C program for finding repeating element in an array
Repeating element of an array in C
In this section, we will learn the Program to Find the repeating element of an array in C programming language. To find the repeated elements in an array we require two loops. One will be used for array traversal and the other one is used for comparing the current element with all other elements of the array.

Example
Input : arr[5] = [10, 10, 20, 30, 30]
Output : 10 30
Explanation: 10 occurs 2 times and 30 also occurs 2 times in the given input array
Method :
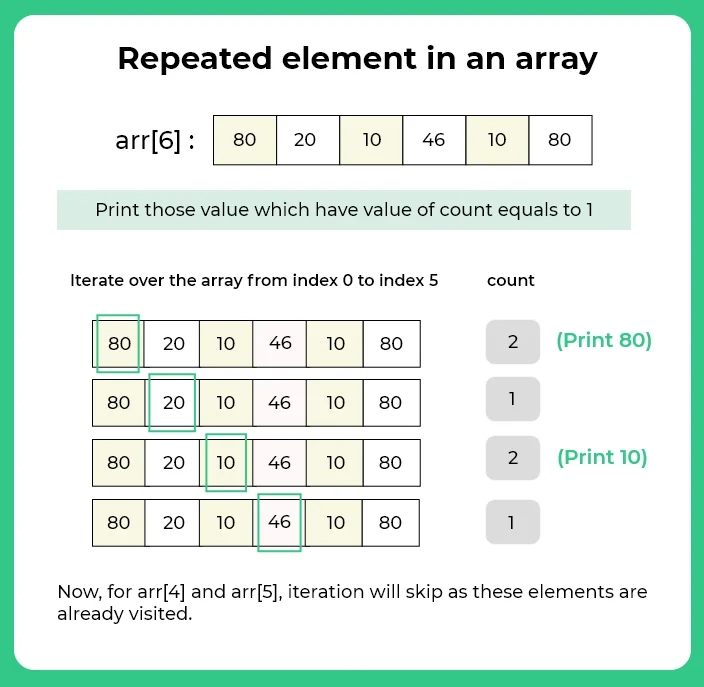
In this method we will count the frequency of each elements using two for loops, and whose frequency is not equal to 1 then print that element.
- To check the status of visited elements create a array of size n.
- Run a loop from index 0 to n and check if (visited[i]==1) then skip that element.
- Otherwise create a variable count = 1 to keep the count of frequency.
- Run a loop from index i+1 to n
- Check if(arr[i]==arr[j]), then increment the count by 1 and set visited[j]=1.
- After complete iteration of inner for loop, check if(count > 1), then print that element.
Time and Space Complexity :
- Time Complexity : O(n2)
- Space Complexity : O(n)
In this method we basically count the frequency of each element. To know more about the counting of the frequency of element in C, you can check out the page given below :
Code in C
Run
// Main function to run the program
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[] = {20, 30, 10, 2, 10, 20, 30, 11};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int visited[n];
for(int i=0; i < n; i++){
// only if unvisited
if(visited[i] == 0){
int count = 1;
for(int j = i+1; j < n; j++) {
// if appears again in the array
if(arr[i] == arr[j])
{ // increase count & mark index visited
count++;
visited[j] = 1;
}
} //
if(count > 1)
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
// Time Complexity : O(N^2)
// Space Complexity : O(N)Output :
20 30 10
Method 2
The previous method uses extra O(N) space for the visited array, which is undesirable. We can do the following technique but we have to make sure that the array is sorted. We will use a sorting algorithm to sort the array We have used bubble sort(Time complexity: O(N^2). But you can use Merge Sort or Quick Sort, which will reduce the sorting time complexity to O(n log(n))Code
Run
#include<stdio.h>
// Time Complexity : O(n^2)
// O(n^2) : sort the array and O(n) to count repeating
// using bubble sort to sort the array
// you can use a better sorting algorithm to reduce
// time complexity to O(n log n) to sort
int bubbleSort(int arr[], int size){
for (int i = 0; i < size-1; i++){
// Since, after each iteration righmost i elements are sorted
for (int j = 0; j < size-i-1; j++) if (arr[j] > arr[j+1])
{
int temp = arr[j]; // swap the element
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
// find repeating element
void findRepeating(int arr[], int n){
// Traverse the sorted array
// arr = {3, 10, 10, 11, 20, 20, 30, 30}
int count = 0;
// this step may look like O(n^2) but its actually O(n)
// look closely, we traverse every element only once
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int flag = 0;
// Move the index ahead whenever you encounter duplicates
while (i < n - 1 && arr[i] == arr[i + 1]){
// indicates that we have found duplicate
flag = 1;
i++;
}
// since i++ happened, we need to print previous element
if(flag)
printf("%d, ",(arr[i-1]));
}
return;
}
// Main function to run the program
int main()
{
int arr[] = {20, 30, 10, 2, 10, 20, 30, 11};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
bubbleSort(arr, n);
findRepeating(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// Time Complexity : O(N)
// Space Complexity : O(1)Output
10, 20, 30,



logic is wrong in this code.
I think it will right if count!=1.
Thanks for pointing this out, this has been fixed