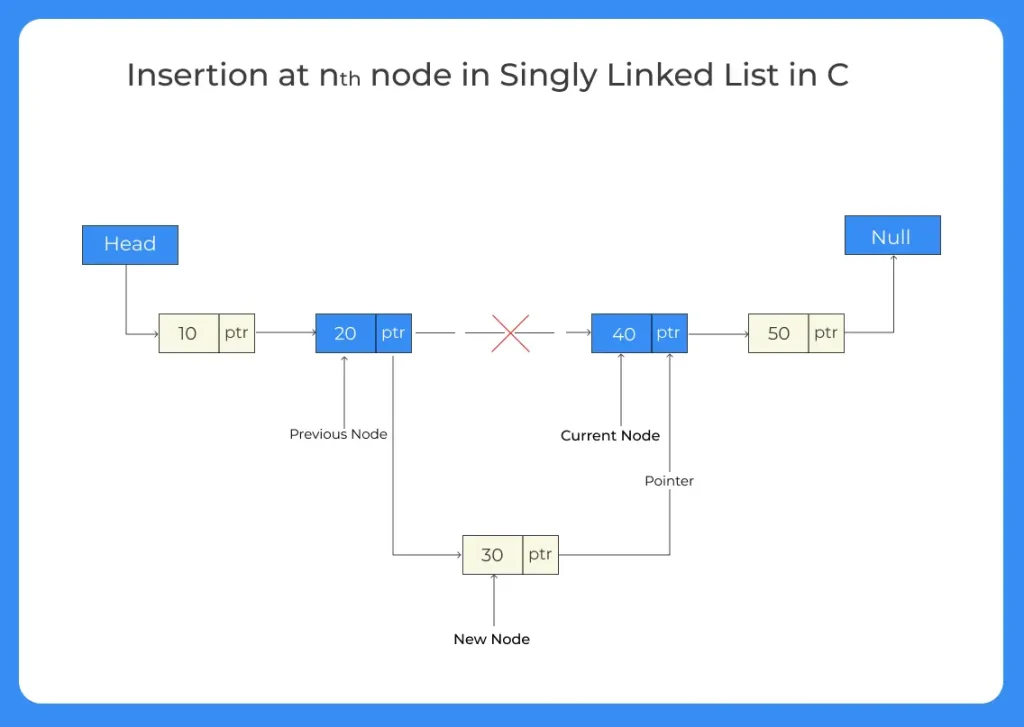
On this page, we will understand how to insert a node in the middle of a singly Linked List. Basically, we will try to insert a new node after some nth node. Lets look at how to do it below –

Steps to Insert node at any position in linked list in C:-
- Traverse the Linked List till the nth node
- Allocate the data and memory for the new node
- Assign the next pointer of the specific nth position node to this new node
- Assign the next pointer of this newNode to (n+1)th node (Nth node’s next)
If inserting after 0th position this means entering at the start
In this step assign new node’s next to the current head and also change the head of Linked List.
Code for Constructing Node of the Singly Linked List:-
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
}; C Program for insertion after the Nth node of the Singly Linked List:-
Let us look at the program below to do linked list insert after nth position
Run
//Linked list insertion at specific position in C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
// required for insertAfter
int getCurrSize (struct Node *node)
{
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
//function to insert after nth node
void insertPosition (int pos, int data, struct Node **head)
{
int size = getCurrSize (*head);
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
// Can't insert if position to insert is greater than size of Linked List
// can insert after negative pos
if (pos < 0 || pos > size)
printf ("Invalid position to insert\n");
// inserting first node
else if (pos == 0)
{
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
else
{
// temp used to traverse the Linked List
struct Node *temp = *head;
// traverse till the nth node
while (--pos)
temp = temp->next;
// assign newNode's next to nth node's next
newNode->next = temp->next;
// assign nth node's next to this new node
temp->next = newNode;
// newNode inserted b/w 3rd and 4th node
}
}
void display (struct Node *node)
{
printf ("Linked List : ");
// as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
int main ()
{
//creating 4 pointers of type struct Node
//So these can point to address of struct type variable
struct Node *head = NULL;
struct Node *node2 = NULL;
struct Node *node3 = NULL;
struct Node *node4 = NULL;
// allocate 3 nodes in the heap
head = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node2 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node3 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node4 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
head->data = 10; // data set for head node
head->next = node2; // next pointer assigned to address of node2
node2->data = 20;
node2->next = node3;
node3->data = 30;
node3->next = node4;
node4->data = 40;
node4->next = NULL;
display (head);
//Inserts data: 15 after the 1st node
insertPosition (1, 15, &head);
//Inserts data: 25 after the 3rd node
insertPosition (3, 25, &head);
//Inserts data: 35 after the 5th node
insertPosition (5, 35, &head);
//Inserts data: 25 after the 7th node
insertPosition (7, 45, &head);
display (head);
// Invalid: can't insert after -2 pos
insertPosition (-2, 100, &head);
// Invalid: Current size 8, trying to enter after 10th pos
insertPosition (10, 200, &head);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List : 10 20 30 40 Linked List : 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 Invalid position to insert Invalid position to insert

Question 1. The nth node in a singly list is accessed via?
(Flipkart – HackerEarth Test)
We can access the nth node in a Singly Linked List by creating a temp node with initialized value as the head reference and then keep moving to the next node n times that is traversing n nodes from the start so that the reference pointer now points towards the nth node, this is true for the nth node in singly linked list, is accessed via (where n>1)




Login/Signup to comment